* cooperating services; composite microservices??; aggregated response;
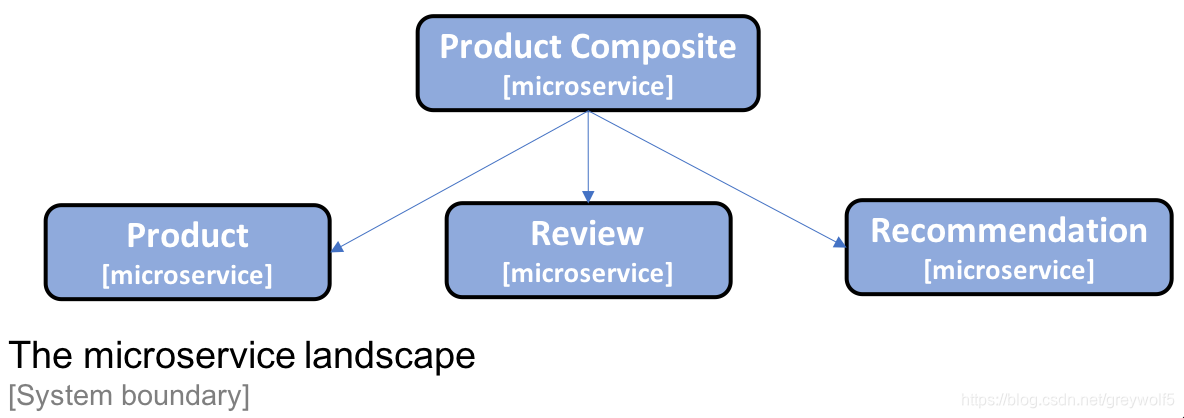
1.introducing the microservice landscape
2. Information handled by microserivces
* business logic, information model, business object,
3.infrustructure-related information
* serviceAddress attribute to all of our response, fomated as hostName/IP address:port
4. Generating skeleton microserivces
* gradle; Spring initializer
5. Spring Initializer to generate skeleton code
* Gradle as a build tool; dependencies on actuator and webflux
* build.gradle,:how to compile, test and package the source code
* plugins are fetched from central maven repositary and spring snapshot and milestone repository.
6. setting up multi project builds in Gradle
*build all microservices with one command
7. Adding RESTFULL APIs
* two projects(api and util) shared by microservice projects
8. Adding an Api and a Util projects
* Java interfaces in order to describe RESTful Api and model classes to describe the data that Api uses in request and response; descipting a RESTful service with a java interface
* a devops perspective, build pipeline, version-controlled independences
9. The api Project
* api project will be packaged as a library; no longer have main class;
* Springboot dependency management, the construction of a fat jar, the creatation of normal jar files, project's own class and property files.
* a plain POJO-based model class;
10. the util project
* java exceptions to proper http status codes, adding error handle section
11.implementing out api
* @componentScan annotation to the main Application class
* add api and util as dependency in gradle.build file
12.adding a composite microservice
* an intergration component that handles the outgoing http requests to the core services; the composite services itself.
* automated unit and integration testing; replacing the integration component with a mock
* runtime properties, address information
13.properties
* a service delivery mechanism
14.Integration component
* RestComponent, RestTemplete is highly configurable
* actual ongoing calls; exhange, getForObject
15. composite API Implementation
* a function point of view
16. add error handling
* a structured and well-thought way
* seperate protocal-specific handling of error, such as http status code, from business logic
17. the global rest controller exception handler
18. Error-handling in api implatation
* classed as best-effort
19. Testing api manually
20. prevent slow lookup of the localhost hostname
* webTestClient
21. add the semi-automated tests of the microservice landscape
* insufficient; hash script, curl, jq





 本文深入探讨微服务架构的实现与优化,包括业务逻辑处理、基础设施配置、RESTful API设计及错误处理策略。从构建骨架服务到集成测试,再到运行时属性设置,全面解析微服务的开发流程。
本文深入探讨微服务架构的实现与优化,包括业务逻辑处理、基础设施配置、RESTful API设计及错误处理策略。从构建骨架服务到集成测试,再到运行时属性设置,全面解析微服务的开发流程。
















 968
968

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








