关注微信公众号(瓠悠笑软件部落),一起学习,一起摸鱼
 ### 路径分隔符
### 路径分隔符
在windows平台,是反斜杠 \ . 在 OSX 或者 Linux 系统里面,是正斜杠 / . os.path.join() 函数会根据所处平台选择对应的分隔符
import os
os.path.join('usr', 'bin', 'spam')
# 输出内容
'usr/bin/spam'
os.getcwd()
# 输出内容是
'/home/ldat/my-repo/PythonLearn'
#切换目录
os.chdir('/home/sesh/')
# 创建目录
os.makedirs('/home/sesh/my-new-folds/')
handling absolute and relative paths
- os.path.abspath(path) 将返回给定参数的绝对路径。
- os.path.isabs(path) 如果给的路径是绝对路径,将返回True.r如果是相对路径,将返回False
- os.path.relpath(path, start) 将返回基于 start 路径的相对路径,如果没有提供start,将会使用当前的路径作为 start 路径。
Calling os.path.dirname(path) will return a string of everything that comes
before the last slash in the path argument. Calling os.path.basename(path) will
return a string of everything that comes after the last slash in the path argu-
ment. The dir name and base name of a path are outlined in Figure 8-4.
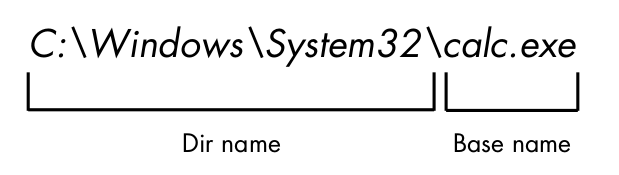
If you need a path’s dir name and base name together, you can just call
os.path.split() to get a tuple value with these two strings, like so:
>>> path = os.getcwd()
>>> os.path.dirname(path)
'/home/huxing/my-repo'
>>> os.path.basename(path)
'PythonLearn'
>>> os.path.split(path)
('/home/huxing/my-repo', 'PythonLearn')
>>> path.split(os.path.sep)
['', 'home', 'huxing', 'my-repo', 'PythonLearn']
>>>
查询文件大小和文件夹内容
- os.path.getsize(path) 返回给定路径参数下的文件的大小。单位是bytes
- os.listdir(path) 返回给定路径参数下所有的文件名参数。(注意这个函数是在 os 模块下,不是在 os.path 路径下)
>>> os.listdir('.')
['lower.py', 'passingReference.py', 'MultipleAssignmentTrick.py', 'cat.py', 'insertList.py', 'guessNumber.py', 'magic8Ball2.py', 'regexLearn.py', 'spiral.py', 'listSortByKey.py', 'negation.py', 'dictionaryLoop.py', 'bulletPointAdder2.py', 'chat.py', 'hourse.py', 'collaz.py', 'indexString.py', 'picnicTable.py', 'leanTurtle2.py', 'pyperclipLearn.py', 'ticTacToe.py', 'learnFunction.py', 'pipReLearn.py', 'tree.py', 'isPhoneNumber.py', 'collatz2.py', 'delList.py', 'guessTheNumber.py', 'subRegex.py', 'splitString.py', 'prison.py', 'plusReLearn.py', 'dataMunging.py', 'loopList.py', 'tree2.py', 'inputWord.py', 'bulletPointAdder.py', 'multilineComments.py', 'star.py', 'complexRegex.py', 'circle.py', 'sameName2.py', 'global.py', 'copyList.py', 'sameName.py', 'displayInventory.py', 'phoneAndEmail.py', 'test.py', 'printTable.py', 'stripString.py', 'pw.py', 'forward2.py', 'learnFun.py', 'prettyCharacterCount.py', 'joinString.py', '.leanTurtle3.py.swp', 'sortList.py', 'littleKid.py', '__pycache__', 'anyShape.py', 'learnLoop.py', 'func.py', 'hexagon.py', 'findAllRex.py', 'zeroDivide.py', 'totalBrought.py', 'password.py', 'validateInput.py', 'move.py', 'flower.py', 'collatz3.py', 'SecretPassword.txt', 'leanTurtle.py', 'list.py', 'matchEverything.py', 'leanTurtle3.py', '.ifLearn.py.swp', 'whileTrue.py', 'dashedLine.py', 'catnapping.py', 'while.py', 'ifLearn.py', 'caseInsensitive.py', 'starReLearn.py', 'characterCount.py', 'optionReLearn.py', 'justString.py', 'birthdays.py']
>>> os.path.getsize('.')
