See also: Lemmings1, Lemmings2, and Lemmings3.
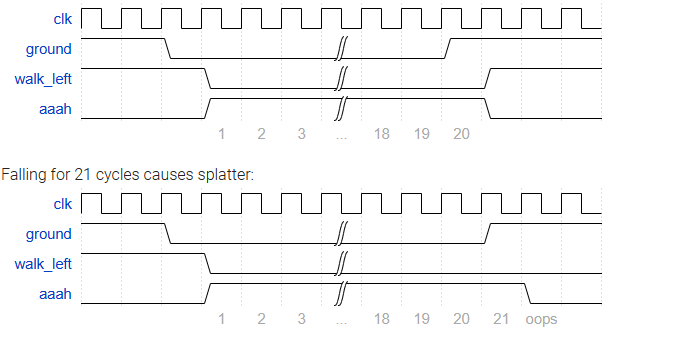
Although Lemmings can walk, fall, and dig, Lemmings aren't invulnerable. If a Lemming falls for too long then hits the ground, it can splatter. In particular, if a Lemming falls for more than 20 clock cycles then hits the ground, it will splatter and cease walking, falling, or digging (all 4 outputs become 0), forever (Or until the FSM gets reset). There is no upper limit on how far a Lemming can fall before hitting the ground. Lemmings only splatter when hitting the ground; they do not splatter in mid-air.
Extend your finite state machine to model this behaviour.
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset, // Freshly brainwashed Lemmings walk left.
input bump_left,
input bump_right,
input ground,
input dig,
output walk_left,
output walk_right,
output aaah,
output digging );
parameter LEFT = 3'b000,
DIG_L = 3'b110,
FALL_L = 3'b111,
SPLAT = 3'b101,
RIGHT = 3'b001,
DIG_R = 3'b010,
FALL_R = 3'b011;
reg [2:0] state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
reg [4:0] cnt_fall;
reg fall_flag;
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset)
if(areset)
cnt_fall <= 5'd0;
else if(next_state == FALL_L || next_state == FALL_R)
cnt_fall <= cnt_fall + 1;
else
cnt_fall <= 0;
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset)
if(areset)
fall_flag <= 0;
else if(cnt_fall == 20)
fall_flag <= 1;
else
fall_flag <= fall_flag;
always@ (posedge clk or posedge areset)
if(areset)
state <= LEFT;
else
state <= next_state;
always@(*)
case (state)
LEFT:
if(ground == 0)
next_state <= FALL_L;
else if(dig)
next_state <= DIG_L;
else if(bump_left)
next_state <= RIGHT;
else
next_state <= LEFT;
DIG_L:
if(ground == 0)
next_state <= FALL_L;
else
next_state <= DIG_L;
FALL_L:
if(ground) begin
if(fall_flag)
next_state <= SPLAT;
else
next_state <= LEFT;
end
else
next_state <= FALL_L;
SPLAT:
next_state <= SPLAT;
RIGHT:
if(ground == 0)
next_state <= FALL_R;
else if(dig)
next_state <= DIG_R;
else if(bump_right)
next_state <= LEFT;
else
next_state <= RIGHT;
DIG_R:
if(ground == 0)
next_state <= FALL_R;
else
next_state <= DIG_R;
FALL_R:
if(ground) begin
if(fall_flag)
next_state <= SPLAT;
else
next_state <= RIGHT;
end
else
next_state <= FALL_R;
default:
next_state <= LEFT;
endcase
assign walk_left = (state == LEFT);
assign walk_right = (state == RIGHT);
assign aaah = (state == FALL_R || state == FALL_L);
assign digging = ((state == DIG_R || state == DIG_L ));
endmodule





 这篇文章描述了一种基于有限状态机(FSM)的方法来模拟lemmings的行为,包括行走、挖掘、碰撞和落地后的反应。关键逻辑在于计数落地次数和判断是否发生溅射,当lemming连续落下超过20次时,会停止活动。
这篇文章描述了一种基于有限状态机(FSM)的方法来模拟lemmings的行为,包括行走、挖掘、碰撞和落地后的反应。关键逻辑在于计数落地次数和判断是否发生溅射,当lemming连续落下超过20次时,会停止活动。

















 1376
1376

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










