一些网络接口通常都要求在特定时间返回,如果超时则应该中止。这里考虑在python编程中的一个通用实现,即通过装饰器来装饰指定的函数,设定容许的执行时长和超时时的返回结果,在限定时长内完成的函数才返回其结果,超出限定时长的函数将被中止。
思路
思考起来,应该可以基于python的并发机制以及操作系统的信号机制来实现。比如线程、进程、协程或者操作系统信号。如下逐一验证。
信号
Ubuntu
类unix系统提供了signal机制,可以用来杀死进程。结合alarm定时器的机制,可以实现定时退出,并返回。如下代码给出了示例,在ubuntu上测试通过。
import signal
import time
from print_report import print_with_time
# 定义信号处理函数
def timeout_handler(signum, frame):
print_with_time("triger timeout :{signum} {frame}")
raise TimeoutError("Function execution timed out.")
# 定义超时装饰器
def timeout_decorator(timeout=5, timeout_return="Function timed out, returning specific value."):
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
# 设置信号和超时时间
signal.signal(signal.SIGALRM, timeout_handler)
signal.alarm(timeout)
# 调用被装饰的函数
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 取消信号
signal.alarm(0)
return result
except TimeoutError:
return timeout_return
return wrapper
return decorator
# 使用装饰器修饰函数
@timeout_decorator(timeout=5)
def example_function(secs):
print_with_time(f"in example_function {secs}")
# 模拟一个可能耗时较长的操作
time.sleep(secs)
print_with_time(f"ou example_function {secs}")
return "example_function original result {secs}"
# 调用函数
print_with_time(None)
print_with_time("begin")
print_with_time(example_function(4)) # 2 秒内完成
print_with_time(example_function(5)) # 5 秒超时
print_with_time("end")
运行效果如下:

Windows
但是这个实现依赖操作系统的消息或信号机制。window的消息机制不同,所以不能实现同样的效果。windows上一个最接近的实现是基于线程的定时机制。如下代码:
import threading
import functools
import time
import os
from print_report import print_with_time
def timeout(seconds, timeout_result=None):
"""
基于 threading.Timer 的超时装饰器。
:param seconds: 超时时间(秒)。
:param timeout_result: 超时时的返回结果。
"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
def interrupt():
print_with_time("timeout ,exit")
os._exit(1) # 强制退出当前线程
print_with_time("timeout ,raise exception")
raise TimeoutError(0)
timer = threading.Timer(seconds, interrupt)
timer.start()
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
timer.cancel() # 取消定时器
return result
except TimeoutError:
print_with_time(f"Function {func.__name__} timed out, returning timeout result.")
return timeout_result
except Exception as exp:
print_with_time (exp)
return timeout_result
return wrapper
return decorator
@timeout(seconds=10, timeout_result="Timeout!")
def long_running_function(secs):
print_with_time(f"in long_running_function {secs}")
time.sleep(secs)
print_with_time(f"ou long_running_function {secs}")
return f"long_running_function Finished in {secs} seconds."
