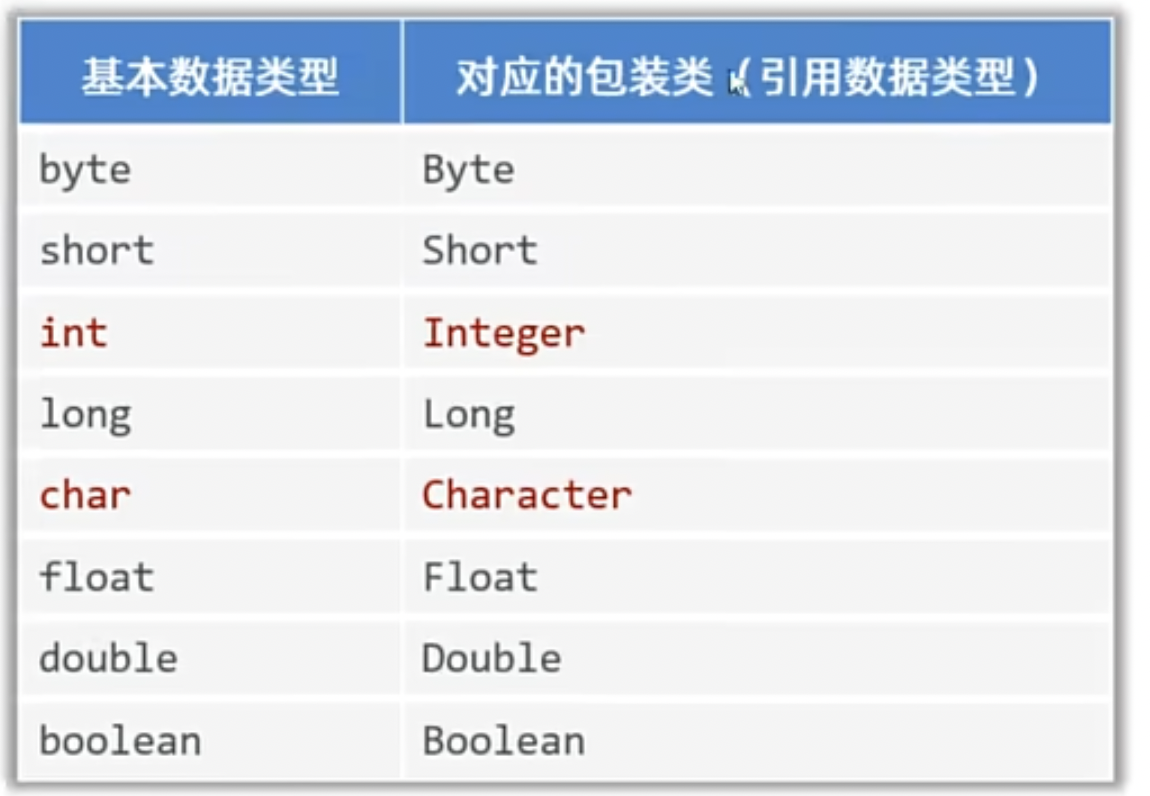
Java 中有 8 种基本数据类型,分别是 :
byte、short、int、long、float、double、char、boolean。
Java 的泛型机制要求:泛型参数必须是引用类型,而不能是基本数据类型。
包装类
为了能让基本数据类型用于泛型,Java 提供了对应的包装类,
包装类就是把基本数据类型的数据包装成对象的类型。
以下示例展示了 ArrayList 使用 Integer 而不是 int 的情况:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 正确:使用包装类 Integer
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
integerList.add(1);
integerList.add(2);
System.out.println(integerList);
// 错误:不能使用基本数据类型 int
// List<int> intList = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
在这个示例中,List<Integer> 是正确的,因为 Integer 属于引用类型;而 List<int> 会产生编译错误,因为 int 是基本数据类型。
装箱和拆箱
装箱:把基本数据类型变为包装类类型的过程叫做装箱
拆箱:把包装类类型变为基本数据类型的过程叫做拆箱
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 10;
//装箱操作,新建一个Integer类型对象,将i的值放入对象的某个属性中
Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(i);
Integer integer2 = new Integer(i);
//拆箱操作,将Integer对象中的值取出,放到一个基本的数据类型中
int j = integer1.intValue();
}
}
Java 提供了自动装箱和拆箱机制,能够在基本数据类型和对应的包装类之间自动转换。例如:
Integer num = 10; // 自动装箱,将 int 类型的 10 转换为 Integer 类型
int value = num; // 自动拆箱,将 Integer 类型的 num 转换为 int 类型
这样,在使用 ArrayList<Integer> 时,你可以直接添加 int 类型的值,Java 会自动进行装箱操作。
【思考】:
public class Test {
//下面代码输出什么,为什么?
