题目:
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
解法1:
直接改变结点的值,代码比较简单但是不符合题目要求
c++:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur && cur->next){
swap(cur->val, cur->next->val);
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return head;
}
};
解法2:迭代法
首先查看链表的结点个数 如果结点为空 或者有一个结点,则直接返回head
新建头结点 注意 别忘 dummy.next = head;
新建指向头结点的指针cur
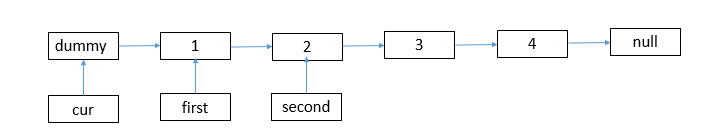
first->next = second->next;
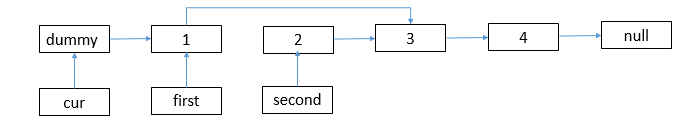
second->next = first;
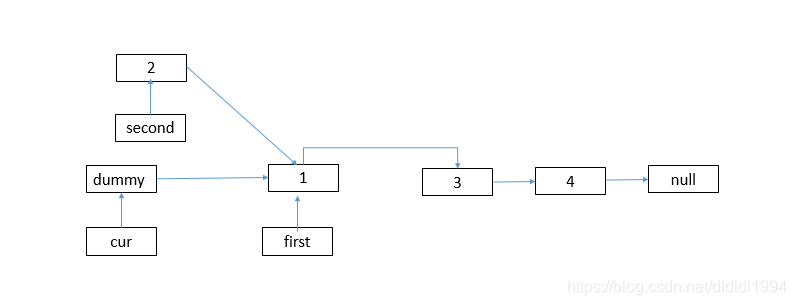
cur->next = second;
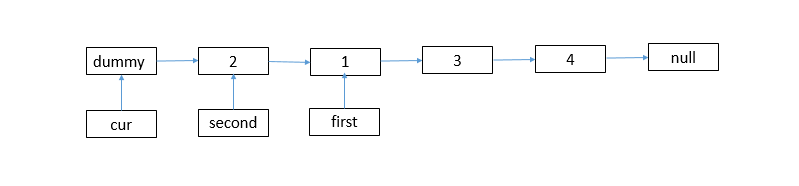
cur = cur->next->next;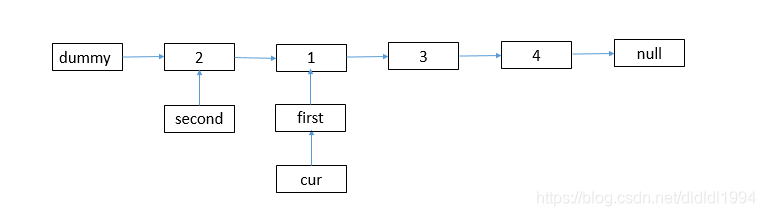
c++:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode dummy(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode* cur = &dummy;
while(cur->next && cur->next->next){
ListNode* first = cur->next;
ListNode* second = cur->next->next;
first->next = second->next;
second->next = first;
cur->next = second;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
java:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
ListNode first = cur.next;
ListNode second = cur.next.next;
first.next = second.next;
second.next = first;
cur.next = second;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head or not head.next: return head
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
cur = dummy
while cur.next and cur.next.next:
first = cur.next
second = cur.next.next
first.next = second.next
second.next = first
cur.next = second
cur = cur.next.next
return dummy.next
解法3:
递归法
1->2->3->4
递归法求解 考虑最后一步 后面的结点都排好了 只需要交换前两个结点就好了
c++:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* temp = head->next;
head->next = swapPairs(head->next->next);
temp->next = head;
return temp;
}
};
java:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(head.next.next);
temp.next = head;
return temp;
}
}
Python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head or not head.next: return head
temp = head.next
head.next = self.swapPairs(head.next.next)
temp.next = head
return temp








 博客围绕链表相邻节点交换问题展开,要求不修改节点值,仅改变节点本身。给出三种解法,包括直接改变节点值(不符合要求)、迭代法和递归法,并分别给出了C++、Java、Python的代码示例。
博客围绕链表相邻节点交换问题展开,要求不修改节点值,仅改变节点本身。给出三种解法,包括直接改变节点值(不符合要求)、迭代法和递归法,并分别给出了C++、Java、Python的代码示例。
















 354
354

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








