目录
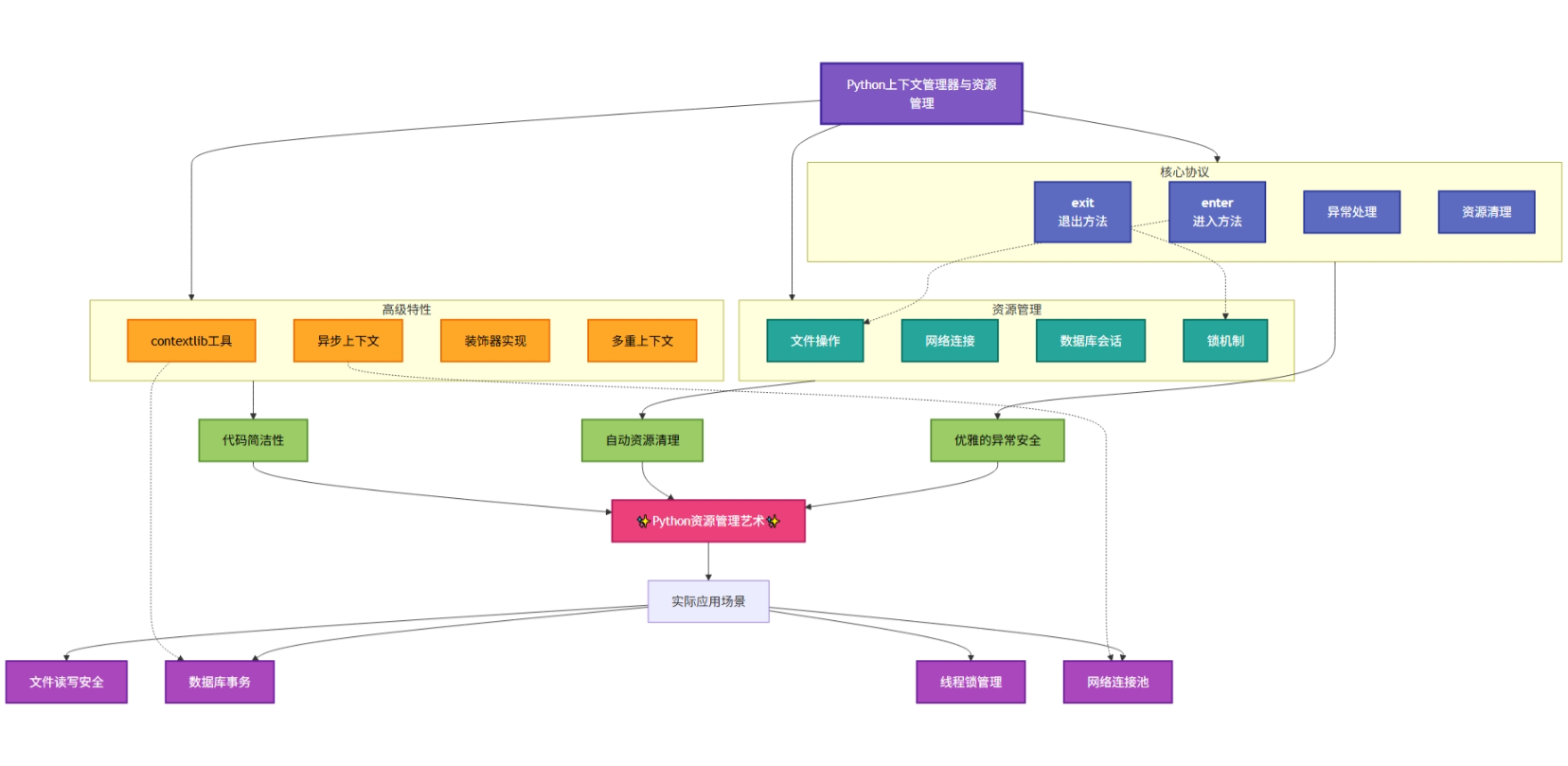
上下文管理器
上下文管理器是实现了特殊方法__enter__和__exit__的对象,用于定义代码块执行前后的初始化和清理操作。典型应用场景包括文件操作、数据库连接、线程锁等资源管理。
with的工作机制
class ContextManagerBasics:
"""上下文管理器基础概念演示"""
@staticmethod
def demonstrate_with_statement():
print("=== with语句基本用法 ===")
# 传统文件操作方式
print("1. 传统方式(容易忘记关闭文件):")
try:
file = open('example.txt', 'w')
file.write('Hello World')
file.close() # 容易忘记
print("文件操作完成")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
# 使用with语句
print("\n2. 使用with语句(自动管理资源):")
try:
with open('example.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write('Hello World with context manager')
print("文件自动关闭")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
class SimpleContextManager:
"""简单的上下文管理器示例"""
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def __enter__(self):
print(f"进入上下文: {self.name}")
return self # 返回给as后的变量
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
print(f"退出上下文: {self.name}")
if exc_type:
print(f"异常类型: {exc_type.__name__}")
print(f"异常值: {exc_value}")
return False # 不抑制异常
return True
def do_something(self):
print(f"在 {self.name} 中执行操作")
@staticmethod
def demonstrate_context_manager_protocol():
print("\n=== 上下文管理器协议演示 ===")
# 正常执行
print("1. 正常执行:")
with ContextManagerBasics.SimpleContextManager("测试管理器") as cm:
cm.do_something()
# 异常情况
print("\n2. 异常情况:")
try:
with ContextManagerBasics.SimpleContextManager("异常测试") as cm:
cm.do_something()
raise ValueError("模拟异常")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"捕获异常: {e}")
def test_context_manager_basics():
"""测试上下文管理器基础"""
basics = ContextManagerBasics()
basics.demonstrate_with_statement()
basics.demonstrate_context_manager_protocol()
test_context_manager_basics()
class DetailedContextManager:
"""详细展示上下文管理器执行流程"""
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
print(f"初始化上下文管理器: {self.name}")
def __enter__(self):
print(f"__enter__ 被调用: {self.name}")
print(f"获取资源...")
# 模拟资源获取
self.resource = f"Resource-{self.name}"
print(f"资源获取成功: {self.resource}")
return self.resource
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
print(f"__exit__ 被调用: {self.name}")
print(f"异常类型: {exc_type}")
print(f"异常值: {exc_value}")
print(f"追踪信息: {traceback is not None}")
# 清理资源
print(f"清理资源: {self.resource}")
del self.resource
if exc_type is None:
print("正常退出")
else:
print(f"异常退出: {exc_type.__name__}")
