1、参考:Node.js 模块系统 | 菜鸟教程
2、实践、截图
2.1、导入模块
2.2.1、
自定义模块导出与导入(CommonJS 模块)
1、导出模块:使用 module.exports 或 exports 将函数、对象或变量导出。
2、导入模块:使用 require() 导入模块。
在 Node.js 中,引入一个模块非常简单,如下我们创建一个 main.js 文件并引入 hello 模块,代码如下:
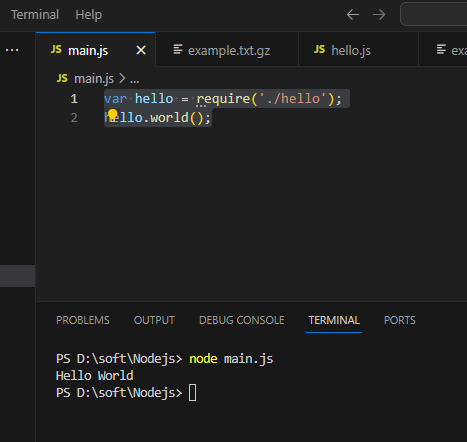
var hello = require('./hello');
hello.world();以上实例中,代码 require('./hello') 引入了当前目录下的 hello.js 文件(./ 为当前目录,node.js 文件默认后缀为 .js)。
Node.js 提供了 exports 和 require 两个对象,其中 exports 是模块公开的接口,require 用于从外部获取一个模块的接口,即所获取模块的 exports 对象。
接下来我们就来创建 hello.js 文件,代码如下:
exports.world = function() {
console.log('Hello World');
}执行node main.js,输出如下:
2.1.2、使用module
hello.js 文件代码:
// hello.js
function Hello() {
var name;
this.setName = function(thyName) {
name = thyName;
};
this.sayHello = function() {
console.log('Hello ' + name);
};
};
module.exports = Hello;这样就可以直接获得这个对象了:
main.js 文件代码:
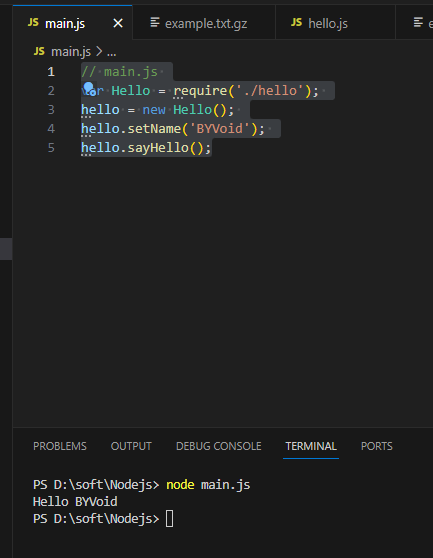
// main.js
var Hello = require('./hello');
hello = new Hello();
hello.setName('BYVoid');
hello.sayHello();模块接口的唯一变化是使用 module.exports = Hello 代替了 exports.world = function(){}。 在外部引用该模块时,其接口对象就是要输出的 Hello 对象本身,而不是原先的 exports。
输出如下:
module.exports 与 exports 的区别:
module.exports是导出对象的真正引用。exports是module.exports的快捷方式。不能直接赋值exports = ...,否则会断开引用。
2.2、自定义模块导出与导入(ES 模块)
ES 模块使用 import 和 export,是现代 JavaScript 的模块规范。
- ES 模块使用
import和export关键字,需将文件扩展名设置为.mjs,或者在package.json中声明"type": "module"。 - ES 模块支持静态导入(
import ... from ...)和动态导入(import())。
// myModule.mjs
export function greet(name) {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
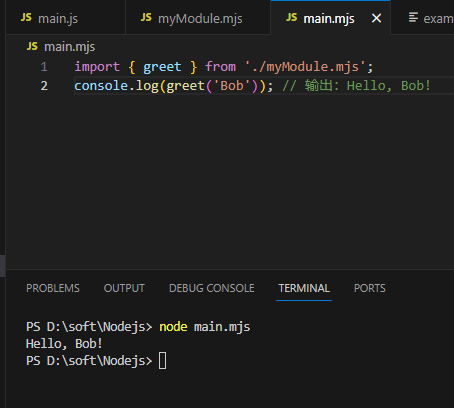
// main.mjs
import { greet } from './myModule.mjs';
console.log(greet('Bob')); // 输出:Hello, Bob!输出如下:





















 295
295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








