目录
测试理论与方法论
软件测试生命周期(STLC)
软件测试生命周期(Software Testing Life Cycle, STLC)是测试活动的系统化过程,它与软件开发生命周期(SDLC)紧密结合,确保软件质量目标的达成。
需求分析阶段
主要活动:分析业务需求、识别测试范围、确定环境要求
产出物:需求追溯矩阵(RTM)、测试策略、工作量估算
目标:确保所有需求都被测试覆盖
测试计划阶段
主要活动:制定测试策略、资源规划、风险评估
产出物:测试计划文档、资源分配计划、风险策略
目标:为整个测试过程制定详细的执行计划
测试设计阶段
主要活动:设计测试用例、准备测试数据、设计环境
产出物:测试用例文档、测试数据集、环境指南
目标:创建详细的测试执行方案
环境搭建阶段
主要活动:搭建测试环境、配置工具、执行冒烟测试
产出物:可用的测试环境、配置文档、冒烟测试报告
目标:确保测试环境准备就绪
测试执行阶段
主要活动:执行测试用例、记录结果、报告缺陷
产出物:测试执行报告、缺陷报告、测试日志
目标:发现并报告软件缺陷
测试关闭阶段
主要活动:评估测试完成度、总结经验教训、归档工件
产出物:测试总结报告、经验教训文档、归档文件
目标:完成测试过程并总结经验
测试级别详解
单元测试(Unit Testing)
import unittest
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
class Calculator:
"""计算器类 - 用于演示单元测试"""
def __init__(self):
self.history = []
def add(self, a, b):
"""加法运算"""
if not isinstance(a, (int, float)) or not isinstance(b, (int, float)):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
result = a + b
self.history.append(f"{a} + {b} = {result}")
return result
def divide(self, a, b):
"""除法运算"""
if not isinstance(a, (int, float)) or not isinstance(b, (int, float)):
raise TypeError("参数必须是数字")
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("除数不能为零")
result = a / b
self.history.append(f"{a} / {b} = {result}")
return result
def get_history(self):
"""获取计算历史"""
return self.history.copy()
def clear_history(self):
"""清空历史记录"""
self.history.clear()
class TestCalculator(unittest.TestCase):
"""计算器单元测试"""
def setUp(self):
"""测试前准备"""
self.calc = Calculator()
def tearDown(self):
"""测试后清理"""
self.calc.clear_history()
def test_add_positive_numbers(self):
"""测试正数加法"""
result = self.calc.add(2, 3)
self.assertEqual(result, 5)
self.assertIn("2 + 3 = 5", self.calc.get_history())
def test_add_negative_numbers(self):
"""测试负数加法"""
result = self.calc.add(-2, -3)
self.assertEqual(result, -5)
def test_add_mixed_numbers(self):
"""测试正负数混合加法"""
result = self.calc.add(5, -3)
self.assertEqual(result, 2)
def test_add_floating_point(self):
"""测试浮点数加法"""
result = self.calc.add(2.5, 3.7)
self.assertAlmostEqual(result, 6.2, places=1)
def test_add_invalid_type(self):
"""测试无效类型输入"""
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
self.calc.add("2", 3)
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
self.calc.add(2, None)
def test_divide_normal_case(self):
"""测试正常除法"""
result = self.calc.divide(10, 2)
self.assertEqual(result, 5)
def test_divide_by_zero(self):
"""测试除零异常"""
with self.assertRaises(ValueError) as context:
self.calc.divide(10, 0)
self.assertEqual(str(context.exception), "除数不能为零")
def test_divide_floating_result(self):
"""测试产生浮点数结果的除法"""
result = self.calc.divide(7, 3)
self.assertAlmostEqual(result, 2.333, places=3)
def test_history_functionality(self):
"""测试历史记录功能"""
self.calc.add(1, 2)
self.calc.divide(6, 3)
history = self.calc.get_history()
self.assertEqual(len(history), 2)
self.assertIn("1 + 2 = 3", history)
self.assertIn("6 / 3 = 2", history)
def test_clear_history(self):
"""测试清空历史记录"""
self.calc.add(1, 2)
self.calc.clear_history()
history = self.calc.get_history()
self.assertEqual(len(history), 0)
class UnitTestBestPractices:
"""单元测试最佳实践指南"""
@staticmethod
def demonstrate_test_doubles():
"""演示测试替身的使用"""
# Mock对象示例
class EmailService:
def send_email(self, to, subject, body):
# 实际发送邮件的逻辑
pass
class UserNotification:
def __init__(self, email_service):
self.email_service = email_service
def notify_user(self, user_email, message):
try:
self.email_service.send_email(
user_email,
"系统通知",
message
)
return True
except Exception:
return False
# 测试用例
mock_email_service = Mock()
notification = UserNotification(mock_email_service)
# 执行测试
result = notification.notify_user("test@example.com", "测试消息")
# 验证
assert result is True
mock_email_service.send_email.assert_called_once_with(
"test@example.com",
"系统通知",
"测试消息"
)
print("Mock对象测试通过")
@staticmethod
def demonstrate_patch_decorator():
"""演示Patch装饰器的使用"""
class FileProcessor:
def read_config(self, filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
return f.read()
def process_file(self, filename):
content = self.read_config(filename)
return content.upper()
# 使用patch装饰器测试
@patch('builtins.open')
def test_file_processing(mock_open):
mock_open.return_value.__enter__.return_value.read.return_value = "hello world"
processor = FileProcessor()
result = processor.process_file("test.txt")
assert result == "HELLO WORLD"
mock_open.assert_called_once_with("test.txt", 'r')
print("Patch装饰器测试通过")
test_file_processing()
# 运行单元测试示例
def run_unit_tests():
"""运行单元测试"""
print("=== 单元测试执行 ===")
# 创建测试套件
suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(TestCalculator)
# 运行测试
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity=2)
result = runner.run(suite)
print(f"\n测试结果:")
print(f"运行测试: {result.testsRun}")
print(f"失败: {len(result.failures)}")
print(f"错误: {len(result.errors)}")
# 演示最佳实践
practices = UnitTestBestPractices()
practices.demonstrate_test_doubles()
practices.demonstrate_patch_decorator()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_unit_tests()单一职责原则:计算器类专注于计算和历史管理,测试类专注于验证功能,职责分明。
异常测试:不仅测试正常流程,也覆盖异常分支,保证代码健壮。
测试环境隔离:每个测试用例前后清理状态,避免测试间相互影响。
使用Mock和Patch:模拟外部依赖和I/O操作,提升测试效率和稳定性。
详细断言:不仅断言结果,还验证调用次数和参数,确保行为符合预期。
集成测试(Integration Testing)
import requests
import sqlite3
from typing import Dict, Optional
class DatabaseManager:
"""数据库管理器"""
def __init__(self, db_path=":memory:"):
self.db_path = db_path
self.connection = None
self.init_database()
