5 Business logic vulnerabilities 业务逻辑漏洞
目录
- In this section, we’ll introduce the concept of business logic vulnerabilities and explain how they can arise due to flawed assumptions about user behavior. 它们是如何因对用户行为的错误假设而产生的。
- We’ll discuss the potential impact of logic flaws and teach you how they can be exploited. You can also practice what you’ve learned using our interactive labs, which are based on real bugs that we’ve encountered in the wild.
- Finally, we’ll provide some general best practices to help you prevent these kinds of logic flaws arising in your own applications.
一、What
-
Business logic vulnerabilities are flaws in the design and implementation of an application that allow an attacker to elicit unintended behavior. 应用程序的设计和实现中允许攻击者引发意外行为
-
This potentially enables attackers to manipulate legitimate functionality to achieve a malicious怀有恶意的;恶毒的goal. 操作合法功能
-
These flaws are generally the result of failing to anticipate unusual application states that may occur and, consequently, failing to handle them safely.由于未能预料到可能发生的不寻常的应用程序状态
-
In this context, the term “business logic” simply refers to the set of rules that define how the application operates. As these rules aren’t always directly related to a business, the associated vulnerabilities are also known as “application logic vulnerabilities” or simply “logic flaws”.术语“业务逻辑”只是指定义应用程序如何操作的规则集。由于这些规则并不总是与业务直接相关,因此相关的漏洞也称为“应用程序逻辑漏洞”或简单地称为“逻辑缺陷”。
-
Logic flaws are often invisible to people who aren’t explicitly looking for them as they typically won’t be exposed by normal use of the application. 通常不会被公开
-
However, an attacker may be able to exploit behavioral quirks by interacting with the application in ways that developers never intended.攻击者可能通过与应用程序以开发人员从未想过的方式交互来利用行为怪癖。
-
One of the main purposes of business logic is to enforce the rules and constraints that were defined when designing the application or functionality. Broadly speaking, the business rules dictate how the application should react when a given scenario occurs. This includes preventing users from doing things that will have a negative impact on the business or that simply don’t make sense.业务逻辑的主要目的之一是实施在设计应用程序或功能时定义的规则和约束。一般来说,业务规则规定了当给定场景发生时应用程序应该如何作出反应。这包括防止用户做那些会对业务产生负面影响或根本没有意义的事情。
-
Flaws in the logic can allow attackers to circumvent these rules. 绕过
-
For example, they might be able to complete a transaction without going through the intended purchase workflow. 他们可以在不经过预期的购买工作流的情况下完成交易
-
In other cases, broken or non-existent validation of user-supplied data might allow users to make arbitrary changes to transaction-critical values or submit nonsensical input. By passing unexpected values into server-side logic, an attacker can potentially induce the application to do something that it isn’t supposed to.损坏或不存在用户提供的数据验证可能允许用户对事务临界值进行任意更改或提交无意义的输入。通过向服务器端逻辑传递意外的值,攻击者可以潜在地诱导应用程序做一些它不应该做的事情。
-
Logic-based vulnerabilities can be extremely diverse and are often unique to the application and its specific functionality. 应用程序功能特有的
-
Identifying them often requires a certain amount of human knowledge, such as an understanding of the business domain or what goals an attacker might have in a given context. This makes them difficult to detect using automated vulnerability scanners. As a result, logic flaws are a great target for bug bounty hunters and manual testers in general. 逻辑漏洞成为了属类中的赏金猎人和手动测试人员的理想目标
二、业务逻辑漏洞如何产生
-
Business logic vulnerabilities often arise because the design and development teams make flawed assumptions about how users will interact with the application. 有缺陷的假设:用户和应用交互
-
These bad assumptions can lead to inadequate validation of user input. 可能导致用户输入的验证不足 For example, if the developers assume that users will pass data exclusively via a web browser, the application may rely entirely on weak client-side controls to validate input. These are easily bypassed by an attacker using an intercepting proxy. 仅通过Web浏览器传递数据,应用程序可能完全依赖弱客户端控件来验证输入。攻击者可以使用拦截代理很容易地绕过它们。
-
Ultimately, this means that when an attacker deviates from the expected user behavior, the application fails to take appropriate steps to prevent this and, subsequently, fails to handle the situation safely.最终,这意味着当攻击者偏离预期的用户行为时,应用程序无法采取适当的步骤来防止这种情况,进而无法安全地处理这种情况。
-
Logic flaws are particularly common in overly complicated systems that even the development team themselves do not fully understand.在开发团队自己都不能完全理解的过于复杂的系统中逻辑缺陷尤其常见。
-
To avoid logic flaws, developers need to understand the application as a whole.