# 测试
print_with_time(None)
print_with_time("begin")
print_with_time(long_running_function(2)) # 2 秒内完成
print_with_time(long_running_function(15)) # 5 秒超时
print_with_time("end")
但是这个并未能实现全部效果。如果使用os._exit(1)则整个进程会被中止。获得如下输出:

如果使用抛出异常的机制,则还是需要等待15s。并获得如下输出:
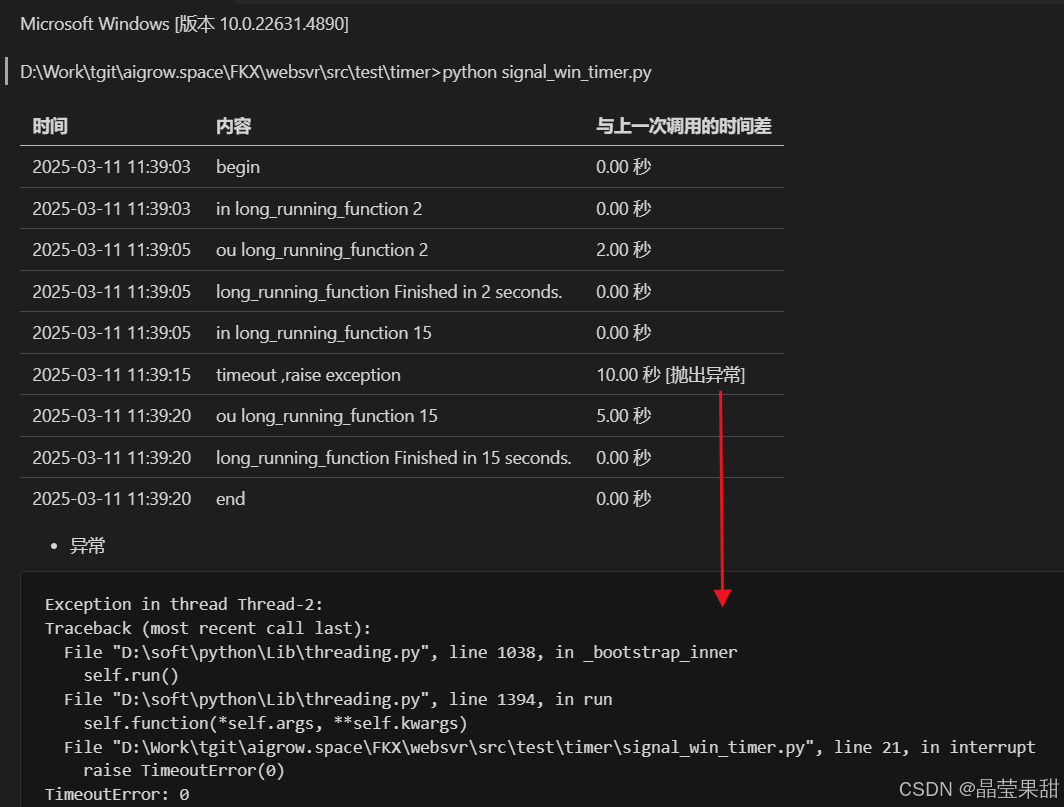
小结
通过信号量或者事件的机制,无法获得更好的操作系统兼容性,windows下无法获得简单实现就可预期的效果。
协程
通过asyncio可以实现此能力。只是会要求函数应该是async修饰的。这个问题不大,对需要限时返回的非async函数包装下即可。如下代码演示如何使用asyncios来实现限时返回。
import asyncio
import functools
from print_report import print_with_time
def asyncio_timeout(seconds, timeout_result=None):
"""
基于协程的超时装饰器。
:param seconds: 超时时间(秒)。
:param timeout_result: 超时时的返回结果。
"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
return await asyncio.wait_for(func(*args, **kwargs), timeout=seconds)
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
print_with_time(f"❗Function {func.__name__} timed out, returning timeout result.")
return timeout_result
return wrapper
return decorator
import time
from print_report import print_with_time
# 测试函数
async def async_long_running_function(secs):
print_with_time(f"in async_long_running_function ...{secs}")
await asyncio.sleep(secs)
print_with_time(f"ou async_long_running_function {secs}")
return f"async_long_running_function Finished in {secs} seconds."