def init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
self.connection = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
# 创建用户表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
username TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
# 创建订单表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS orders (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
user_id INTEGER,
product_name TEXT NOT NULL,
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
total_amount DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
status TEXT DEFAULT 'pending',
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users (id)
)
''')
self.connection.commit()
def create_user(self, username: str, email: str) -> int:
"""创建用户"""
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(
"INSERT INTO users (username, email) VALUES (?, ?)",
(username, email)
)
self.connection.commit()
return cursor.lastrowid
def get_user(self, user_id: int) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""获取用户信息"""
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(
"SELECT id, username, email, created_at FROM users WHERE id = ?",
(user_id,)
)
row = cursor.fetchone()
if row:
return {
'id': row[0],
'username': row[1],
'email': row[2],
'created_at': row[3]
}
return None
def create_order(self, user_id: int, product_name: str,
quantity: int, total_amount: float) -> int:
"""创建订单"""
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(
"INSERT INTO orders (user_id, product_name, quantity, total_amount) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)",
(user_id, product_name, quantity, total_amount)
)
self.connection.commit()
return cursor.lastrowid
class NotificationService:
"""通知服务"""
def __init__(self, api_url: str):
self.api_url = api_url
def send_notification(self, user_email: str, message: str) -> bool:
"""发送通知"""
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{self.api_url}/notifications",
json={
'email': user_email,
'message': message
},
timeout=5
)
return response.status_code == 200
except Exception:
return False
class OrderService:
"""订单服务"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager,
notification_service: NotificationService):
self.db = db_manager
self.notification = notification_service
def create_order(self, user_id: int, product_name: str,
quantity: int, unit_price: float) -> Dict:
"""创建订单"""
# 验证用户是否存在
user = self.db.get_user(user_id)
if not user:
raise ValueError("用户不存在")
# 计算总金额
total_amount = quantity * unit_price
# 创建订单
order_id = self.db.create_order(
user_id, product_name, quantity, total_amount
)
# 发送通知
message = f"您的订单 #{order_id} 已创建成功,商品:{product_name},数量:{quantity},总金额:¥{total_amount}"
notification_sent = self.notification.send_notification(
user['email'], message
)
return {
'order_id': order_id,
'user_id': user_id,
'product_name': product_name,
'quantity': quantity,
'total_amount': total_amount,
'notification_sent': notification_sent
}
class IntegrationTestSuite:
"""集成测试套件"""
def __init__(self):
self.test_results = []
def setup_test_environment(self):
"""设置测试环境"""
self.db = DatabaseManager(":memory:") # 创建测试数据库
# 创建模拟通知服务
self.notification_service = NotificationService("http://mock-api.test")
# 创建订单服务
self.order_service = OrderService(self.db, self.notification_service)
print("集成测试环境设置完成")
def test_database_integration(self):
print("\n=== 数据库集成测试 ===")
try:
# 测试用户创建
user_id = self.db.create_user("testuser", "test@example.com")
assert user_id > 0, "用户创建失败"
# 测试用户查询
user = self.db.get_user(user_id)
assert user is not None, "用户查询失败"
assert user['username'] == "testuser", "用户信息不匹配"
# 测试订单创建
order_id = self.db.create_order(user_id, "测试商品", 2, 99.99)
assert order_id > 0, "订单创建失败"
self.test_results.append({
'test': '数据库集成测试',
'status': 'PASS',
'details': f'用户ID: {user_id}, 订单ID: {order_id}'
})
print("✓ 数据库集成测试通过")
except Exception as e:
self.test_results.append({
'test': '数据库集成测试',
'status': 'FAIL',
'details': str(e)
})
print(f"✗ 数据库集成测试失败: {e}")
def test_service_integration_with_mock(self):
print("\n=== 服务集成测试(Mock) ===")
try:
# 创建测试用户
user_id = self.db.create_user("integrationuser", "integration@test.com")
# Mock通知服务
from unittest.mock import Mock
mock_notification = Mock()
mock_notification.send_notification.return_value = True
# 创建使用Mock服务的订单服务
mock_order_service = OrderService(self.db, mock_notification)
# 测试订单创建
order_result = mock_order_service.create_order(
user_id, "集成测试商品", 1, 50.0
)
# 验证结果
assert order_result['order_id'] > 0, "订单创建失败"
assert order_result['notification_sent'] is True, "通知发送状态错误"
# 验证Mock调用
mock_notification.send_notification.assert_called_once()
self.test_results.append({
'test': '服务集成测试(Mock)',
'status': 'PASS',
'details': f'订单ID: {order_result["order_id"]}'
})
print("✓ 服务集成测试(Mock)通过")
except Exception as e:
self.test_results.append({
'test': '服务集成测试(Mock)',
'status': 'FAIL',
'details': str(e)
})
print(f"✗ 服务集成测试(Mock)失败: {e}")
def test_end_to_end_workflow(self):
"""测试端到端工作流"""
print("\n=== 端到端工作流测试 ===")
try:
# 设置Mock HTTP服务器响应
from unittest.mock import patch
with patch('requests.post') as mock_post:
# 配置Mock响应
mock_response = Mock()
mock_response.status_code = 200
mock_post.return_value = mock_response
# 创建用户
user_id = self.db.create_user("e2euser", "e2e@test.com")
# 创建订单(完整工作流)
order_result = self.order_service.create_order(
user_id, "端到端测试商品", 3, 25.99
)
# 验证工作流
assert order_result['order_id'] > 0, "订单ID无效"