-
This includes being aware of how different functions can be combined in unexpected ways. 了解不同的功能如何以意想不到的方式组合。- - Developers working on large code bases may not have an intimate understanding of how all areas of the application work. 在大型代码基础上工作的开发人员可能不了解应用程序的所有领域是如何工作的。
-
Someone working on one component could make flawed assumptions about how another component works and, as a result, inadvertently introduce serious logic flaws. 在一个组件上工作的人可能会对另一个组件的工作方式做出有缺陷的假设,从而无意中引入严重的逻辑缺陷。
-
If the developers do not explicitly document any assumptions that are being made, it is easy for these kinds of vulnerabilities to creep into an application. 如果开发人员没有明确地记录正在进行的任何假设,那么这些类型的漏洞很容易潜入应用程序。
三、impacts
-
The impact of business logic vulnerabilities can, at times, be fairly trivial. It is a broad category and the impact is highly variable.业务逻辑漏洞的影响有时可能相当微不足道。这是一个广泛的类别,影响是高度可变的。
-
However, any unintended behavior can potentially lead to high-severity attacks if an attacker is able to manipulate the application in the right way. For this reason, quirky logic should ideally be fixed even if you can’t work out how to exploit it yourself. There is always a risk that someone else will be able to.如果攻击者能够以正确的方式操作应用程序,那么任何意外的行为都可能导致严重的攻击。因此,理想情况下,古怪的逻辑应该是固定的,即使你自己不能想出如何利用它。总有一个风险,别人也有可能。
-
Fundamentally, the impact of any logic flaw depends on what functionality it is related to. If the flaw is in the authentication mechanism, for example, this could have a serious impact on your overall security. Attackers could potentially exploit this for privilege escalation, or to bypass authentication entirely, gaining access to sensitive data and functionality. This also exposes an increased attack surface for other exploits.从根本上说,任何逻辑缺陷的影响取决于它与什么功能相关。例如,如果缺陷是在身份验证机制中,这可能会对您的整体安全性产生严重影响。攻击者可能利用这一点来升级权限,或者完全绕过身份验证,获得对敏感数据和功能的访问权。这也增加了其他漏洞的攻击面。
-
Flawed logic in financial transactions can obviously lead to massive losses for the business through stolen funds, fraud, and so on.金融交易中的错误逻辑显然会通过资金被盗、欺诈等方式给企业带来巨大损失
-
You should also note that even though logic flaws may not allow an attacker to benefit directly, they could still allow a malicious party to damage the business in some way. 即使逻辑缺陷可能不允许攻击者直接受益,他们仍然可能允许恶意方以某种方式破坏业务。
四、examples
The best way to understand business logic vulnerabilities is to look at real-world cases and learn from the mistakes that were made. We’ve provided concrete examples of a variety of common logic flaws, as well as some deliberately vulnerable websites so that you can practice exploiting these vulnerabilities yourself.
- Business logic vulnerabilities are relatively specific to the context in which they occur. However, although individual instances of logic flaws differ hugely, they can share many common themes. In particular, they can be loosely grouped based on the initial mistakes that introduced the vulnerability in the first place.业务逻辑漏洞相对特定于它们发生的上下文。然而,尽管逻辑缺陷的个别实例差别很大,但它们可以共享许多共同的主题。特别是,可以根据最初引入漏洞的错误松散地对它们进行分组。
In this section, we’ll look at examples of some typical mistakes that design and development teams make and show you how they can directly lead to business logic flaws. Whether you’re developing your own applications, or auditing 审计existing ones, you can take the lessons learned from these examples and apply the same critical thinking to other applications that you encounter.