# 测试装饰器
def test_decorator(decorator, func, timeout_secs, test_cases):
print_with_time(f"Testing {decorator.__name__} with {func.__name__}:")
decorated_func = decorator(timeout_secs, "Timeout!")(func)
for secs, expected_result in test_cases:
start_time = time.time()
if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(decorated_func):
result = asyncio.run(decorated_func(secs))
else:
result = decorated_func(secs)
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
print_with_time(f"Input: {secs}s, Result: {result}, Time: {elapsed_time:.2f}s")
# 测试用例
test_cases = [
(2, "Finished in 2 seconds."), # 不超时
(5, "Timeout!"), # 超时
(1, "Finished in 1 seconds."), # 不超时
(4, "Timeout!"), # 超时
(300, "Finished in 3 seconds."), # 超时
]
# 运行测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 测试协程装饰器
print("# asyncio")
print_with_time(None)
print_with_time("this is the beginning.")
test_decorator(asyncio_timeout, async_long_running_function, 3, test_cases)
print_with_time("this is the end.")
得到如下结果,符合预期。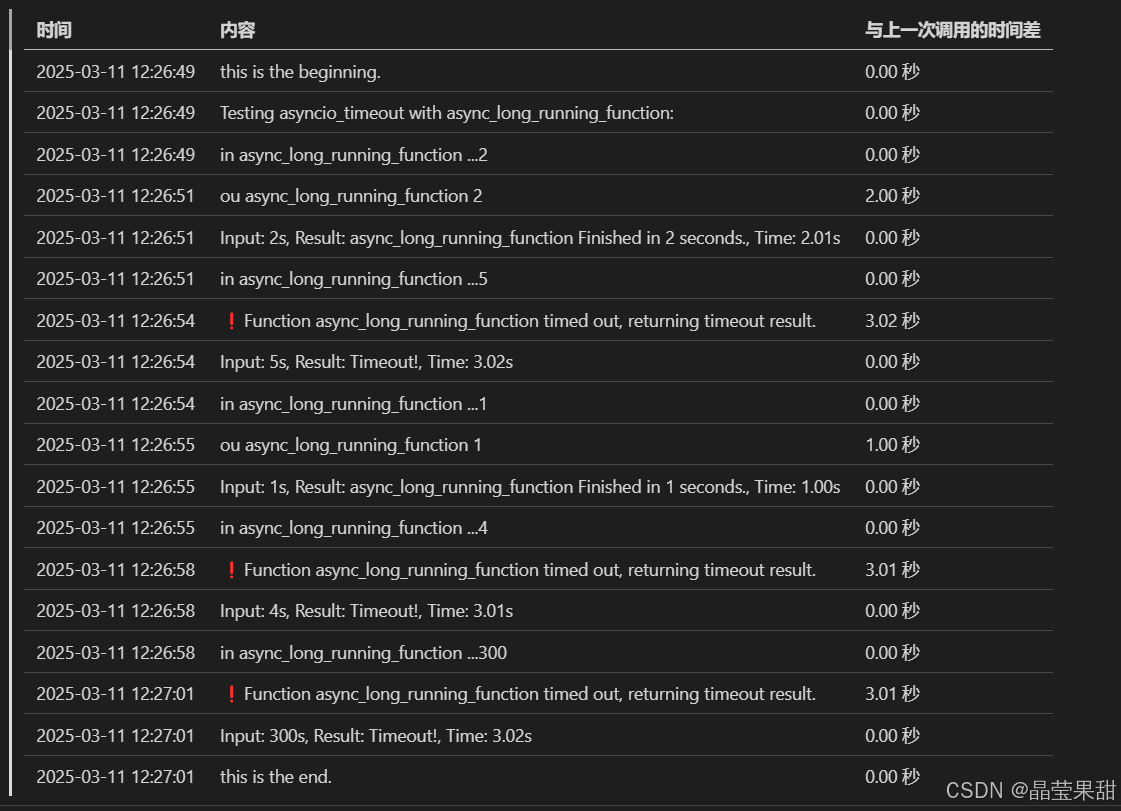
小结
如果是因为等待io,需要限时返回。基于asyncio是一个最佳实现。
线程
基于线程实现限时返回,在pyton下有一定限制,主要是线程不能被中断。基于定时器抛出的异常并没有被正执行的线程捕获。只能自行检查是否超时,给出对应结果。线程还是会持续执行下去。并没有如协程一样被中断。
import threading
import functools
import time
from print_report import print_with_time
def threading_timeout(seconds, timeout_result=None):
"""
基于线程的超时装饰器。
:param seconds: 超时时间(秒)。
:param timeout_result: 超时时的返回结果。
"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
result = timeout_result
exception = None
def target():
nonlocal result, exception
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
exception = e
thread = threading.Thread(target=target)
thread.start()
thread.join(timeout=seconds)
if thread.is_alive():
print_with_time(f"❗Function {func.__name__} timed out, returning timeout result.")