assert order_result['total_amount'] == 77.97, "总金额计算错误"
assert order_result['notification_sent'] is True, "通知发送失败"
# 验证HTTP调用
mock_post.assert_called_once()
call_args = mock_post.call_args
assert call_args[1]['json']['email'] == "e2e@test.com"
self.test_results.append({
'test': '端到端工作流测试',
'status': 'PASS',
'details': f'完整工作流执行成功,订单总金额: {order_result["total_amount"]}'
})
print("✓ 端到端工作流测试通过")
except Exception as e:
self.test_results.append({
'test': '端到端工作流测试',
'status': 'FAIL',
'details': str(e)
})
print(f"✗ 端到端工作流测试失败: {e}")
def test_error_handling_integration(self):
"""测试错误处理集成"""
print("\n=== 错误处理集成测试 ===")
try:
# 测试用户不存在的情况
try:
self.order_service.create_order(9999, "不存在用户测试", 1, 10.0)
assert False, "应该抛出用户不存在异常"
except ValueError as e:
assert str(e) == "用户不存在", "异常信息不正确"
# 测试通知服务失败的情况
from unittest.mock import patch
with patch('requests.post') as mock_post:
# 模拟网络异常
mock_post.side_effect = requests.exceptions.RequestException("网络错误")
user_id = self.db.create_user("erroruser", "error@test.com")
order_result = self.order_service.create_order(
user_id, "错误处理测试", 1, 15.0
)
# 订单应该创建成功,但通知发送失败
assert order_result['order_id'] > 0, "订单应该创建成功"
assert order_result['notification_sent'] is False, "通知应该发送失败"
self.test_results.append({
'test': '错误处理集成测试',
'status': 'PASS',
'details': '异常处理正确'
})
print("✓ 错误处理集成测试通过")
except Exception as e:
self.test_results.append({
'test': '错误处理集成测试',
'status': 'FAIL',
'details': str(e)
})
print(f"✗ 错误处理集成测试失败: {e}")
def run_all_tests(self):
"""运行所有集成测试"""
self.setup_test_environment()
self.test_database_integration()
self.test_service_integration_with_mock()
self.test_end_to_end_workflow()
self.test_error_handling_integration()
# 生成测试报告
self.generate_test_report()
def generate_test_report(self):
"""生成测试报告"""
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("集成测试报告")
print("="*50)
total_tests = len(self.test_results)
passed_tests = len([r for r in self.test_results if r['status'] == 'PASS'])
failed_tests = total_tests - passed_tests
print(f"总测试数: {total_tests}")
print(f"通过: {passed_tests}")
print(f"失败: {failed_tests}")
print(f"通过率: {passed_tests/total_tests*100:.1f}%")
print("\n详细结果:")
for result in self.test_results:
status_symbol = "✓" if result['status'] == 'PASS' else "✗"
print(f"{status_symbol} {result['test']}: {result['details']}")
# 运行集成测试示例
def run_integration_tests():
test_suite = IntegrationTestSuite()
test_suite.run_all_tests()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_integration_tests()测试环境搭建
使用内存SQLite数据库,避免对真实数据产生影响。通过构造函数注入依赖,方便替换通知服务为Mock对象。
测试用例分类
数据库集成测试:验证用户和订单的创建与查询功能,确保数据库操作正确。
服务集成测试(Mock):使用 unittest.mock.Mock 模拟通知服务,验证订单服务逻辑独立于外部依赖。
端到端工作流测试:利用 unittest.mock.patch 模拟HTTP请求,测试完整订单创建和通知发送流程。
错误处理测试:覆盖用户不存在异常和通知服务异常,确保系统健壮性。
Mock与Patch的应用
Mock对象模拟通知服务,控制返回值,验证调用次数和参数,提升测试独立性。
Patch装饰器替换 requests.post,模拟网络请求响应,避免真实网络调用,提高测试速度和稳定性。
系统测试(System Testing)
import time
import psutil
from dataclasses import dataclass
import concurrent.futures
@dataclass
class PerformanceMetrics:
"""性能指标"""
response_time: float
throughput: float
cpu_usage: float
memory_usage: float
error_rate: float
class SystemTestFramework:
"""系统测试框架"""
def __init__(self):
self.test_results = {}
self.performance_data = []
def functional_system_test(self):
print("=== 功能性系统测试 ===")
test_cases = [
{
'name': '用户注册流程',
'description': '测试完整的用户注册流程',
'steps': [
'访问注册页面',
'填写用户信息',
'提交注册表单',
'验证邮箱',
'完成注册'
],
'expected_result': '用户成功注册并可以登录'
},
{
'name': '订单处理流程',
'description': '测试从下单到完成的整个流程',
'steps': [
'用户登录',
'浏览商品',
'添加到购物车',
'结算支付',
'订单处理',
'发货配送'
],
'expected_result': '订单成功完成并用户收到商品'
},
{
'name': '搜索功能测试',
'description': '测试搜索功能的准确性和性能',
'steps': [
'输入搜索关键词',
'执行搜索',
'验证搜索结果',
'测试搜索过滤',
'测试搜索排序'
],
'expected_result': '搜索结果准确且响应迅速'
}
]
for test_case in test_cases:
result = self._execute_functional_test(test_case)
self.test_results[test_case['name']] = result
print(f"测试用例: {test_case['name']}")
print(f"状态: {'通过' if result['passed'] else '失败'}")
if not result['passed']:
print(f"失败原因: {result['failure_reason']}")
print()
def _execute_functional_test(self, test_case):
"""执行功能测试"""
try:
# 模拟测试执行
print(f"执行测试: {test_case['description']}")
for step in test_case['steps']:
print(f" 执行步骤: {step}")
time.sleep(0.1) # 模拟执行时间
# 模拟测试结果验证
success_rate = 0.9 # 90%的成功率
import random
passed = random.random() < success_rate
return {
'passed': passed,
'execution_time': len(test_case['steps']) * 0.1,
'failure_reason': None if passed else "模拟测试失败"
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'passed': False,
'execution_time': 0,
'failure_reason': str(e)
}
def performance_system_test(self):
print("=== 性能系统测试 ===")
self._load_test() # 负载测试
self._stress_test() # 压力测试
self._volume_test() # 容量测试
def _load_test(self):
print("执行负载测试...")
def simulate_user_request():
"""模拟用户请求"""
start_time = time.time()
# 模拟处理时间
processing_time = 0.1 + (time.time() % 0.05)
time.sleep(processing_time)
end_time = time.time()
response_time = end_time - start_time
return {
'response_time': response_time,
'success': True,
'timestamp': end_time
}
# 模拟100个并发用户
concurrent_users = 100
requests_per_user = 10
start_time = time.time()
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=concurrent_users) as executor:
futures = []
for user in range(concurrent_users):
for request in range(requests_per_user):
future = executor.submit(simulate_user_request)
futures.append(future)
# 收集结果
results = []