1.对客户端控件的过度信任
Excessive trust in client-side controls
-
A fundamentally flawed assumption is that users will only interact with the application via the provided web interface. This is especially dangerous because it leads to the further assumption that client-side validation will prevent users from supplying malicious input. However, an attacker can simply use tools such as Burp Proxy to tamper with the data after it has been sent by the browser but before it is passed into the server-side logic. This effectively renders the client-side controls useless.一个根本错误的假设是,用户只会通过提供的web界面与应用程序交互。这尤其危险,因为它会导致进一步的假设,即客户端验证将阻止用户提供恶意输入。然而,攻击者可以简单地使用Burp Proxy等工具篡改由浏览器发送的数据,但在数据被传递到服务器端逻辑之前。这有效地使客户端控件变得无用。
-
Accepting data at face value, without performing proper integrity checks and server-side validation, can allow an attacker to do all kinds of damage with relatively minimal effort. Exactly what they are able to achieve is dependent on the functionality and what it is doing with the controllable data. In the right context, this kind of flaw can have devastating consequences for both business-related functionality and the security of the website itself. 按表面价值接受数据,而不执行适当的完整性检查和服务器端验证,可能使攻击者以相对较小的努力进行各种破坏。它们所能达到的效果取决于其功能以及对可控数据的处理。在适当的情况下,这种缺陷可能会对商业相关的功能和网站本身的安全造成毁灭性的后果
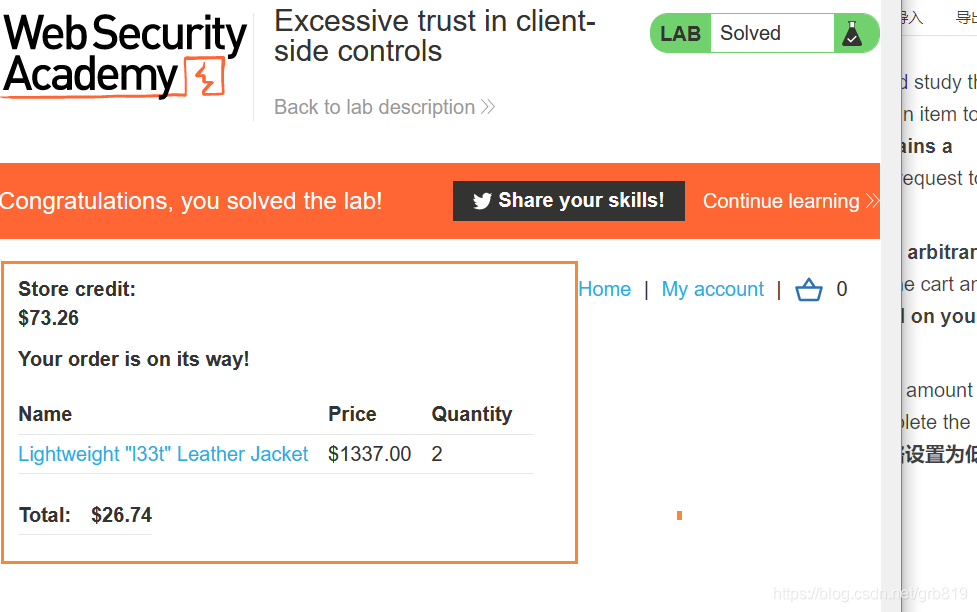
Lab: Excessive trust in client-side controls
This lab doesn’t adequately validate user input. You can exploit a logic flaw in its purchasing workflow to buy items for an unintended price. To solve the lab, buy a
"Lightweight l33t leather jacket".
You can log in to your own account using the following credentials:
wiener:peter
- With Burp running, log in and attempt to buy the leather jacket. The order is rejected because you don’t have enough store credit.
