一级缓存
也叫做本地缓存:SqlSession
1.与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中
2.如果查询相同的数据,会直接从缓存中拿,没有必要重新再次查询数据库
测试
1.开启日志(一级缓存默认自动开启)
2.测试在一个Session中查询两次相同的记录
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("======================================================");
User user2 = mapper.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user==user2);
sqlSession.close();
3.查看日志输出
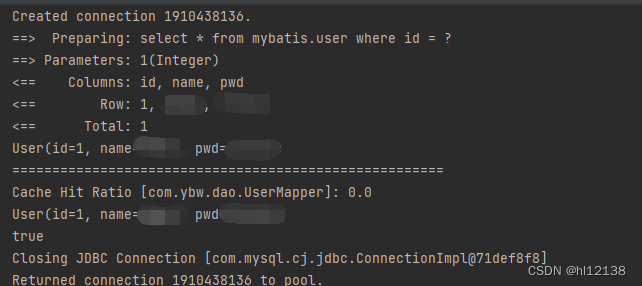
4.一级缓存缓存失效的情况(默认是开启的,在一次SqlSession中有效)
1.查询不同的东西
2.增删改操作,可能会改变原来的数据,所以必定会刷新缓存
3.查询不同的Mapper.xml
4.手动清除缓存sqlSession.clearCache();
二级缓存
要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
<cache/>
不过建议是在mybatis-config.xml的settings中添加以下这行(说明需要用二级缓存),默认就是true
<settings>
<!-- 开启全局缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
二级缓存的话可以在一次会话关闭之后继续使用缓存
测试
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
sqlSession.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user2 = mapper2.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user==user2);
sqlSession2.close();
}
查看日志
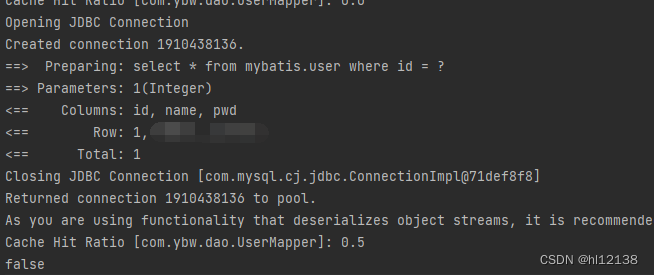
注意如果没有在cache标签中readOnly=“true”,则需要序列化我们的实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
官网解释:
readOnly(只读)属性可以被设置为 true 或 false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。这就提供了可观的性能提升。而可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。 速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
缓存的顺序
1.先看二级缓存中有没有
2.再看一级缓存中有没有
3.最后查询数据库




















 1523
1523

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