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 100;
Integer b = 100;
Integer c = 200;
Integer d = 200;
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(c == d);
}
//结果为:
//true
//false
}
为什么是这种结果呢,这跟我们装箱中的valueOf(int i)这个方法有关系,我们来看源码:
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
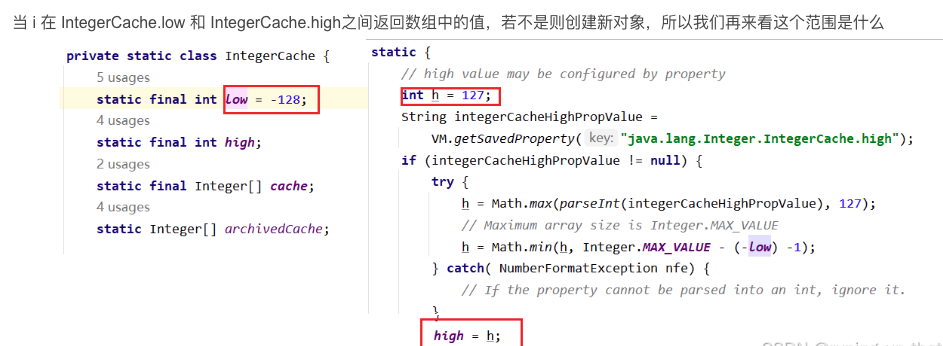
100在这个区域内,返回同一个数,所以输出true,
而200不在,所以创建了两个新对象,所以输出false。
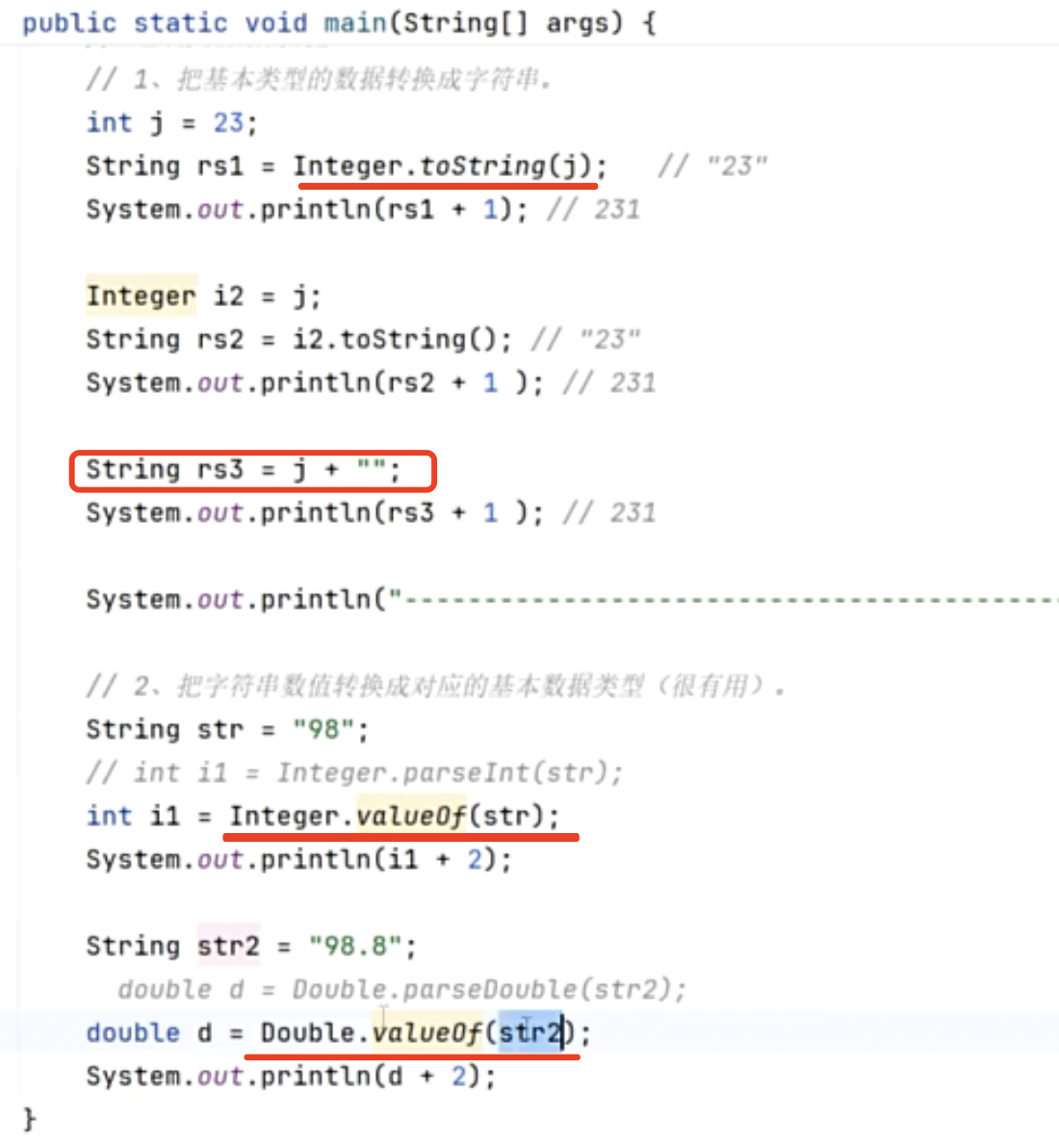
包装类的其他功能





















 1064
1064

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








