题目如下:
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
Above is a 3 x 7 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
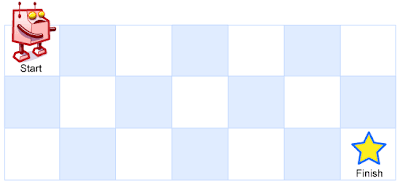
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
分析如下:
目前知道的三种解法,动态规划,排列组合,递归。
第一种,动态规划,比较好想。对于任意一点(x,y),要么是从(x,y)的左相邻点(x,y-1)过来,要么是从(x,y)的上相邻点(x-1,y)过来。如果用f(x,y)来表示robot走到点(x,y)时的走法,那么f(x,y)=f(x-1,y)+f(x,y-1)。其中,base条件是。当(x,y)位于最上面一行或者最左边一列时,由于robot要么向右走要么向下走,显然只能有1种走法,即f(x,y)=1 if(x==1 or y==0)。这个做法的时间复杂度为O(m,n),空间复杂度为O(m,n)。如果稍微优化一下,空间复杂度是可以降低为O(min(m,n))的。见下面代码。
第二种,排列组合,挺巧妙的,正好在Cracking the Code Interview书中看到了这种解法。robot从第(1,1)点走到了第(m,n)点。它只能向右或者向下,不管它怎么走,它必然向右走了m-1步,向下走了n-1步。一共走了m-1+n-1步。而不同的走法,本质是向右或者向下构成的m-1+n-1长度的序列不同。走法的总数目,本质上是m-1+n-1个总步数中选出m-1个代表向右走的走法的个数,这个问题的另一种表述是,走法的总数目,本质上是m-1+n-1个总步数中选出n-1个代表向下走的走法的个数。这其实正是组合的小性质。
C(a+b, a)=C(a+b, b)
这样题目就转换为了一个数学计算了,求C(m-1+n-1, m-1)。
第三种,递归的做法。
比较耗时间,我用OJ尝试着提交了一下递归的做法,发现超时了。
我的代码:
// version 1 动态规划 bottom-up
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int ** arr = new int* [m];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
arr[i]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
arr[i][0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
arr[0][i]=1;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
arr[i][j]=arr[i-1][j]+arr[i][j-1];
}
}
return arr[m-1][n-1];
}
};// version 2 动态规划 bottom-up 空间复杂度由O(m*n)变化为O(min(m,n));
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int s=(m<n)?m:n;
int l=(m>n)?m:n;
int * arr= new int [s];
for(int j=0;j<s;j++)
arr[j]=1;
for(int i=1;i<l;i++){
for(int j=1;j<s;j++){
arr[j]+=arr[j-1];
}
}
return arr[s-1];
}
};// version 3 组合数学角度求从m-1+n-1个数种选出m-1个数的组合的数目,即C(m-1+n-1, m-1)的数目。
class Solution {
public:
unsigned long long get_factorial(unsigned long long k){ //计算阶乘
if(k==0)
return 1;
else
return k*get_factorial(k-1);
}
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
unsigned long long b=0; //防止溢出,用unsigned long long
unsigned long long c=0;
if(m<n){ //从m-1和n-1中选出一个较小的数,节省计算时间。因为C(m+n, n)和C(m+n, m)计算结果相等,所以可以这么简化。
b=m-1;
c=n-1;
}else{
b=n-1;
c=m-1;
}
unsigned long long res=1;
unsigned long long keep_b=b;
while(b>0){
res*=(b+c);
b--;
}
res=res/get_factorial(keep_b);
return (int)res;
}
};// 提交时发现超时了。
class Solution {
public:
int _uniquePaths4(int r, int c, int m, int n) {
if(r==m-1&&c==n-1) //到达目的地,说明发掘了一条可行路径。
return 1;
if(r>=m||c>=n) ////这行不能少,否则递归没有终止条件,无限运行下去直到爆栈。
return 0;
return _uniquePaths4(r+1, c,m,n)+_uniquePaths4(r, c+1,m,n);
}
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
return _uniquePaths4(0,0, m, n);
}
};update: 2014-11-09
使用排列组合的方法来做。和上面的排列组合方法思路基本一致。代码更简洁。
class Solution {
private:
long long cal_factorial(long a, long start = 1) {
long long res= 1;
while (a >= start) {
res *= a;
a--;
}
return res;
}
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int max_mn = m>n?m:n; //尽可能使得乘积较小,防止溢出
long long a = cal_factorial(m + n - 2, max_mn);
long long b = cal_factorial(m + n - 2 - max_mn + 1);
long long result = a/b;
return result;
}
};







 本文探讨了一个机器人在限定网格内从起点到终点的不同路径数量计算问题。提供了三种解决方案:动态规划、排列组合及递归方法,并详细阐述了每种方法的实现细节与优缺点。
本文探讨了一个机器人在限定网格内从起点到终点的不同路径数量计算问题。提供了三种解决方案:动态规划、排列组合及递归方法,并详细阐述了每种方法的实现细节与优缺点。
















 333
333

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








