文章目录
1、首先要找到 所查属性 所在的节点
2、查节点的属性值
一、节点表示
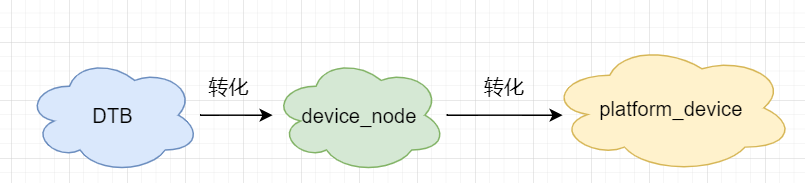
dts文件经过dtc工具编译后,才能被uboot加载到内存的指定位置。
内核从该位置获取到dtb文件进行解析,内核会将dtb文件中的节点都用 device_node 表示。
若 device_node 含有 compatible属性,那么 内核还会由此 device_node 生成 platform_device。
/include/linux/of.h
struct device_node {
const char *name; //节点名
const char *type; //设备类型,如今少用
phandle phandle;
const char *full_name; //完整名字
struct fwnode_handle fwnode;
struct property *properties; //表示节点的各个属性
struct property *deadprops;
struct device_node *parent; //父节点
struct device_node *child; //子节点
struct device_node *sibling;
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ)
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
unsigned long _flags;
void *data;
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans;
#endif
};
若设备树中的节点具有 cmpatible 属性的话, struct device_node 还会被进一步转化为 struct platform_device
二、查节点
可以从四种信息来查找节点:
路径,类型,名字,compatible
incldue/linux/of.h
1、根据路径找到节点
of_find_node_by_path()函数
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_path(const char *path);
参数:
path:查找的节点名。如 "/led",表示查找根节点下的 led 节点
返回值:
成功:device_node表示的节点
失败:NULL
2、根据设备类型(“device_type“属性)来查找节点
of_find_node_by_type()函数
设备树官方文档不建议使用
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_type(struct device_node *from, const char *type);
参数:
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点开始查找
type:要查找的设备类型值
3、根据节点名字("name"属性)来查找节点
of_find_node_by_name()函数
不建议使用
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_name(struct device_node *from,const char *name);
4、根据 conpatible属性值 来查找节点
of_find_compatible_node()函数
struct device_node *of_find_compatible_node(struct device_node *from,const char *type, const char *compat);
参数:
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点开始查找
type:指定 device_type 属性值
compat:指定 compatible 属性值
返回值:
成功:device_node表示的节点
失败:NULL
三、查节点的属性值
incldue/linux/of.h
用来表示节点中的一个属性
struct property {
char *name; //属性名
int length; //属性长度
void *value; //属性值
struct property *next; //下一个属性
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
unsigned long _flags;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_PROMTREE)
unsigned int unique_id;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ)
struct bin_attribute attr;
#endif
};
1、根据节点的属性名字来查找属性值
of_find_property()函数
依据:节点+属性名
struct property *of_find_property(const struct device_node *np,const char *name,int *lenp);
参数:
np:device_node表示的节点
name:查找的属性名字
lenp:属性值的字节数,此参数为传出参数
返回值:
成功:property表示的属性
失败:NULL
案例:
test_property {
test_name = “hello”;
};
name:“hello”
lenp = 6
2、读取一个数据类型32位无符号整数的属性值
of_property_read_u32()函数
static inline int of_property_read_u32(const struct device_node *np,const char *propname,
u32 *out_value);
参数:
np:属性所在的节点
propname:查找的属性名字
out_value:属性值的整数值,传出参数
返回值:
成功:0
失败:负值
3、读取数据类型为32位无符号整数数组的属性值
of_property_read_u32_array()函数
int of_property_read_u32_array(const struct device_node *np,const char *propname,u32 *out_values,size_t sz)
np:device_node表示的节点
name:查找的属性名字
out_value:读取到的数组值
sz :要读取的数组元素数量
4、读取数据类型为字符串的属性值
of_property_read_string()函数
int of_property_read_string(struct device_node *np,const char *propname,const char **out_string)
参数:
np:device_node表示的节点
proname:查找的属性名字
out_string:读取到的字符串值,传出参数
返回值:
成功:0
失败:负值
四、驱动源码
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_address.h>
#define DEV_NAME "get_dts_info"
#define DEV_CNT (1)
//定义字符设备的设备号
static dev_t led_devno;
//定义字符设备结构体chr_dev
static struct cdev led_chr_dev;
//创建类
struct class *led_chrdev_class;
struct device_node *led_device_node; //led的设备树节点
struct device_node *rgb_led_red_device_node; //rgb_led_red 红灯节点
struct property *rgb_led_red_property; //定义属性结构体指针
int size = 0 ;
unsigned int out_values[18]; //保存读取得到的REG 属性值
/*.open 函数*/
