执行普通的su命令,条件是设备root,且允许应用执行su命令
// 公共函数:执行命令并获取输出
private fun executeProcess(command: Array<String>): String {
var process: Process? = null
val output = StringBuilder()
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command)
output.append(readProcessOutput(process))
} catch (e: Exception) {
output.append("Exception: ").append(e.message)
} finally {
process?.destroy()
}
return logAndReturn("execSuCommand", command.joinToString(" "), output.toString())
}
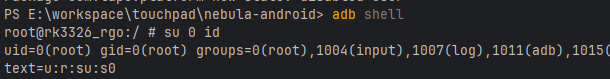
比如可以通过 executeProces(listof(“su”,"0","id"))来测试是否有su执行权限
相当于执行
2. 另外一种执行,是交互式命令,在命令执行的输出流中再写命令,并执行等待结果
private fun execSu548Command(command: String): String {
val output = StringBuilder()
var process: Process? = null
try {
// 获取 su 权限
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("su 548")
val os = process.outputStream
val dos = DataOutputStream(os)
// 写入要执行的命令
dos.writeBytes(command + "\n")
dos.writeBytes("exit\n")
dos.flush()
// 读取标准输出
val reader = BufferedReader(
InputStreamReader(process.inputStream)
)
var line: String?
while ((reader.readLine().also { line = it }) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n")
}
// 读取错误输出
val errorReader = BufferedReader(
InputStreamReader(process.errorStream)
)
while ((errorReader.readLine().also { line = it }) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n")
}
// 等待执行结束
process.waitFor()
} catch (e: java.lang.Exception) {
output.append("Exception: ").append(e.message)
} finally {
if (process != null) {
process.destroy()
}
}
val result = output.toString().trim { it <= ' ' }
LogUtils.d("$TAG execSuCommand $command,result $result")
return result
}
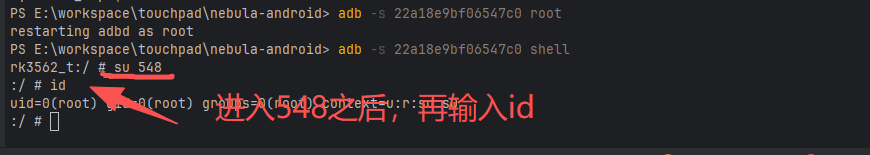
相当于




















 1294
1294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