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
result = future.result()
results.append(result)
end_time = time.time()
total_time = end_time - start_time
# 计算性能指标
response_times = [r['response_time'] for r in results]
avg_response_time = sum(response_times) / len(response_times)
max_response_time = max(response_times)
throughput = len(results) / total_time
print(f"负载测试结果:")
print(f" 总请求数: {len(results)}")
print(f" 平均响应时间: {avg_response_time:.3f}秒")
print(f" 最大响应时间: {max_response_time:.3f}秒")
print(f" 吞吐量: {throughput:.2f} 请求/秒")
# 记录性能数据
self.performance_data.append(PerformanceMetrics(
response_time=avg_response_time,
throughput=throughput,
cpu_usage=psutil.cpu_percent(),
memory_usage=psutil.virtual_memory().percent,
error_rate=0.0
))
def _stress_test(self):
print("\n执行压力测试...")
# 逐步增加负载直到系统崩溃
for load_level in [50, 100, 200, 500, 1000]:
print(f"测试负载级别: {load_level} 并发用户")
try:
success_count = 0
total_requests = load_level * 5
def stress_request():
try:
time.sleep(0.01) # 模拟快速请求
return True
except:
return False
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=load_level) as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(stress_request) for _ in range(total_requests)]
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures, timeout=10):
if future.result():
success_count += 1
success_rate = success_count / total_requests
print(f" 成功率: {success_rate:.2%}")
if success_rate < 0.95: # 成功率低于95%认为达到压力临界点
print(f" 系统在{load_level}并发时达到压力临界点")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f" 负载级别 {load_level} 时系统失败: {e}")
break
def _volume_test(self):
print("\n执行容量测试...")
# 测试大数据量处理
data_sizes = [1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000]
for size in data_sizes:
print(f"测试数据量: {size} 条记录")
start_time = time.time()
# 模拟数据处理
data = list(range(size))
processed_data = [x * 2 for x in data] # 简单的数据处理
end_time = time.time()
processing_time = end_time - start_time
print(f" 处理时间: {processing_time:.3f}秒")
if processing_time == 0:
processing_time = 1e-6 # 1微秒,避免除零
print(f" 处理速度: {size/processing_time:.0f} 条/秒")
# 检查内存使用
memory_usage = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
print(f" 内存使用率: {memory_usage:.1f}%")
if memory_usage > 80: # 内存使用率超过80%
print(f" 警告: 内存使用率过高")
def security_system_test(self):
print("=== 安全性系统测试 ===")
security_tests = [
{
'name': 'SQL注入测试',
'description': '测试系统对SQL注入攻击的防护',
'attack_vectors': [
"'; DROP TABLE users; --",
"' OR '1'='1",
"admin'--",
"' UNION SELECT * FROM users --"
]
},
{
'name': 'XSS攻击测试',
'description': '测试跨站脚本攻击防护',
'attack_vectors': [
"<script>alert('XSS')</script>",
"javascript:alert('XSS')",
"<img src=x onerror=alert('XSS')>",
"<svg onload=alert('XSS')>"
]
},
{
'name': '身份验证测试',
'description': '测试身份验证机制的安全性',
'test_scenarios': [
'弱密码策略测试',
'会话管理测试',
'权限控制测试',
'多因素认证测试'
]
}
]
for test in security_tests:
print(f"执行安全测试: {test['name']}")
print(f"描述: {test['description']}")
# 模拟安全测试执行
vulnerabilities_found = 0
if 'attack_vectors' in test:
for vector in test['attack_vectors']:
# 模拟攻击向量测试
is_vulnerable = self._test_attack_vector(vector)
if is_vulnerable:
vulnerabilities_found += 1
print(f" 发现漏洞: {vector}")
if 'test_scenarios' in test:
for scenario in test['test_scenarios']:
# 模拟场景测试
result = self._test_security_scenario(scenario)
if not result['passed']:
vulnerabilities_found += 1
print(f" 安全问题: {scenario}")
if vulnerabilities_found == 0:
print(f" 未发现安全漏洞")
else:
print(f" 发现 {vulnerabilities_found} 个安全问题")
print()
def _test_attack_vector(self, vector):
"""测试攻击向量"""
# 模拟攻击检测,大部分情况下系统应该能防护
import random
return random.random() < 0.1 # 10%的概率发现漏洞
def _test_security_scenario(self, scenario):
"""测试安全场景"""
# 模拟安全场景测试
import random
passed = random.random() > 0.15 # 85%的通过率
return {
'passed': passed,
'details': f"测试场景: {scenario}"
}
def usability_system_test(self):
print("=== 可用性系统测试 ===")
usability_metrics = {
'页面加载时间': {
'target': '< 3秒',
'current': '2.1秒',
'status': '通过'
},
'用户界面响应性': {
'target': '< 200ms',
'current': '150ms',
'status': '通过'
},
'操作步骤简化度': {
'target': '< 5步完成主要任务',
'current': '3步',
'status': '通过'
},
'错误消息清晰度': {
'target': '用户能理解并知道如何修正',
'current': '82%用户理解',
'status': '需改进'
},
'帮助文档完整性': {
'target': '覆盖所有主要功能',
'current': '90%覆盖',
'status': '良好'
}
}
for metric, data in usability_metrics.items():
print(f"{metric}:")
print(f" 目标: {data['target']}")
print(f" 当前: {data['current']}")
print(f" 状态: {data['status']}")
print()
def compatibility_system_test(self):
print("=== 兼容性系统测试 ===")
# 浏览器兼容性测试
browsers = ['Chrome', 'Firefox', 'Safari', 'Edge', 'IE11']
browser_results = {}
for browser in browsers:
# 模拟浏览器测试
compatibility_score = self._test_browser_compatibility(browser)
browser_results[browser] = compatibility_score
print(f"{browser}: {compatibility_score:.1f}%兼容")
print()
# 操作系统兼容性测试
operating_systems = ['Windows 10', 'macOS', 'Ubuntu', 'iOS', 'Android']
os_results = {}
for os in operating_systems:
# 模拟操作系统测试
compatibility_score = self._test_os_compatibility(os)
os_results[os] = compatibility_score
print(f"{os}: {compatibility_score:.1f}%兼容")
# 生成兼容性报告
avg_browser_compatibility = sum(browser_results.values()) / len(browser_results)
avg_os_compatibility = sum(os_results.values()) / len(os_results)
print(f"\n兼容性总结:")
print(f"平均浏览器兼容性: {avg_browser_compatibility:.1f}%")
print(f"平均操作系统兼容性: {avg_os_compatibility:.1f}%")
def _test_browser_compatibility(self, browser):
"""测试浏览器兼容性"""