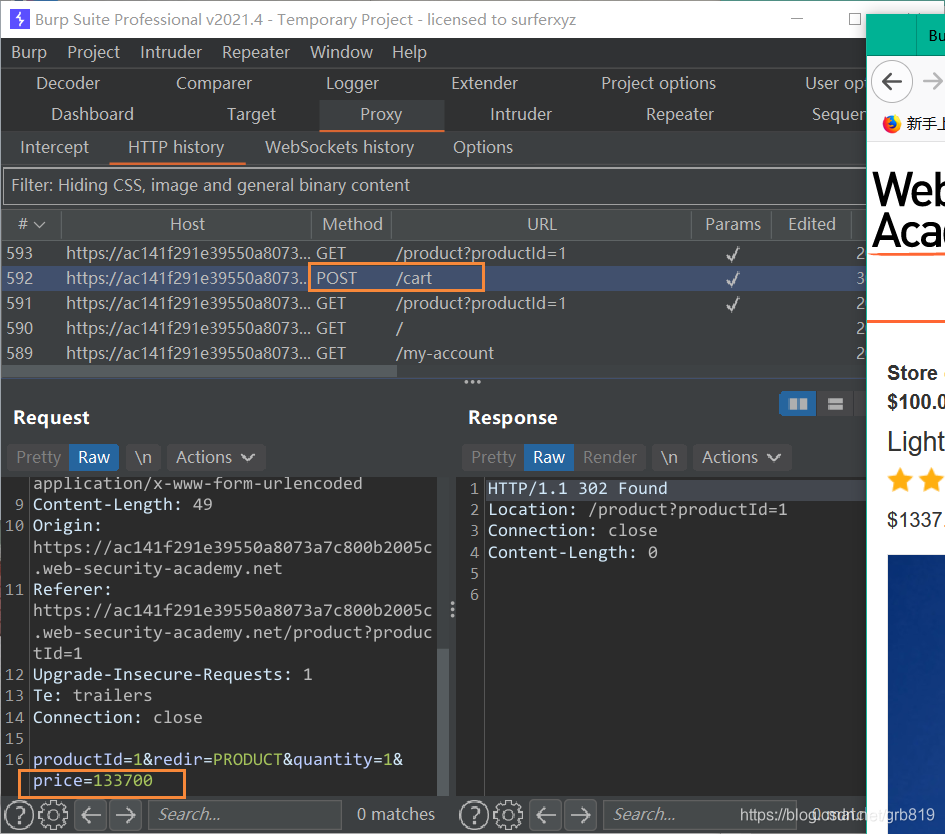
- In Burp, go to “Proxy” > “HTTP history” and study the order process. Notice that when you add an item to your cart, the corresponding request contains a
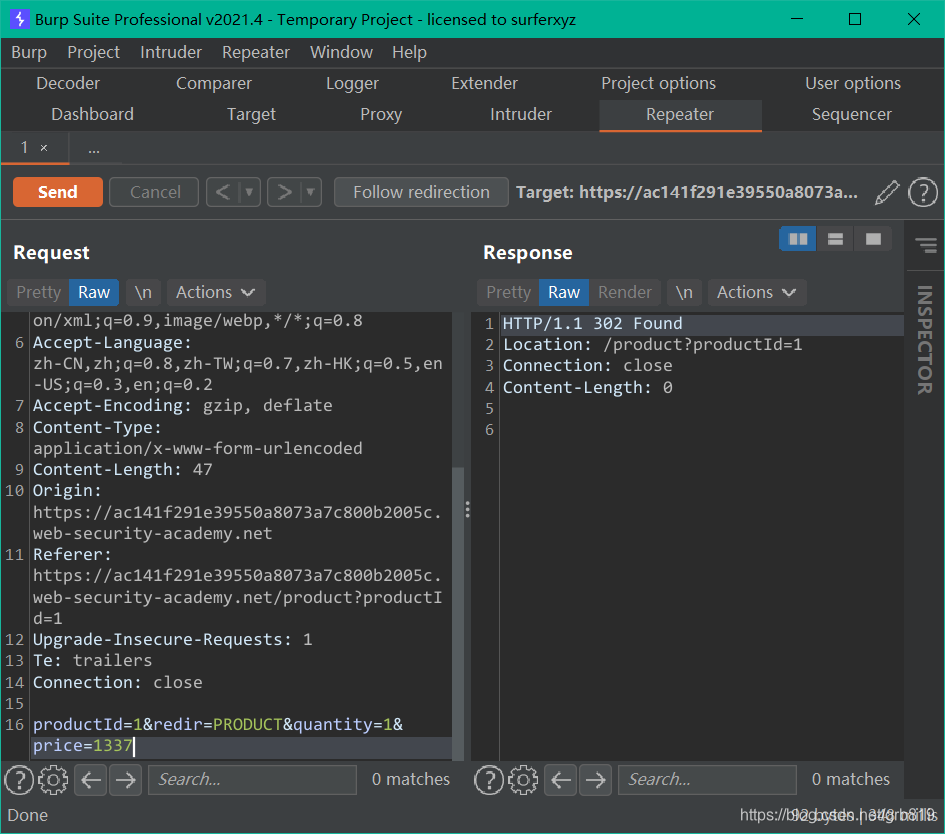
priceparameter. Send thePOST /cartrequest to Burp Repeater. - In Burp Repeater, change the price to an arbitrary integer and send the request. Refresh the cart and confirm that the price has changed based on your input.
