openssl客户端和服务器
- SSH分客户端openssh-client和openssh-server
- 如果你只是想登陆别的机器的SSH只需要安装openssh-client(ubuntu有默认安装,如果没有则sudoapt-get install openssh-client),如果要使本机开放SSH服务就需要安装openssh-server。
1 openSSH客户端的安装与配置
Ubuntu缺省已经安装了ssh client。
sudo apt-get install ssh 或者 sudo apt-get installopenssh-client
ssh-keygen //(按回车设置默认值)
按缺省生成id_rsa和id_rsa.pub文件,分别是私钥和公钥,存储于/home/xywu/.ssh/id_rsa。
说明:如果sudo apt-get insall ssh出错,无法安装可使用sudo apt-get install openssh-client进行安装。
假定服务器ip为192.168.1.1,ssh服务的端口号为22,服务器上有个用户为root;
用ssh登录服务器的命令为:
2 openssl服务端
Ubuntu缺省没有安装SSH Server,使用以下命令安装:
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
然后确认sshserver是否启动了:(或用“netstat -tlp”命令)
sudo ps -e|grep ssh
如果只有ssh-agent那ssh-server还没有启动,需要sudo service ssh start,如果看到sshd那说明ssh-server已经启动了。
如果没有则可以这样启动:
sudo service ssh start
事实上如果没什么特别需求,到这里 OpenSSH Server 就算安装好了。但是进一步设置一下,可以让 OpenSSH 登录时间更短,并且更加安全。这一切都是通过修改 openssh 的配置文件 sshd_config 实现的。
3 SSH配置
ssh-server配置文件位于/etc/ssh/sshd_config,在这里可以定义SSH的服务端口,默认端口是22,你可以自己定义成其他端口号,如222。然后重启SSH服务:
sudo service ssh restart
通过修改配置文件/etc/ssh/sshd_config,可以改ssh登录端口和禁止root登录。改端口可以防止被端口扫描。
sudo cp/etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.original
sudo chmod a-w /etc/ssh/sshd_config.original
gedit /etc/ssh/sshd_config
将sshd_config 改成一下形式:
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.101 2017/03/14 07:19:07 djm Exp $
# This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See
# sshd_config(5) for more information.
# This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin
# The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with
# OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where
# possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the
# default value.
Port 22
#AddressFamily any
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
#ListenAddress ::
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
#HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
# Ciphers and keying
#RekeyLimit default none
# Logging
#SyslogFacility AUTH
#LogLevel INFO
# Authentication:
#LoginGraceTime 2m
PermitRootLogin yes
#StrictModes yes
#MaxAuthTries 6
#MaxSessions 10
#PubkeyAuthentication yes
# Expect .ssh/authorized_keys2 to be disregarded by default in future.
#AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys .ssh/authorized_keys2
#AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none
#AuthorizedKeysCommand none
#AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody
# For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts
#HostbasedAuthentication no
# Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for
# HostbasedAuthentication
#IgnoreUserKnownHosts no
# Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files
#IgnoreRhosts yes