static int led_chr_dev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
int error_status = -1;
printk("\n open form device \n");
/*获取DTS属性信息*/
led_device_node = of_find_node_by_path("/test_led");
if(led_device_node == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get led_device_node failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
/*根据 led_device_node 设备节点结构体输出节点的基本信息*/
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s",led_device_node->name); //输出节点名
printk(KERN_ALERT "child name: %s",led_device_node->child->name); //输出子节点的节点名
/*获取 rgb_led_red_device_node 的子节点*/
rgb_led_red_device_node = of_get_next_child(led_device_node,NULL);
if(rgb_led_red_device_node == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get rgb_led_red_device_node failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s",rgb_led_red_device_node->name); //输出节点名
printk(KERN_ALERT "parent name: %s",rgb_led_red_device_node->parent->name); //输出父节点的节点名
/*获取 rgb_led_red_device_node 节点 的"compatible" 属性 */
rgb_led_red_property = of_find_property(rgb_led_red_device_node,"compatible",&size);
if(rgb_led_red_property == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get rgb_led_red_property failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT "size = : %d",size); //实际读取得到的长度
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s",rgb_led_red_property->name); //输出属性名
printk(KERN_ALERT "length: %d",rgb_led_red_property->length); //输出属性长度
printk(KERN_ALERT "value : %s",(char*)rgb_led_red_property->value); //属性值
/*获取 reg 地址属性*/
error_status = of_property_read_u32_array(rgb_led_red_device_node,"reg",out_values, 2);
if(error_status != 0)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get out_values failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT"0x%08X ", out_values[0]);
printk(KERN_ALERT"0x%08X ", out_values[1]);
return 0;
}
/*.release 函数*/
static int led_chr_dev_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("\nrelease\n");
return 0;
}
/*字符设备操作函数集*/
static struct file_operations led_chr_dev_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_chr_dev_open,
.release = led_chr_dev_release,
};
/*
*驱动初始化函数
*/
static int __init led_chrdev_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
printk("led chrdev init\n");
//第一步
//采用动态分配的方式,获取设备编号,次设备号为0,
//设备名称为EmbedCharDev,可通过命令cat /proc/devices查看
//DEV_CNT为1,当前只申请一个设备编号
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&led_devno, 0, DEV_CNT, DEV_NAME);
if(ret < 0){
printk("fail to alloc led_devno\n");
goto alloc_err;
}
led_chrdev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "led_chrdev");
//第二步
//关联字符设备结构体cdev与文件操作结构体file_operations
cdev_init(&led_chr_dev, &led_chr_dev_fops);
//第三步
//添加设备至cdev_map散列表中
ret = cdev_add(&led_chr_dev, led_devno, DEV_CNT);
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("fail to add cdev\n");
goto add_err;
}
//创建设备
device_create(led_chrdev_class, NULL, led_devno, NULL,
DEV_NAME);
return 0;
add_err:
//添加设备失败时,需要注销设备号
unregister_chrdev_region(led_devno, DEV_CNT);
alloc_err:
return ret;
}
/*
*驱动注销函数
*/
static void __exit led_chrdev_exit(void)
{
printk("chrdev exit\n");
device_destroy(led_chrdev_class, led_devno); //清除设备
cdev_del(&led_chr_dev); //清除设备号
unregister_chrdev_region(led_devno, DEV_CNT); //取消注册字符设备
class_destroy(led_chrdev_class); //清除类
}
module_init(led_chrdev_init);
module_exit(led_chrdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");





 本文详细介绍了设备树(DTS)在Linux内核中的表示及使用,包括通过节点路径、设备类型、名字和compatible属性查找设备节点,以及如何读取节点属性值。文章还提供了一个驱动源码示例,展示如何在驱动程序中利用DTS信息进行操作。
本文详细介绍了设备树(DTS)在Linux内核中的表示及使用,包括通过节点路径、设备类型、名字和compatible属性查找设备节点,以及如何读取节点属性值。文章还提供了一个驱动源码示例,展示如何在驱动程序中利用DTS信息进行操作。
















 600
600

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








