文章目录
入口之Spring与Dubbo集成
XML配置
先看一段XML下的Dubbo服务配置
<!-- 指定dubbo项目名称 -->
<dubbo:application name="application_provider" />
<!-- 使用zookeeper做注册中心暴露服务地址 -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" />
<!-- 用dubbo协议在20880端口暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<!-- 声明需要暴露的服务接口 ref指向接口实现类 首字母小写 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.dubbo.demo.Provider"
ref="demoService" />
其他标签的配置说明,具体参考官网SCHEMA配置参考手册
XML配置解析
Dubbo这种标签定义Bean的方法,实际上是有一套自己的配置文件标签规范,Spring也允许开发者定义自己的XML SCHEMA,只是Spring有如下约定
- 自定义的标签模板XSD文件,需要在
META-INF/spring.schemas中指定,dubbo中的配置文件XML模板为dubbo.xsd文件,有兴趣的可以去看看xsd文件规范,这里不展开说明。配置文件有了,还得有一个类来解析配置文件。

- 自定义的XSD文件解析类,需要在
META-INF/spring.handlers中指定xsd文件的解析类,dubbo中指定解析类如下,DubboNamespaceHandler即为Dubbo配置文件的解析类

看下DubboNamespaceHandler的实现,可以看到针对不同的配置标签有不同的解析

本文重点是服务暴露,因此重点关注service标签的解析,可以看到其XML中的Service最终会转化为一个ServiceBean类
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
ServiceBean也是分析Dubbo服务导出的入口
ServiceBean与Spring的整合
Dubbo的启动依赖于Spring的启动,Dubbo服务在接收到Spring容器的刷新事件后,会执行服务暴露、导出工作,看下ServiceBean是如何与Spring整合在一起的。
看下ServiceBean的类定义
public class ServiceBean<T> extends ServiceConfig<T> implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>, BeanNameAware {
//省略其他变量、方法
private static transient ApplicationContext SPRING_CONTEXT;
private transient String beanName;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
if (isDelay() && !isExported() && !isUnexported()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("The service ready on spring started. service: " + getInterface());
}
export();
}
}
}
明确如下几点
- ServiceBean继承自
ServiceConfig,因此ServiceBean中保留有Dubbo服务相关的配置,如导出的接口interfaceName、要导出的方法methods等 - ServiceBean实现了
ApplicationContextAware、BeanNameAware接口,因此能获取到Spring的上下文对象ApplicationContext以及bean的beanName。如图所示
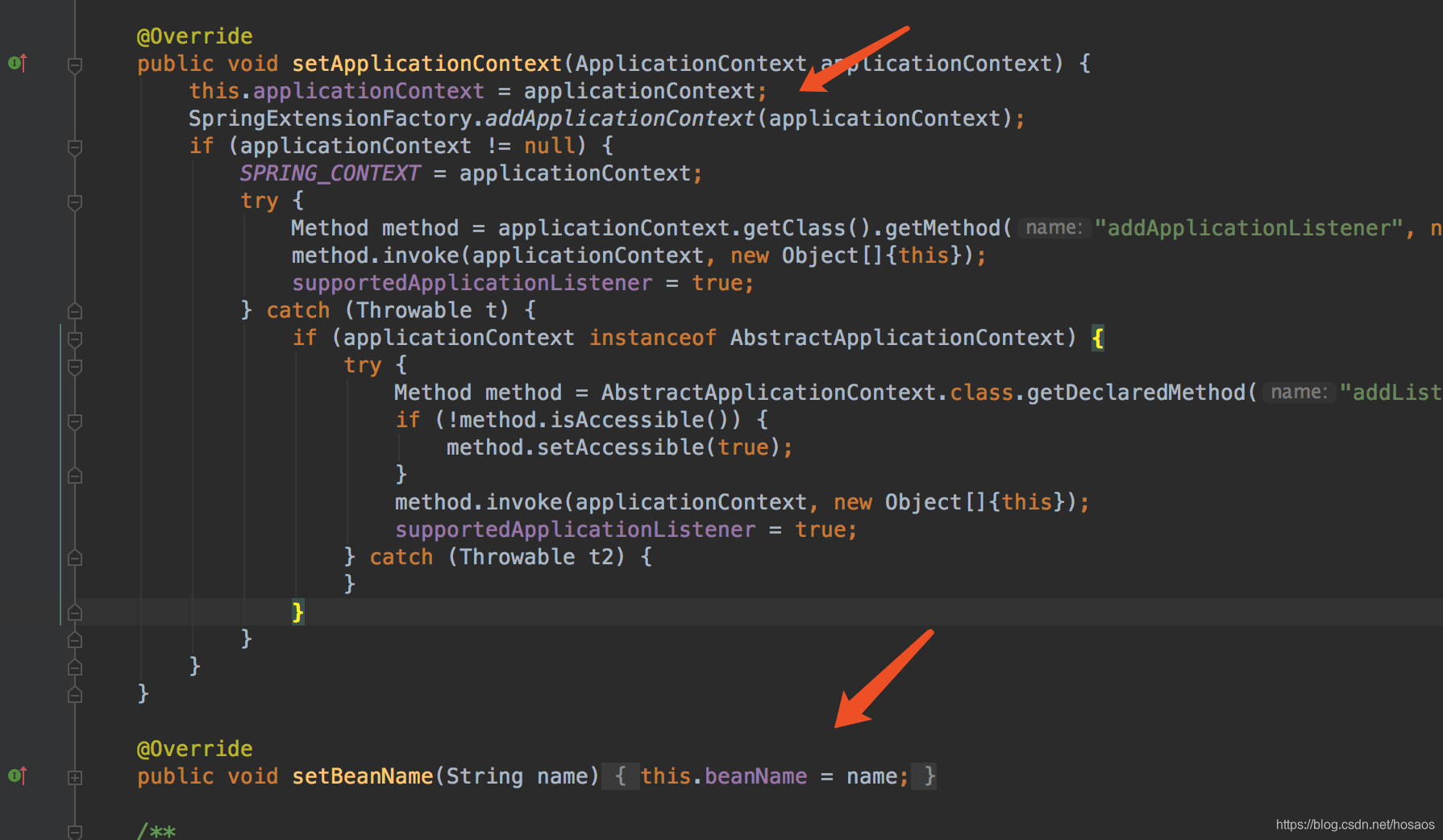
- 实现了
InitializingBean,DisposableBean因此能在Dubbo服务对应的bean初始化完成时执行延迟导出工作,!isDelay()标识延迟导出,即delay>0时,isDelay返回false,在afterPropertiesSet方法中进行服务导出,表示延迟到Spring容器初始化完成时暴露服务