return timeout_result
elif exception is not None:
raise exception
else:
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
可特别注意下红色框部分,超时之后还是会执行完函数。
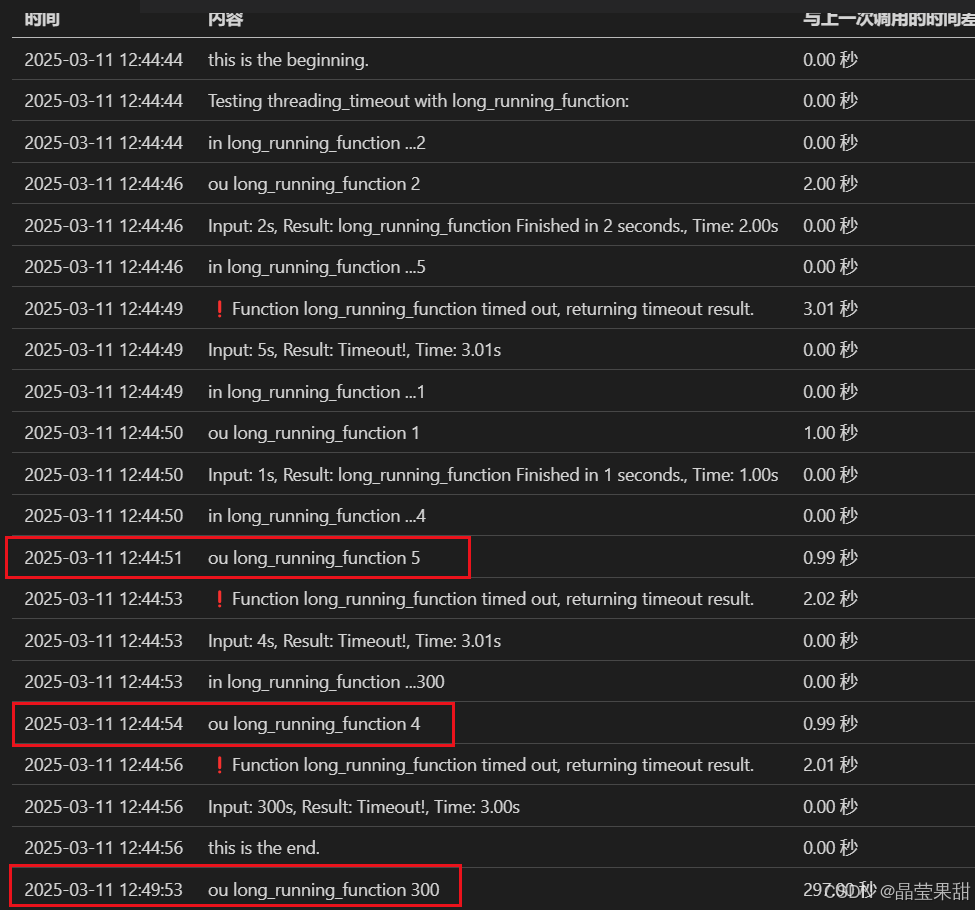
小结
线程当然可达到目的。进入过可配合超时的事件变量,做一些判定后优雅退出,就更好。但是明显不如asyncio来得直接。如果希望限时返回的函数不是自己写的
进程
进程颗粒度更大,实现起来更直观。
import multiprocessing
import functools
import time
from print_report import print_with_time
# 将 target 函数移到顶层
def target(queue, func, args, kwargs):
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
queue.put(result)
except Exception as e:
queue.put(e)
def multiprocessing_timeout(seconds, timeout_result=None):
"""
基于进程的超时装饰器。
:param seconds: 超时时间(秒)。
:param timeout_result: 超时时的返回结果。
"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
process = multiprocessing.Process(
target=target,
args=(queue, func, args, kwargs))
process.start()
process.join(timeout=seconds)
if process.is_alive():
print_with_time(f"Function {func.__name__} timed out, returning timeout result.")