4096
>>> os.path.getsize('./lower.py')
159
>>>
统计文件夹包含的文件的大小
#! /usr/bin/python3
import os
total_size = 0
# 感觉这里没有统计完整,如果包含的是文件夹,并没有遍历统计该文件夹下文件的大小
for file_name in os.listdir('.'):
total_size = total_size + os.path.getsize(os.path.join('.', file_name))
print(str(total_size))
print(str(os.path.getsize('.')))
# 输出内容是
54326
4096
# 看来 os.path.getsize('.') 获取的大小并不是这个文件和其所包含的所有子文件的大小
检查路径是否有效
- os.path.exists(path) 如果给的参数路径能够找到对应的文件或者文件夹,返回True,否则返回False.
- os.path.isfile(path) 如果给的参数路径能够找到对应的文件,返回True,否则返回False.
- os.path,isdir(path) 如果给的参数路径能够找到对应的文件夹,返回True,否则返回False.
文件的读写操作
Python 中 read 或者 write 文件分为三步:
- 调用 open() 函数,返回一个 File object. open 方法默认以只读模式打开文件。
- 调用 File object 的 read() 方法读取内容, 调用 File object 的 write() 方法写内容
- 调用 File object 的 close() 方法关闭文件。
File object 的readlines()方法将返回list对象,每个元素就是文件中的每一行。
写文件操作
如果要写文件,就不能以只读模式打开文件,而是要用 写模式(write mode) 或者 追加模式(append mode)
- w write mode eg: open(‘filename.txt’, w)
- a append mode eg: open(‘filename.txt’, a)
如果传给 open() 方法的文件名没有在磁盘上找到对应的文件,那使用 写模式 或者 追加模式 都会创建一个新的,空白的文件。 在完成读取或者写文件操作后,别忘了调用close() 方法关闭文件,特别是后面代码会再次打开文件的时候。
#! /usr/bin/python3
baconFile = open('bacon.txt', 'w')
baconFile.write('Hello world\n')
baconFile.close()
baconFile = open('bacon.txt', 'a')
baconFile.write('Bacon is not a vegettable.')
baconFile.close()
baconFile = open('bacon.txt')
content = baconFile.read()
baconFile.close()
print(content)
# 输出内容
Hello world
Bacon is not a vegettable.
shelve module
可以用 shelve module 来保存变量, 这种模式将变量保存在一个二进制格式的文件中,再次打开的时候,就可以读取之前写进去的变量。
#! /usr/bin/python3
import shelve
shelfFile = shelve.open('mydata')
cats = ['Zophie', 'Pooka', 'Simon']
shelfFile['cats'] = cats
shelfFile.close()
# 下面是读取变量
#! /usr/bin/python3
import shelve
shelfFile = shelve.open('mydata')
print(type(shelfFile))
print(shelfFile['cats'])
print(list(shelfFile.keys()))
print(list(shelfFile.values()))
shelfFile.close()
# 输出的内容是
<class 'shelve.DbfilenameShelf'>
['Zophie', 'Pooka', 'Simon']
['cats']
[['Zophie', 'Pooka', 'Simon']]