# To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here!
PasswordAuthentication no
#PermitEmptyPasswords no
# Change to yes to enable challenge-response passwords (beware issues with
# some PAM modules and threads)
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
# Kerberos options
#KerberosAuthentication no
#KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes
#KerberosTicketCleanup yes
#KerberosGetAFSToken no
# GSSAPI options
#GSSAPIAuthentication no
#GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes
#GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes
#GSSAPIKeyExchange no
# Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing,
# and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will
# be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and
# PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration,
# PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass
# the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password".
# If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without
# PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication
# and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'.
UsePAM yes
#AllowAgentForwarding yes
#AllowTcpForwarding yes
#GatewayPorts no
X11Forwarding yes
#X11DisplayOffset 10
#X11UseLocalhost yes
#PermitTTY yes
PrintMotd no
#PrintLastLog yes
#TCPKeepAlive yes
#UseLogin no
#PermitUserEnvironment no
#Compression delayed
#ClientAliveInterval 0
#ClientAliveCountMax 3
#UseDNS no
#PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid
#MaxStartups 10:30:100
#PermitTunnel no
#ChrootDirectory none
#VersionAddendum none
# no default banner path
#Banner none
# Allow client to pass locale environment variables
AcceptEnv LANG LC_*
# override default of no subsystems
Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server
# Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis
#Match User anoncvs
# X11Forwarding no
# AllowTcpForwarding no
# PermitTTY no
# ForceCommand cvs server
配置完成后重启:
sudo service ssh restart
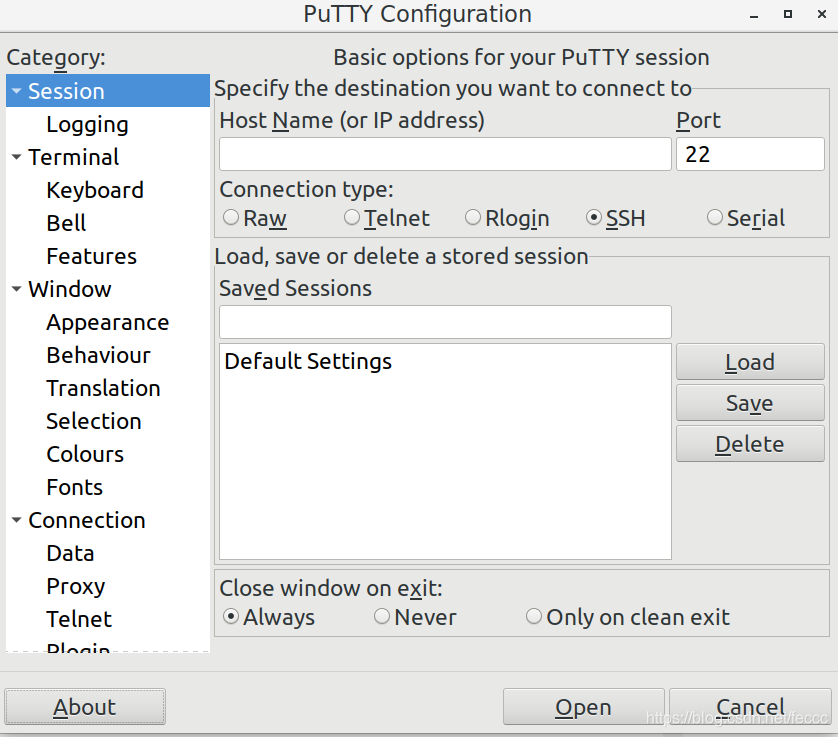
4 使用putty远程登录
安装putty
sudo apt-get install putty
sudo putty
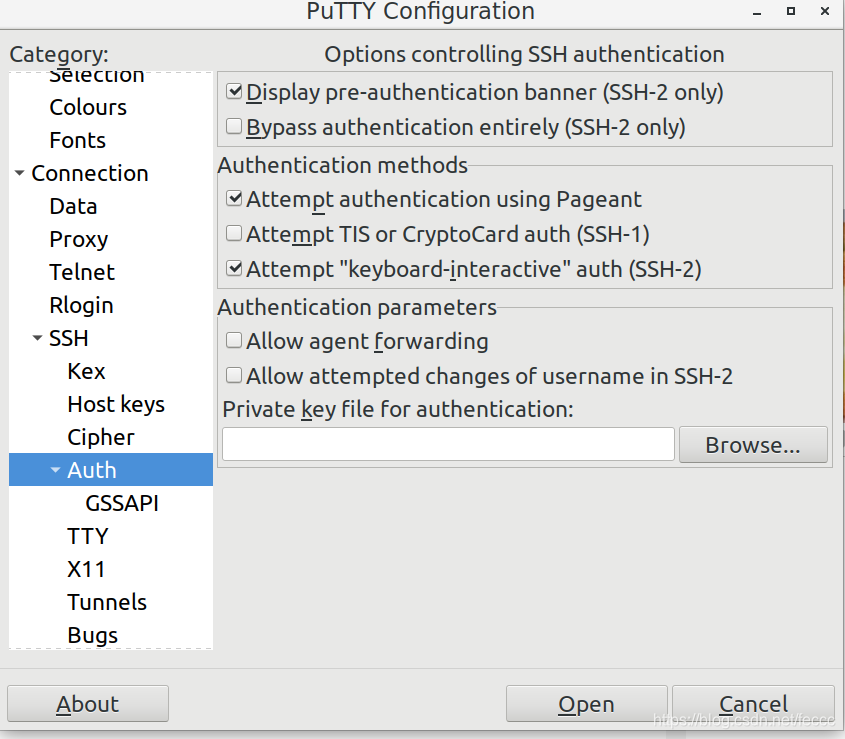
添加ssh私钥





 本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu 18.04上安装和配置OpenSSH客户端和服务端。首先,讲解了openssl在SSH中的作用,以及如何安装和验证openssh-client。接着,介绍了如何安装openssh-server,启动和检查SSH服务状态。此外,还讨论了如何通过修改sshd_config文件来定制SSH服务的安全性和效率,包括更改端口和禁止root登录。最后,提到了使用Putty进行远程登录的步骤。
本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu 18.04上安装和配置OpenSSH客户端和服务端。首先,讲解了openssl在SSH中的作用,以及如何安装和验证openssh-client。接着,介绍了如何安装openssh-server,启动和检查SSH服务状态。此外,还讨论了如何通过修改sshd_config文件来定制SSH服务的安全性和效率,包括更改端口和禁止root登录。最后,提到了使用Putty进行远程登录的步骤。
















 3920
3920

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