# 模拟不同浏览器的兼容性评分
import random
base_score = 85
variation = random.uniform(-10, 15)
return min(100, max(0, base_score + variation))
def _test_os_compatibility(self, os):
"""测试操作系统兼容性"""
# 模拟不同操作系统的兼容性评分
import random
base_score = 90
variation = random.uniform(-5, 10)
return min(100, max(0, base_score + variation))
def run_all_system_tests(self):
"""运行所有系统测试"""
print("开始系统测试执行...\n")
self.functional_system_test()
self.performance_system_test()
self.security_system_test()
self.usability_system_test()
self.compatibility_system_test()
self._generate_system_test_report()
def _generate_system_test_report(self):
"""生成系统测试报告"""
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("系统测试总结报告")
print("="*60)
# 功能测试总结
total_functional = len(self.test_results)
passed_functional = len([r for r in self.test_results.values() if r['passed']])
print(f"功能测试:")
print(f" 总测试用例: {total_functional}")
print(f" 通过: {passed_functional}")
print(f" 失败: {total_functional - passed_functional}")
print(f" 通过率: {passed_functional/total_functional*100:.1f}%")
# 性能测试总结
if self.performance_data:
latest_perf = self.performance_data[-1]
print(f"\n性能测试:")
print(f" 平均响应时间: {latest_perf.response_time:.3f}秒")
print(f" 系统吞吐量: {latest_perf.throughput:.2f} 请求/秒")
print(f" CPU使用率: {latest_perf.cpu_usage:.1f}%")
print(f" 内存使用率: {latest_perf.memory_usage:.1f}%")
print(f"\n测试完成时间: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}")
# 运行系统测试示例
def run_system_tests():
framework = SystemTestFramework()
framework.run_all_system_tests()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_system_tests()代码实现了一个功能全面的系统测试框架,涵盖功能测试、性能测试、安全测试、可用性测试和兼容性测试五大核心维度。通过模拟真实业务场景和用户行为,框架能够全面评估系统的稳定性、响应速度、安全防护能力以及用户体验。
功能测试模块通过定义详细的测试用例,逐步执行关键业务流程,验证系统功能的正确性和完整性。性能测试包括负载测试、压力测试和容量测试,利用多线程模拟高并发请求,评估系统在不同负载下的响应时间、吞吐量和资源使用情况。安全测试针对常见攻击手段如SQL注入和XSS攻击进行模拟检测,同时涵盖身份验证等关键安全场景,保障系统安全性。可用性测试关注用户界面响应速度、操作简便性及错误提示的友好性,确保良好的用户体验。兼容性测试则模拟主流浏览器和操作系统环境,评估系统的跨平台适配能力。
验收测试(Acceptance Testing)
验收测试是由最终用户或业务代表执行的测试,目的是确认软件系统满足业务需求和用户期望。它通常基于用户故事(User Stories)和业务需求定义验收标准(Acceptance Criteria),通过具体的测试场景验证功能的正确性和完整性。
验收测试的主要目标包括:1)验证功能是否符合需求规格;2)确认业务流程的完整性和正确性;3)评估系统的用户体验和可用性;4)发现潜在的业务风险和缺陷
测试类型分类
功能测试 vs 非功能测试
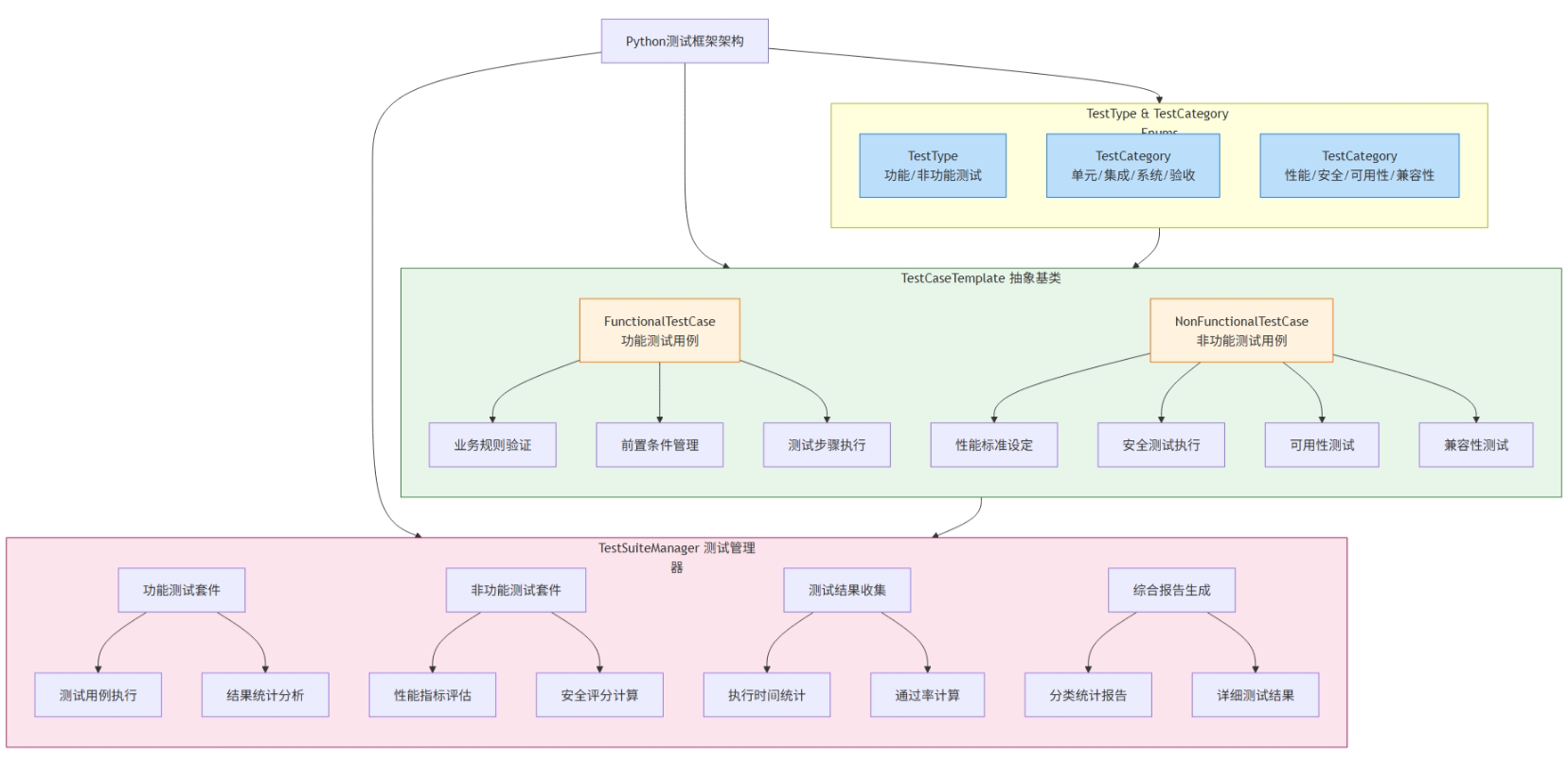
黑盒、白盒、灰盒测试技术
黑盒测试技术
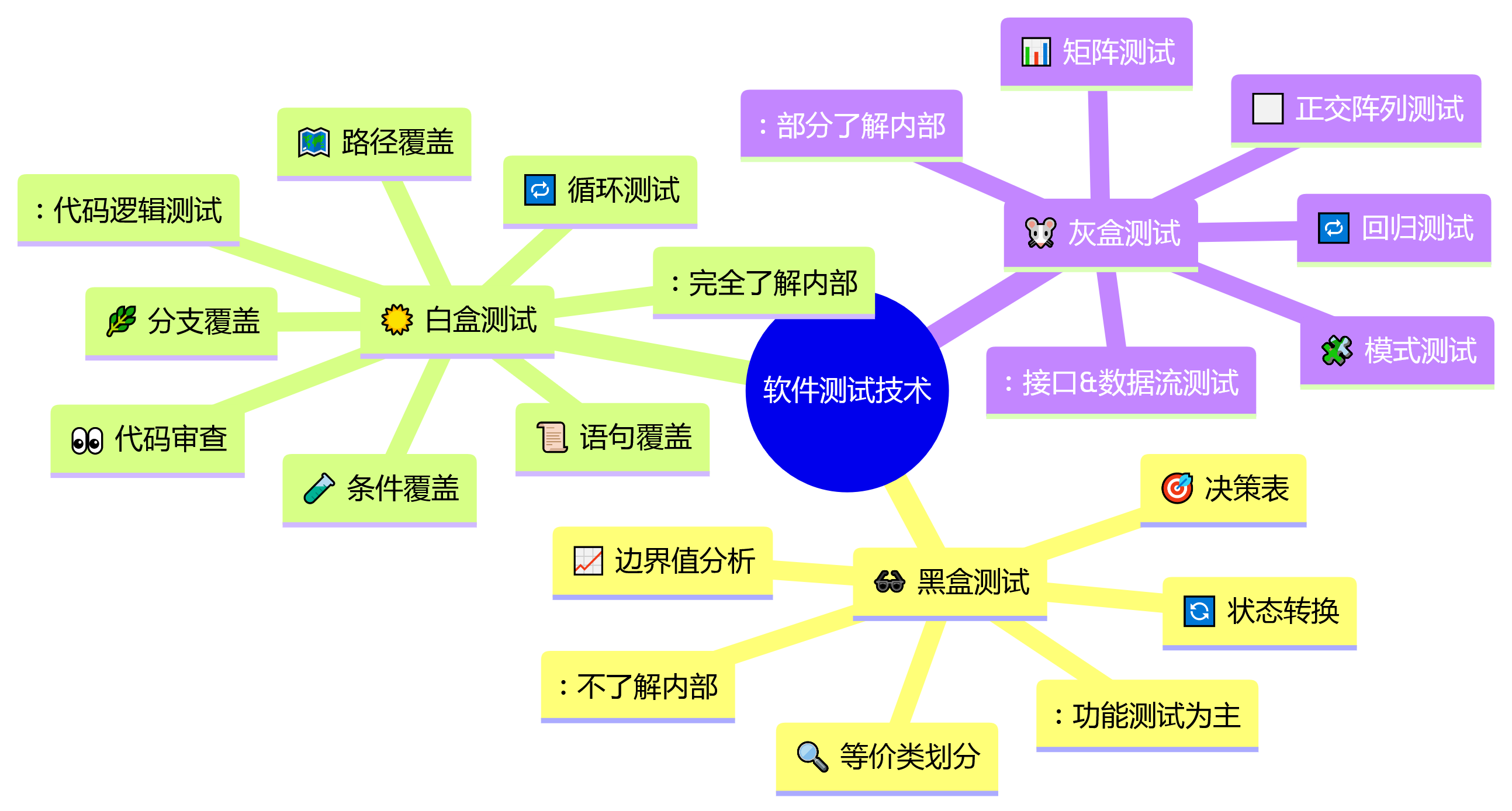
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Tuple
import itertools
from enum import Enum
class BoundaryType(Enum):
LOWER_VALID = "lower_valid"
LOWER_INVALID = "lower_invalid"
UPPER_VALID = "upper_valid"
UPPER_INVALID = "upper_invalid"
ON_BOUNDARY = "on_boundary"
class BlackBoxTestTechnique:
"""黑盒测试技术集合"""
@staticmethod
def equivalence_partitioning(input_range: Dict, test_data: List[Any]) -> Dict:
"""等价类划分技术"""
print("=== 等价类划分测试 ===")
partitions = {
'valid_partitions': [],
'invalid_partitions': [],
'test_cases': []
}
# 定义等价类
if 'min' in input_range and 'max' in input_range:
min_val, max_val = input_range['min'], input_range['max']
# 有效等价类
partitions['valid_partitions'].append({
'description': f'有效范围: {min_val} <= x <= {max_val}',
'range': (min_val, max_val),
'representative': (min_val + max_val) // 2
})
# 无效等价类
partitions['invalid_partitions'].append({
'description': f'小于最小值: x < {min_val}',
'range': (float('-inf'), min_val - 1),
'representative': min_val - 1
})
partitions['invalid_partitions'].append({
'description': f'大于最大值: x > {max_val}',
'range': (max_val + 1, float('inf')),
'representative': max_val + 1
})
# 为每个等价类生成测试用例
test_case_id = 1
for partition in partitions['valid_partitions']:
test_case = {
'id': f'EQ_VALID_{test_case_id}',
'partition_type': 'valid',
'description': partition['description'],
'input_value': partition['representative'],
'expected_result': 'success'
}
partitions['test_cases'].append(test_case)
test_case_id += 1
for partition in partitions['invalid_partitions']:
test_case = {
'id': f'EQ_INVALID_{test_case_id}',
'partition_type': 'invalid',
'description': partition['description'],
'input_value': partition['representative'],
'expected_result': 'error'
}
partitions['test_cases'].append(test_case)
test_case_id += 1
# 输出测试用例
for test_case in partitions['test_cases']:
print(f"测试用例 {test_case['id']}:")
print(f" 描述: {test_case['description']}")
print(f" 输入: {test_case['input_value']}")
print(f" 预期: {test_case['expected_result']}")
print()
return partitions
@staticmethod
def boundary_value_analysis(input_range: Dict) -> List[Dict]:
"""边界值分析技术"""
print("=== 边界值分析测试 ===")
boundary_tests = []
if 'min' in input_range and 'max' in input_range:
min_val, max_val = input_range['min'], input_range['max']
# 定义边界值测试用例
boundary_cases = [
{
'type': BoundaryType.LOWER_INVALID,
'value': min_val - 1,
'description': f'最小值边界下方: {min_val - 1}',
'expected': 'error'
},
{
'type': BoundaryType.LOWER_VALID,
'value': min_val,
'description': f'最小值边界: {min_val}',
'expected': 'success'
},
{
'type': BoundaryType.ON_BOUNDARY,
'value': min_val + 1,
'description': f'最小值边界上方: {min_val + 1}',
'expected': 'success'
},
{
'type': BoundaryType.ON_BOUNDARY,
'value': max_val - 1,
'description': f'最大值边界下方: {max_val - 1}',
'expected': 'success'
},
{
'type': BoundaryType.UPPER_VALID,
'value': max_val,
'description': f'最大值边界: {max_val}',
'expected': 'success'
},
{
'type': BoundaryType.UPPER_INVALID,
'value': max_val + 1,
'description': f'最大值边界上方: {max_val + 1}',
'expected': 'error'
}
]
for i, case in enumerate(boundary_cases, 1):
test_case = {
'id': f'BV_{i:03d}',