- Repeat this process to set the price to any amount less than your available store credit. Complete the order to solve the lab. 重复此过程,将价格设置为低于可用商店积分的任何金额。

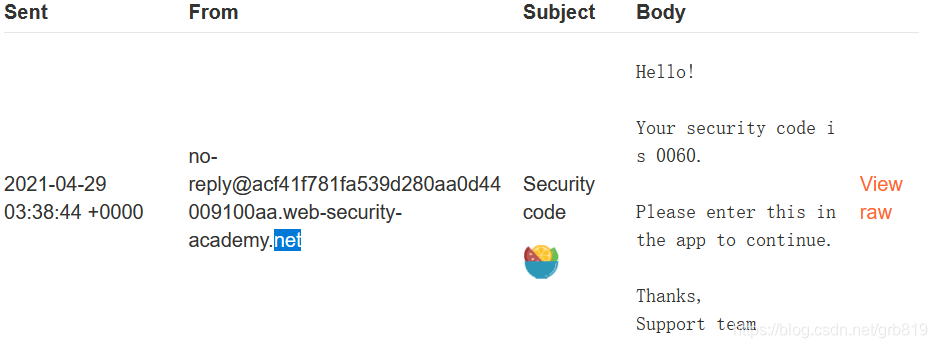
Lab: 2FA broken logic
This lab’s two-factor authentication is vulnerable due to its flawed logic. To solve the lab, access Carlos’s account page.
Your credentials: wiener:peter
Victim's username: carlos
You also have access to the email server to receive your 2FA verification code.
- With Burp running, log in to your own account and investigate the 2FA verification process. Notice that in the
POST /login2request, the verify parameter is used to determine which user’s account is being accessed. - Log out of your account.
- Send the
GET /login2request to Burp Repeater. Change the value of the verify parameter tocarlosand send the request. This ensures that a temporary 2FA code is generated for Carlos. - Go to the login page and enter your username and password. Then, submit an invalid 2FA code.
- Send the
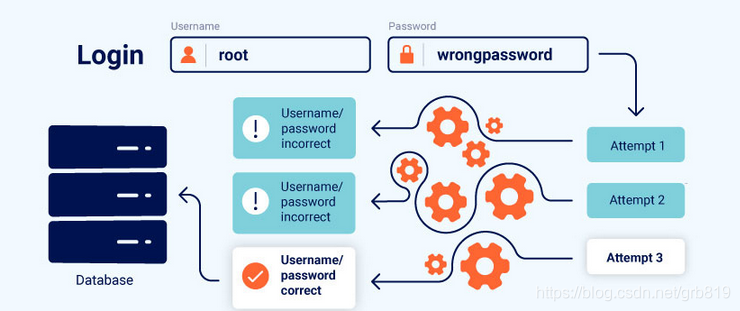
POST /login2request to Burp Intruder. In Burp Intruder, set theverifyparameter tocarlosand add a payload position to themfa-codeparameter. Brute-force the verification code. - Load the 302 response in your browser.
- Click “My account” to solve the lab.





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 2015
2015

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