# 返回True表示抑制异常,False表示不抑制
return False
def test_detailed_execution_flow():
"""测试详细执行流程"""
print("=== 详细执行流程演示 ===")
print("1. 正常执行流程:")
with DetailedContextManager("正常流程") as resource:
print(f"使用资源: {resource}")
print("执行业务逻辑...")
print("\n2. 异常执行流程:")
try:
with DetailedContextManager("异常流程") as resource:
print(f"使用资源: {resource}")
print("执行业务逻辑...")
raise RuntimeError("业务逻辑异常")
except RuntimeError as e:
print(f"最终捕获异常: {e}")
test_detailed_execution_flow()上下文管理器协议:__enter__:进入上下文时调用,负责资源的初始化和返回。__exit__(exc_type, exc_value, traceback):退出上下文时调用,负责资源释放和异常处理。
exc_type等参数用于判断代码块是否抛出异常,便于做相应处理。
with语句优势:自动调用__enter__和__exit__,简化资源管理代码。无论代码块是否异常,均保证资源正确释放。支持异常捕获和抑制,增强代码健壮性。
异常处理机制:如果__exit__返回False或None,异常会继续向外抛出。返回True则表示异常被抑制,不再传播。通过打印和捕获异常,示例清晰展示了异常传递过程。
1、基础上下文管理器示例
ContextManagerBasics类演示了传统文件操作与with语句的对比,以及自定义上下文管理器的协议实现:demonstrate_with_statement方法展示了传统文件操作容易忘记关闭文件的问题,和with语句自动管理资源的优势。
内嵌的SimpleContextManager类实现了__enter__和__exit__方法,支持上下文管理协议。
demonstrate_context_manager_protocol方法演示了正常执行和异常情况下上下文管理器的行为,展示异常传递与处理。
2、详细执行流程示例
DetailedContextManager类通过丰富的打印信息,展示了上下文管理器的执行细节:__enter__方法模拟资源获取过程,返回资源对象。__exit__方法接收异常信息,打印异常类型和值,执行资源清理。根据异常情况决定是否抑制异常(返回True抑制,False不抑制)。
test_detailed_execution_flow函数分别演示了正常流程和异常流程,展示异常如何被捕获和传递。
自定义上下文管理器设计
基于类的上下文管理器
import threading
import time
from typing import Optional
class TimerContextManager:
"""计时器上下文管理器"""
def __init__(self, operation_name: str = "操作", precision: int = 4):
self.operation_name = operation_name
self.precision = precision
self.start_time: Optional[float] = None
self.end_time: Optional[float] = None
def __enter__(self):
print(f"开始计时: {self.operation_name}")
self.start_time = time.time()
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.end_time = time.time()
duration = self.end_time - self.start_time
if exc_type is None:
print(f"{self.operation_name} 完成,耗时: {duration:.{self.precision}f}秒")
else:
print(f"{self.operation_name} 异常结束,耗时: {duration:.{self.precision}f}秒")
return False # 不抑制异常
@property
def duration(self) -> Optional[float]:
"""获取执行时间"""
if self.start_time and self.end_time:
return self.end_time - self.start_time
return None
class ThreadSafeLockManager:
"""线程安全锁管理器"""
def __init__(self, lock: threading.Lock, timeout: Optional[float] = None):
self.lock = lock
self.timeout = timeout
self.acquired = False
def __enter__(self):
print(f"尝试获取锁...")
