104.二叉树的最大深度
Leetcode

树的最大深度就是根节点的高度。求高度用后序遍历,求深度用前序遍历。也可以用层序遍历,每遍历一层,depth += 1.
下图是卡哥视频里的截图

class solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
return self.getdepth(root)
def getdepth(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
leftheight = self.getdepth(node.left) #左
rightheight = self.getdepth(node.right) #右
height = 1 + max(leftheight, rightheight) #中
return height
559. n叉树的最大深度
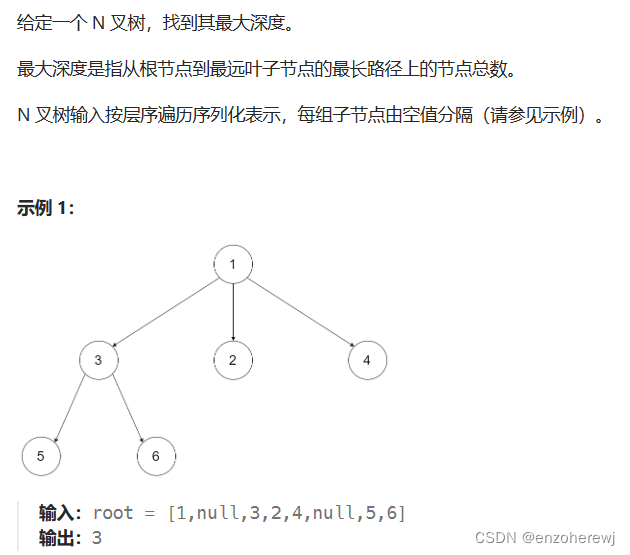
代码
递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
return self.getDepth(root)
def getDepth(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
left = self.getDepth(root.left)
right = self.getDepth(root.right)
return 1 + max(left, right)
迭代
层序遍历 bfs
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
q = deque([root])
depth = 0
while q:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
for child in node.children:
q.append(child)
return depth
dfs-------栈
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
stack = [(root, 1)]
max_depth = 0
while stack:
node, depth = stack.pop()
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
for child in node.children:
stack.append((child, depth + 1))
return max_depth
111.二叉树的最小深度

思路
求最小深度和最大深度的思路有些不一样。因为最小深度的定义如下:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点(左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点)的最短路径上的节点数量

如果只是在递归的时候return 1 + min(left, right)那么对于上图就会返回最小深度为1。所以,我们需要针对这种情况写多一些case。
求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
代码
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left = self.minDepth(root.left)
right = self.minDepth(root.right)
if root.left and not root.right:
return 1 + left
elif not root.left and root.right:
return 1 + right
elif not root.left and not root.right:
return 1
else:
return 1 + min(left, right)
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
思路
第一种使用后序遍历的方式来记录node个数
第二种利用完全二叉树的性质。
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h h h 层,则该层包含的节点在 [ 1 , 2 ( h − 1 ) ] [1, 2^{(h-1)}] [1,2(h−1)] 区间。
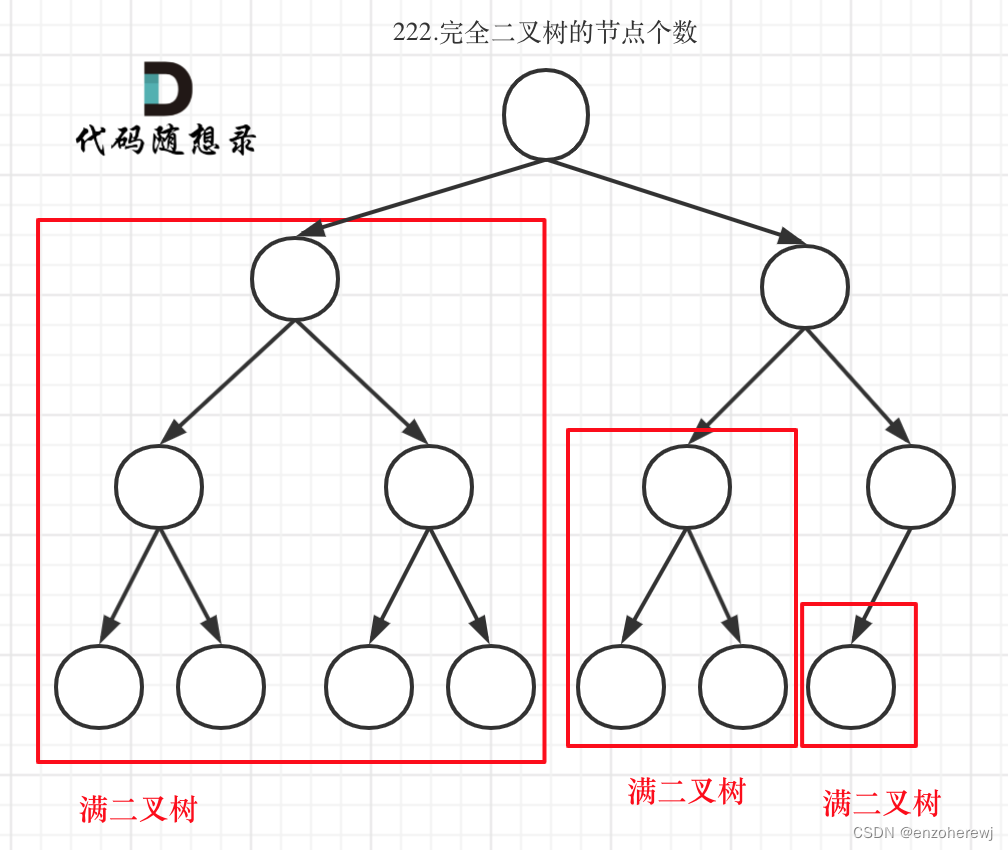
对于完全二叉树,只要左右同时向下遍历,如果长度相等则为满二叉树,那么则可以用
2
h
−
1
2^h - 1
2h−1来计算其中node个数。
代码
后序遍历递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left = self.countNodes(root.left)
right = self.countNodes(root.right)
return 1 + left + right
- 时间复杂度:
O(n) - 空间复杂度:
O(log n),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间(在python里面也是这样吗?)
完全二叉树递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
count = 1
left, right = root.left, root.right
while left and right:
count += 1
left = left.left
right = right.right
if not left and not right:
return 2**count - 1
return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right)
- 时间复杂度:
O(log n × log n) - 空间复杂度:
O(log n)








 文章介绍了如何计算二叉树的最大深度(递归、迭代和层序遍历)、二叉树的最小深度(特殊处理非空子节点情况)、以及n叉树的最大深度和完全二叉树的节点个数两种方法,包括递归和非递归实现。
文章介绍了如何计算二叉树的最大深度(递归、迭代和层序遍历)、二叉树的最小深度(特殊处理非空子节点情况)、以及n叉树的最大深度和完全二叉树的节点个数两种方法,包括递归和非递归实现。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