'boundary_type': case['type'],
'input_value': case['value'],
'description': case['description'],
'expected_result': case['expected']
}
boundary_tests.append(test_case)
print(f"边界测试 {test_case['id']}:")
print(f" 类型: {case['type'].value}")
print(f" 输入: {test_case['input_value']}")
print(f" 描述: {test_case['description']}")
print(f" 预期: {test_case['expected_result']}")
print()
return boundary_tests
@staticmethod
def decision_table_testing(conditions: List[str], actions: List[str],
rules: List[Dict]) -> List[Dict]:
"""决策表测试技术"""
print("=== 决策表测试 ===")
# 生成决策表
print("决策表:")
print(f"{'条件/动作':<20}", end="")
for i, rule in enumerate(rules, 1):
print(f"{'规则' + str(i):<10}", end="")
print()
print("-" * (20 + len(rules) * 10))
# 打印条件
for condition in conditions:
print(f"{condition:<20}", end="")
for rule in rules:
value = rule.get('conditions', {}).get(condition, '-')
print(f"{str(value):<10}", end="")
print()
print("-" * (20 + len(rules) * 10))
# 打印动作
for action in actions:
print(f"{action:<20}", end="")
for rule in rules:
value = rule.get('actions', {}).get(action, '-')
print(f"{str(value):<10}", end="")
print()
# 生成测试用例
test_cases = []
for i, rule in enumerate(rules, 1):
test_case = {
'id': f'DT_{i:03d}',
'rule_id': f'规则{i}',
'conditions': rule.get('conditions', {}),
'expected_actions': rule.get('actions', {}),
'description': f'测试规则{i}的执行'
}
test_cases.append(test_case)
print(f"\n测试用例 {test_case['id']}:")
print(f" 规则: {test_case['rule_id']}")
print(f" 条件: {test_case['conditions']}")
print(f" 预期动作: {test_case['expected_actions']}")
return test_cases
@staticmethod
def state_transition_testing(states: List[str], events: List[str],
transitions: List[Dict]) -> List[Dict]:
"""状态转换测试技术"""
print("=== 状态转换测试 ===")
# 构建状态转换图
transition_map = {}
for transition in transitions:
from_state = transition['from']
event = transition['event']
to_state = transition['to']
if from_state not in transition_map:
transition_map[from_state] = {}
transition_map[from_state][event] = to_state
print("状态转换图:")
for from_state, events_map in transition_map.items():
for event, to_state in events_map.items():
print(f" {from_state} --[{event}]--> {to_state}")
# 生成测试路径
test_paths = []
# 基本路径覆盖
for transition in transitions:
test_path = {
'id': f'ST_{len(test_paths)+1:03d}',
'path_type': 'basic_transition',
'initial_state': transition['from'],
'events': [transition['event']],
'expected_final_state': transition['to'],
'description': f"从{transition['from']}通过{transition['event']}到{transition['to']}"
}
test_paths.append(test_path)
# 路径组合测试
initial_states = list(set(t['from'] for t in transitions))
for initial_state in initial_states[:2]: # 限制数量避免组合爆炸
if initial_state in transition_map:
available_events = list(transition_map[initial_state].keys())
if len(available_events) >= 2:
# 测试事件序列
event_sequence = available_events[:2]
current_state = initial_state
final_state = current_state
for event in event_sequence:
if current_state in transition_map and event in transition_map[current_state]:
final_state = transition_map[current_state][event]
current_state = final_state
else:
break
test_path = {
'id': f'ST_{len(test_paths)+1:03d}',
'path_type': 'sequence_test',
'initial_state': initial_state,
'events': event_sequence,
'expected_final_state': final_state,
'description': f"从{initial_state}执行事件序列{event_sequence}"
}
test_paths.append(test_path)
# 输出测试路径
for test_path in test_paths:
print(f"\n测试路径 {test_path['id']}:")
print(f" 类型: {test_path['path_type']}")
print(f" 起始状态: {test_path['initial_state']}")
print(f" 事件序列: {test_path['events']}")
print(f" 预期最终状态: {test_path['expected_final_state']}")
print(f" 描述: {test_path['description']}")
return test_paths
# 演示黑盒测试技术的使用
def demo_black_box_techniques():
"""演示黑盒测试技术"""
# 1. 等价类划分示例
print("1. 年龄验证功能测试")
age_range = {'min': 18, 'max': 65}
test_data = [15, 18, 25, 65, 70]
eq_partitions = BlackBoxTestTechnique.equivalence_partitioning(age_range, test_data)
print(f"生成了 {len(eq_partitions['test_cases'])} 个等价类测试用例")
# 2. 边界值分析示例
print("\n2. 密码长度验证测试")
password_range = {'min': 8, 'max': 20}
boundary_tests = BlackBoxTestTechnique.boundary_value_analysis(password_range)
print(f"生成了 {len(boundary_tests)} 个边界值测试用例")
# 3. 决策表测试示例
print("\n3. 用户登录决策表测试")
conditions = ['用户名正确', '密码正确', '账户激活']
actions = ['登录成功', '显示错误', '发送激活邮件']
rules = [
{
'conditions': {'用户名正确': True, '密码正确': True, '账户激活': True},
'actions': {'登录成功': True, '显示错误': False, '发送激活邮件': False}
},
{
'conditions': {'用户名正确': True, '密码正确': True, '账户激活': False},
'actions': {'登录成功': False, '显示错误': True, '发送激活邮件': True}
},
{
'conditions': {'用户名正确': True, '密码正确': False, '账户激活': True},
'actions': {'登录成功': False, '显示错误': True, '发送激活邮件': False}
},
{
'conditions': {'用户名正确': False, '密码正确': False, '账户激活': True},
'actions': {'登录成功': False, '显示错误': True, '发送激活邮件': False}
}
]
decision_tests = BlackBoxTestTechnique.decision_table_testing(conditions, actions, rules)
print(f"生成了 {len(decision_tests)} 个决策表测试用例")
# 4. 状态转换测试示例
print("\n4. 订单状态转换测试")
states = ['待支付', '已支付', '已发货', '已完成', '已取消']
events = ['支付', '发货', '确认收货', '取消订单', '退款']
transitions = [
{'from': '待支付', 'event': '支付', 'to': '已支付'},
{'from': '待支付', 'event': '取消订单', 'to': '已取消'},
{'from': '已支付', 'event': '发货', 'to': '已发货'},
{'from': '已支付', 'event': '退款', 'to': '已取消'},
{'from': '已发货', 'event': '确认收货', 'to': '已完成'},
{'from': '已发货', 'event': '退款', 'to': '已取消'}
]
