获取、查询相关
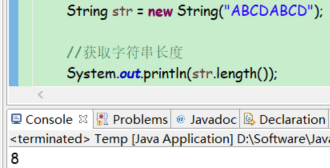
获取字符串长度
public int length()
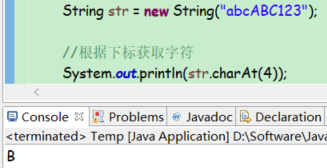
根据下标获取字符(获取字符串中指定位置的字符)
public char charAt(int index)
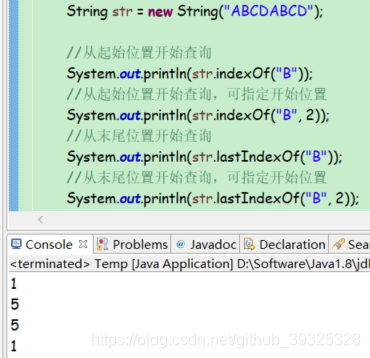
查询字符所在位置
public int indexOf(String str)
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
public int lastIndexOf(String str)
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
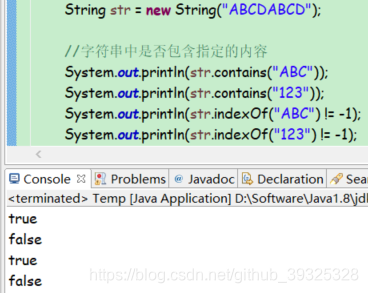
判断相关
是否包含指定的内容
public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
public int indexOf(String str)
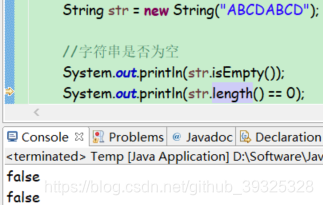
是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
public int length()
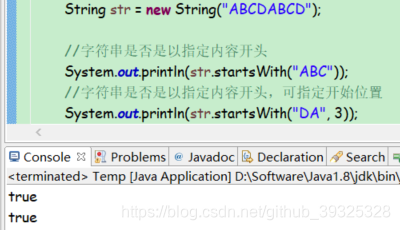
是否是以指定内容开头
public boolean startsWith(String prefix)
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
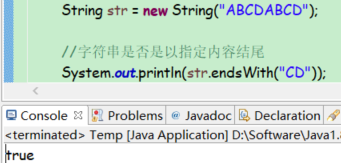
是否是以指定内容结尾
public boolean endsWith(String suffix)
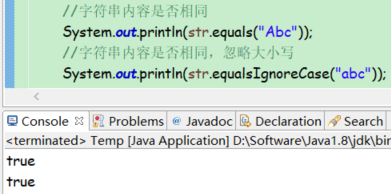
是否内容相同
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
改变内容相关
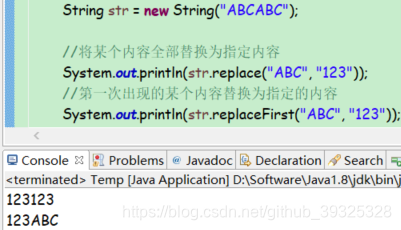
替换
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
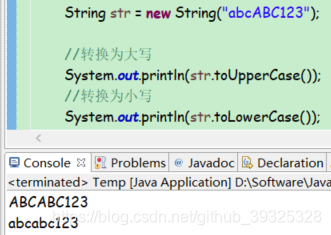
转换大小写
public String toUpperCase()
public String toLowerCase()
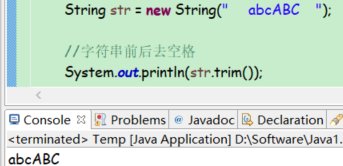
去空格
public String trim()
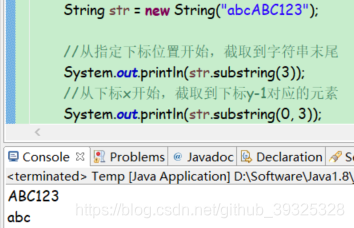
截取
public String substring(int beginIndex)
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
数组相关
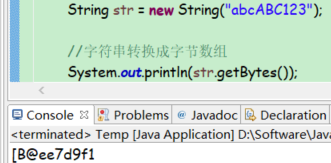
转换成字节数组
public byte[] getBytes()
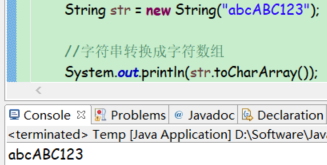
转换成字符数组
public char[] toCharArray()
分割为String[]
public String[] split(String regex)






 本文详细介绍Java中字符串的各种操作方法,包括获取长度、查询字符位置、判断条件、替换内容、转换大小写、截取子串等实用技巧,并涵盖数组转换及分割等功能。
本文详细介绍Java中字符串的各种操作方法,包括获取长度、查询字符位置、判断条件、替换内容、转换大小写、截取子串等实用技巧,并涵盖数组转换及分割等功能。
















 2944
2944

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