- 实现了
ApplicationListener,使得ServiceBean能够接收到Spring容器的刷新事件,在监听到刷新事件时进行服务导出

至此已经清晰了服务导出的入口实在ServiceBean的export方法中
服务暴露
在从代码层面上分析服务暴露过程之前,先上一张Dubbo官方的暴露服务时序图,大家后面好对照着时序图来跟踪、分析源码

先看下ServiceBean#export方法的实现,逻辑简单,分为三步
- 从ProviderConfig中获取export属性、delay属性
- 如果export=false,表示不需要导出,直接return
- 如果配置了延迟导出(delay>0),利用ScheduledExecutorService进行延迟导出
private ProviderConfig provider;
private static final ScheduledExecutorService delayExportExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(new NamedThreadFactory("DubboServiceDelayExporter", true));
public synchronized void export() {
if (provider != null) {
if (export == null) {
export = provider.getExport();
}
if (delay == null) {
delay = provider.getDelay();
}
}
if (export != null && !export) {
return;
}
if (delay != null && delay > 0) {
delayExportExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
doExport();
}
}, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
doExport();
}
}
配置检查
进到ServiceConfig#doExport方法,其主要是做了配置检查操作
protected synchronized void doExport() {
if (unexported) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already unexported!");
}
if (exported) {
return;
}
exported = true;
//步骤一:检测interfaceName合法性
if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:service interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!");
}
checkDefault();
//步骤二:从providerConfig、moduleConfig、applicationConfig中获取参数
if (provider != null) {
if (application == null) {
application = provider.getApplication();
}
if (module == null) {
module = provider.getModule();
}
if (registries == null) {
registries = provider.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = provider.getMonitor();
}
if (protocols == null) {
protocols = provider.getProtocols();
}
}
if (module != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = module.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = module.getMonitor();
}
}
if (application != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = application.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = application.getMonitor







 本文详细解析了Dubbo服务导出和暴露的实现过程,从Spring与Dubbo的集成开始,包括XML配置解析、ServiceBean的Spring整合。接着深入服务暴露的各个环节,如配置检查、多协议服务暴露,特别是Filter责任链的构建,以及NettyServer的创建。通过源码分析,展示了Dubbo如何在服务启动和Spring容器刷新事件中完成服务的导出和远程暴露。
本文详细解析了Dubbo服务导出和暴露的实现过程,从Spring与Dubbo的集成开始,包括XML配置解析、ServiceBean的Spring整合。接着深入服务暴露的各个环节,如配置检查、多协议服务暴露,特别是Filter责任链的构建,以及NettyServer的创建。通过源码分析,展示了Dubbo如何在服务启动和Spring容器刷新事件中完成服务的导出和远程暴露。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 425
425

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