随机题库
#! /usr/bin/python
# randomQuizGenerator.py - Creates quizzes with questions and answers in
# random order, along with the answer key.
import random
# The quiz data. Keys are states and values are their capitals.
capitals = {'Alabama': 'Montgomery', 'Alaska': 'Juneau', 'Arizona': 'Phoenix', 'Arkansas': 'Little Rock', 'California': 'Sacramento', 'Colorado': 'Denver', 'Connecticut': 'Hartford', 'Delaware': 'Dover', 'Florida': 'Tallahassee', 'Georgia': 'Atlanta', 'Hawaii': 'Honolulu', 'Idaho': 'Boise', 'Illinois': 'Springfield', 'Indiana': 'Indianapolis', 'Iowa': 'Des Moines', 'Kansas': 'Topeka', 'Kentucky': 'Frankfort', 'Louisiana': 'Baton Rouge', 'Maine': 'Augusta', 'Maryland': 'Annapolis', 'Massachusetts': 'Boston', 'Michigan': 'Lansing', 'Minnesota': 'Saint Paul', 'Mississippi': 'Jackson', 'Missouri': 'Jefferson City', 'Montana': 'Helena', 'Nebraska': 'Lincoln', 'Nevada': 'Carson City', 'New Hampshire': 'Concord', 'New Jersey': 'Trenton', 'New Mexico': 'Santa Fe', 'New York': 'Albany', 'North Carolina': 'Raleigh', 'North Dakota': 'Bismarck', 'Ohio': 'Columbus', 'Oklahoma': 'Oklahoma City', 'Oregon': 'Salem', 'Pennsylvania': 'Harrisburg', 'Rhode Island': 'Providence', 'South Carolina': 'Columbia', 'South Dakota': 'Pierre', 'Tennessee': 'Nashville', 'Texas': 'Austin', 'Utah': 'Salt Lake City', 'Vermont': 'Montpelier', 'Virginia': 'Richmond', 'Washington': 'Olympia', 'West Virginia': 'Charleston', 'Wisconsin': 'Madison', 'Wyoming': 'Cheyenne'}
# Generate 35 quiz files.
for quizNum in range(35):
# Create the quiz and answer key files.
quizFile = open('capitalsquiz%s.txt' % (quizNum + 1), 'w')
answerKeyFile = open('capitalsquiz_answers%s.txt' % (quizNum + 1), 'w')
# Write out the header for the quiz.
quizFile.write('Name:\n\nDate:\n\nPeriod:\n\n')
quizFile.write((' ' * 20) + 'State Capitalz Quiz (Form %s)' % (quizNum +1))
quizFile.write('\n\n')
# Shuffle the order of the states.
states = list(capitals.keys())
random.shuffle(states)
# Loop through all 50 states, making a question for each.
for questionNum in range(50):
# Get right and wrong answers.
correctAnswer = capitals[states[questionNum]]
wrongAnswers = list(capitals.values())
del wrongAnswers[wrongAnswers.index(correctAnswer)]
wrongAnswers = random.sample(wrongAnswers, 3)
answerOptions = wrongAnswers + [correctAnswer]
random.shuffle(answerOptions)
# Write the question and answer options to the quiz file.
quizFile.write('%s. What is the capital of %s?\n' % (questionNum + 1, states[questionNum]))
for i in range(4):
quizFile.write(' %s. %s\n' % ('ABCD'[i], answerOptions[i]))
quizFile.write('\n')
# Write the answer key to a file.
answerKeyFile.write('%s. %s\n' % (questionNum + 1, 'ABCD'[answerOptions.index(correctAnswer)]))
quizFile.close()
answerKeyFile.close()
缓存粘贴板内容
#! /usr/bin/python3
# mcb.pyw - Saves and loads pieces of text to the clipboard.
# Usage: python mcb.pyw save <keyword> - Saves clipboard to keyword.
# python mcb.pyw <keyword> - Loads keyword to clipboard.
# python mcb.pyw delete <keyword> - Delete keyword related content.
# python mcb.pyw list - Loads all keywords to clipboard.
import shelve, pyperclip, sys
mcbShelf = shelve.open('mcb')
# Save clipboard content.
if len(sys.argv) == 3 and sys.argv[1].lower() == 'save':
mcbShelf[sys.argv[2]] = pyperclip.paste()
elif len(sys.argv) == 3 and sys.argv[1].lower() == 'delete':
del mcbShelf[sys.argv[2]]
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
# List keywords and load content.
if sys.argv[1].lower() == 'list':
pyperclip.copy(str(list(mcbShelf.keys())))
elif sys.argv[1] in mcbShelf:
pyperclip.copy(mcbShelf[sys.argv[1]])
else:
pyperclip.copy('')
mcbShelf.close()






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