state_tests = BlackBoxTestTechnique.state_transition_testing(states, events, transitions)
print(f"生成了 {len(state_tests)} 个状态转换测试用例")
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo_black_box_techniques()实战:测试用例设计实例分析
电商网站注册功能测试用例设计
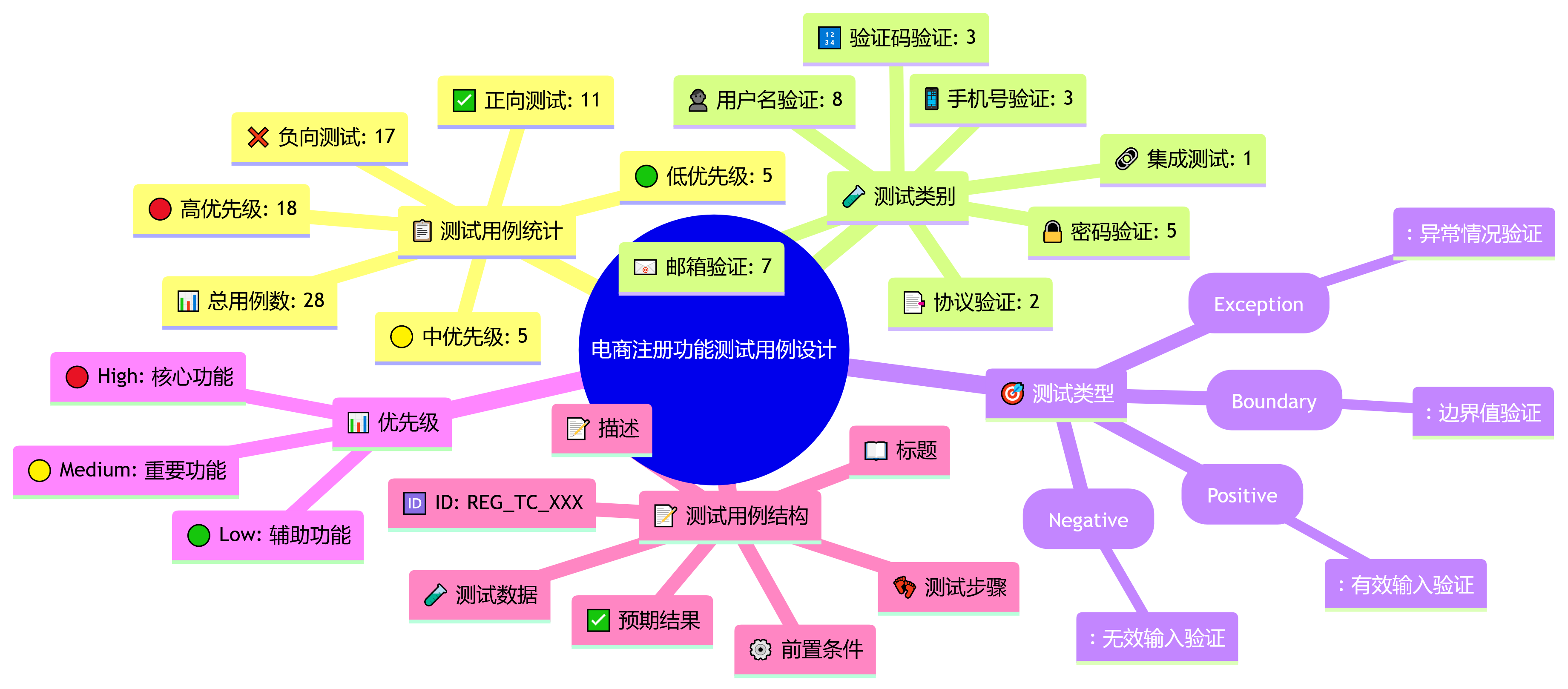
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict
from enum import Enum
class TestCasePriority(Enum):
HIGH = "high"
MEDIUM = "medium"
LOW = "low"
class TestCaseType(Enum):
POSITIVE = "positive"
NEGATIVE = "negative"
BOUNDARY = "boundary"
EXCEPTION = "exception"
@dataclass
class TestCase:
"""测试用例数据类"""
id: str
title: str
description: str
preconditions: List[str]
test_steps: List[str]
expected_results: List[str]
test_data: Dict
priority: TestCasePriority
test_type: TestCaseType
category: str
class ECommerceRegistrationTestDesign:
"""电商网站注册功能测试用例设计"""
def __init__(self):
self.test_cases = []
self.test_case_counter = 1
def generate_all_test_cases(self):
"""生成所有测试用例"""
# 用户名测试用例
self._generate_username_test_cases()
# 邮箱测试用例
self._generate_email_test_cases()
# 密码测试用例
self._generate_password_test_cases()
# 手机号测试用例
self._generate_phone_test_cases()
# 验证码测试用例
self._generate_verification_code_test_cases()
# 协议同意测试用例
self._generate_agreement_test_cases()
# 集成测试用例
self._generate_integration_test_cases()
return self.test_cases
def _generate_test_case_id(self):
"""生成测试用例ID"""
case_id = f"REG_TC_{self.test_case_counter:03d}"
self.test_case_counter += 1
return case_id
def _generate_username_test_cases(self):
"""生成用户名测试用例"""
# 正向测试用例
positive_cases = [
{
'title': '使用有效用户名注册',
'description': '使用符合规则的用户名进行注册',
'test_data': {'username': 'testuser123'},
'expected': '用户名验证通过'
},
{
'title': '使用最短长度用户名注册',
'description': '使用3个字符的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'abc'},
'expected': '用户名验证通过'
},
{
'title': '使用最长长度用户名注册',
'description': '使用20个字符的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'a' * 20},
'expected': '用户名验证通过'
}
]
for case_data in positive_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在用户名输入框输入用户名',
'点击其他输入框或验证按钮'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.POSITIVE,
category='用户名验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
# 负向测试用例
negative_cases = [
{
'title': '用户名长度小于最小值',
'description': '输入少于3个字符的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'ab'},
'expected': '显示用户名长度不足错误提示'
},
{
'title': '用户名长度超过最大值',
'description': '输入超过20个字符的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'a' * 21},
'expected': '显示用户名长度超限错误提示'
},
{
'title': '用户名包含特殊字符',
'description': '输入包含@#$等特殊字符的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'test@user'},
'expected': '显示用户名格式错误提示'
},
{
'title': '用户名为空',
'description': '不输入用户名直接提交',
'test_data': {'username': ''},
'expected': '显示用户名不能为空错误提示'
},
{
'title': '用户名已存在',
'description': '输入已被其他用户注册的用户名',
'test_data': {'username': 'existinguser'},
'expected': '显示用户名已存在错误提示'
}
]
for case_data in negative_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在用户名输入框输入用户名',
'点击其他输入框或验证按钮'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.NEGATIVE,
category='用户名验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_email_test_cases(self):
"""生成邮箱测试用例"""
# 正向测试用例
positive_cases = [
{
'title': '使用有效邮箱地址注册',
'description': '使用标准格式的邮箱地址',
'test_data': {'email': 'test@example.com'},
'expected': '邮箱验证通过'
},
{
'title': '使用带数字的邮箱注册',
'description': '邮箱地址包含数字',
'test_data': {'email': 'test123@example.com'},
'expected': '邮箱验证通过'
},
{
'title': '使用带点号的邮箱注册',
'description': '邮箱地址包含点号分隔',
'test_data': {'email': 'test.user@example.com'},
'expected': '邮箱验证通过'
}
]
for case_data in positive_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在邮箱输入框输入邮箱地址',
'点击验证或提交'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.POSITIVE,
category='邮箱验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
# 负向测试用例
negative_cases = [
{
'title': '邮箱格式不正确',
'description': '输入不符合邮箱格式的字符串',
'test_data': {'email': 'invalidemailformat'},
'expected': '显示邮箱格式错误提示'
},
{
'title': '邮箱缺少@符号',
'description': '邮箱地址缺少@符号',
'test_data': {'email': 'testexample.com'},
'expected': '显示邮箱格式错误提示'
},
{
'title': '邮箱缺少域名',
'description': '邮箱地址缺少域名部分',
'test_data': {'email': 'test@'},
'expected': '显示邮箱格式错误提示'
},
{
'title': '邮箱已被注册',
'description': '使用已被其他用户注册的邮箱',
'test_data': {'email': 'existing@example.com'},
'expected': '显示邮箱已被注册错误提示'
}
]
for case_data in negative_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在邮箱输入框输入邮箱地址',
'点击验证或提交'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.NEGATIVE,
category='邮箱验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_password_test_cases(self):
"""生成密码测试用例"""
# 正向测试用例
positive_cases = [
{
'title': '使用强密码注册',
'description': '包含大小写字母、数字和特殊字符的密码',
'test_data': {'password': 'StrongPass123!'},
'expected': '密码强度验证通过'
},
{
'title': '使用最短长度密码',
'description': '使用8位字符的密码',
'test_data': {'password': 'Pass123!'},
'expected': '密码验证通过'
}
]
for case_data in positive_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在密码输入框输入密码',
'在确认密码框输入相同密码',
'点击验证'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.POSITIVE,
category='密码验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
# 负向测试用例
negative_cases = [
{
'title': '密码长度不足',
'description': '输入少于8个字符的密码',
'test_data': {'password': '123456'},
'expected': '显示密码长度不足错误提示'
},
{
'title': '密码过于简单',
'description': '只包含数字的密码',
'test_data': {'password': '12345678'},
'expected': '显示密码强度不足错误提示'
},
{
'title': '两次密码输入不一致',