process.terminate()
process.join()
return timeout_result
else:
if not queue.empty():
result = queue.get()
if isinstance(result, Exception):
raise result
return result
else:
return timeout_result
return wrapper
return decorator
获得的结果如下:
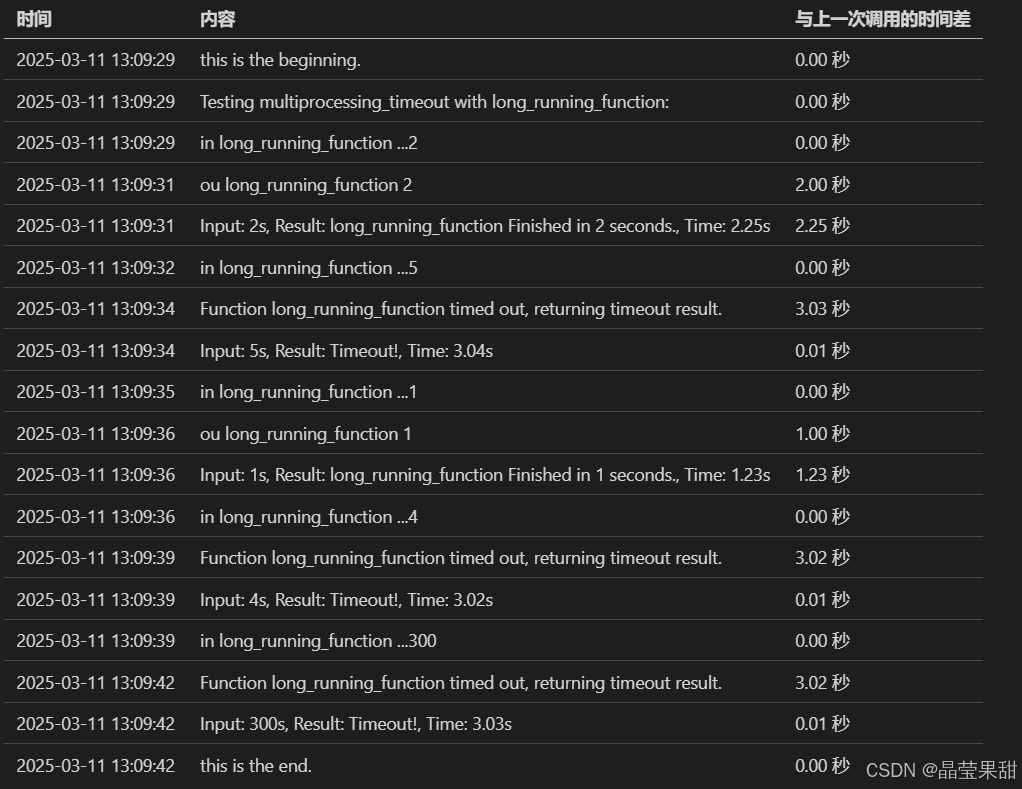
小结
基于进程的实现,结果与完全符合预期。
总结
信号受制于操作系统,兼容性不太好。线程在pyton下并无法中断,实用性打了折扣。协程开销小,要求被修饰函数是async,在io开销大的时候,是最佳选择。进程适用面更大。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