'description': '确认密码与原密码不匹配',
'test_data': {'password': 'Password123!', 'confirm_password': 'Password456!'},
'expected': '显示两次密码不一致错误提示'
}
]
for case_data in negative_cases:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在密码输入框输入密码',
'在确认密码框输入密码',
'点击验证'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.NEGATIVE,
category='密码验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_phone_test_cases(self):
"""生成手机号测试用例"""
# 正向测试用例
positive_cases = [
{
'title': '使用有效手机号注册',
'description': '输入标准11位手机号',
'test_data': {'phone': '13812345678'},
'expected': '手机号验证通过'
}
]
# 负向测试用例
negative_cases = [
{
'title': '手机号位数不正确',
'description': '输入非11位的手机号',
'test_data': {'phone': '1381234567'},
'expected': '显示手机号格式错误提示'
},
{
'title': '手机号已被注册',
'description': '使用已注册的手机号',
'test_data': {'phone': '13800000000'},
'expected': '显示手机号已被注册错误提示'
}
]
all_cases = positive_cases + negative_cases
for case_data in all_cases:
test_type = TestCaseType.POSITIVE if case_data in positive_cases else TestCaseType.NEGATIVE
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'在手机号输入框输入手机号',
'点击获取验证码或验证'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.MEDIUM,
test_type=test_type,
category='手机号验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_verification_code_test_cases(self):
"""生成验证码测试用例"""
test_cases_data = [
{
'title': '输入正确验证码',
'description': '输入接收到的正确验证码',
'test_data': {'verification_code': '123456'},
'expected': '验证码验证通过',
'test_type': TestCaseType.POSITIVE
},
{
'title': '输入错误验证码',
'description': '输入错误的验证码',
'test_data': {'verification_code': '000000'},
'expected': '显示验证码错误提示',
'test_type': TestCaseType.NEGATIVE
},
{
'title': '验证码过期',
'description': '使用超过有效期的验证码',
'test_data': {'verification_code': '123456', 'expired': True},
'expected': '显示验证码已过期提示',
'test_type': TestCaseType.NEGATIVE
}
]
for case_data in test_cases_data:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['已获取验证码'],
test_steps=[
'在验证码输入框输入验证码',
'点击验证'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.MEDIUM,
test_type=case_data['test_type'],
category='验证码验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_agreement_test_cases(self):
"""生成协议同意测试用例"""
test_cases_data = [
{
'title': '同意服务协议后注册',
'description': '勾选同意服务协议复选框',
'test_data': {'agreement_checked': True},
'expected': '允许提交注册',
'test_type': TestCaseType.POSITIVE
},
{
'title': '未同意服务协议注册',
'description': '不勾选服务协议复选框',
'test_data': {'agreement_checked': False},
'expected': '显示必须同意协议的提示',
'test_type': TestCaseType.NEGATIVE
}
]
for case_data in test_cases_data:
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title=case_data['title'],
description=case_data['description'],
preconditions=['填写完所有必填信息'],
test_steps=[
'勾选或不勾选服务协议',
'点击注册按钮'
],
expected_results=[case_data['expected']],
test_data=case_data['test_data'],
priority=TestCasePriority.LOW,
test_type=case_data['test_type'],
category='协议验证'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def _generate_integration_test_cases(self):
"""生成集成测试用例"""
test_case = TestCase(
id=self._generate_test_case_id(),
title='完整注册流程测试',
description='测试用户完整的注册流程',
preconditions=['访问注册页面'],
test_steps=[
'输入有效用户名',
'输入有效邮箱地址',
'输入符合要求的密码',
'确认密码',
'输入有效手机号',
'获取并输入正确验证码',
'勾选同意服务协议',
'点击注册按钮'
],
expected_results=[
'用户名验证通过',
'邮箱验证通过',
'密码强度验证通过',
'密码确认通过',
'手机号验证通过',
'验证码验证通过',
'协议确认通过',
'注册成功,跳转到登录页面或发送激活邮件'
],
test_data={
'username': 'testuser123',
'email': 'test@example.com',
'password': 'StrongPass123!',
'confirm_password': 'StrongPass123!',
'phone': '13812345678',
'verification_code': '123456',
'agreement_checked': True
},
priority=TestCasePriority.HIGH,
test_type=TestCaseType.POSITIVE,
category='集成测试'
)
self.test_cases.append(test_case)
def generate_test_case_report(self):
"""生成测试用例报告"""
print("="*80)
print("电商网站注册功能测试用例设计报告")
print("="*80)
# 统计信息
total_cases = len(self.test_cases)
high_priority = len([tc for tc in self.test_cases if tc.priority == TestCasePriority.HIGH])
medium_priority = len([tc for tc in self.test_cases if tc.priority == TestCasePriority.MEDIUM])
low_priority = len([tc for tc in self.test_cases if tc.priority == TestCasePriority.LOW])
positive_cases = len([tc for tc in self.test_cases if tc.test_type == TestCaseType.POSITIVE])
negative_cases = len([tc for tc in self.test_cases if tc.test_type == TestCaseType.NEGATIVE])
print(f"测试用例总数: {total_cases}")
print(f"高优先级: {high_priority}, 中优先级: {medium_priority}, 低优先级: {low_priority}")
print(f"正向测试: {positive_cases}, 负向测试: {negative_cases}")
# 按类别统计
categories = {}
for tc in self.test_cases:
if tc.category not in categories:
categories[tc.category] = 0
categories[tc.category] += 1
print(f"\n按类别统计:")
for category, count in categories.items():
print(f" {category}: {count} 个用例")
# 详细测试用例列表
print(f"\n详细测试用例列表:")
print("-" * 80)
for tc in self.test_cases:
print(f"ID: {tc.id}")
print(f"标题: {tc.title}")
print(f"类别: {tc.category}")
print(f"优先级: {tc.priority.value}")
print(f"类型: {tc.test_type.value}")
print(f"测试数据: {tc.test_data}")
print("-" * 40)
# 演示测试用例设计
def demo_test_case_design():
"""演示测试用例设计"""
design = ECommerceRegistrationTestDesign()
# 生成所有测试用例
test_cases = design.generate_all_test_cases()
print(f"成功生成 {len(test_cases)} 个测试用例")
# 生成报告
design.generate_test_case_report()
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo_test_case_design()




















 20万+
20万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