try:
self.acquired = self.lock.acquire(timeout=self.timeout)
if self.acquired:
print(f"锁获取成功")
return self
else:
raise TimeoutError(f"获取锁超时 ({self.timeout}秒)")
except Exception as e:
print(f"锁获取失败: {e}")
raise
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
if self.acquired:
self.lock.release()
print(f"锁已释放")
return False
class ResourcePoolManager:
"""资源池管理器"""
def __init__(self, pool_size: int = 5):
self.pool_size = pool_size
self.available_resources = [f"Resource-{i}" for i in range(pool_size)]
self.used_resources = set()
self.lock = threading.Lock()
def __enter__(self):
with self.lock:
if not self.available_resources:
raise RuntimeError("资源池已耗尽")
resource = self.available_resources.pop()
self.used_resources.add(resource)
print(f"获取资源: {resource} (剩余: {len(self.available_resources)})")
return resource
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
# 注意:这里需要知道要释放哪个资源实际使用中可能需要更复杂的设计
pass
def release_resource(self, resource: str):
"""手动释放资源"""
with self.lock:
if resource in self.used_resources:
self.used_resources.remove(resource)
self.available_resources.append(resource)
print(f"释放资源: {resource} (可用: {len(self.available_resources)})")
def test_custom_context_managers():
"""测试自定义上下文管理器"""
print("=== 自定义上下文管理器测试 ===")
# 测试计时器
print("1. 计时器测试:")
with TimerContextManager("数据处理") as timer:
time.sleep(0.1) # 模拟耗时操作
print("正在处理数据...")
print(f"操作耗时: {timer.duration:.4f}秒")
# 测试线程锁
print("\n2. 线程锁测试:")
lock = threading.Lock()
def worker(worker_id: int):
try:
with ThreadSafeLockManager(lock, timeout=1.0):
print(f"工作线程 {worker_id} 开始工作")
time.sleep(0.5)
print(f"工作线程 {worker_id} 完成工作")
except TimeoutError as e:
print(f"工作线程 {worker_id} 超时: {e}")
# 启动多个线程
threads = []
for i in range(3):
t = threading.Thread(target=worker, args=(i,))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
test_custom_context_managers()基于生成器的上下文管理器
from contextlib import contextmanager
import tempfile
import os
import shutil
import time
import logging
class GeneratorContextManagers:
"""基于生成器的上下文管理器示例"""
@staticmethod
@contextmanager
def temporary_directory(prefix: str = "temp_"):
"""临时目录管理器"""
temp_dir = None
try:
temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp(prefix=prefix)
print(f"创建临时目录: {temp_dir}")
yield temp_dir
finally:
if temp_dir and os.path.exists(temp_dir):
shutil.rmtree(temp_dir)
print(f"删除临时目录: {temp_dir}")
@staticmethod
@contextmanager
def database_transaction():
"""数据库事务管理器(模拟)"""
print("开始事务")
transaction_id = f"txn_{int(time.time())}"
try:
yield transaction_id
print("提交事务")
except Exception as e:
print(f"回滚事务: {e}")
raise
finally:
print("事务结束")
@staticmethod
@contextmanager
def performance_monitor(operation: str):
"""性能监控管理器"""
start_time = time.time()
start_memory = 0 # 简化,实际可用psutil获取内存
print(f"开始监控: {operation}")
try:
yield {
'start_time': start_time,
'operation': operation
}
finally:
end_time = time.time()
duration = end_time - start_time
print(f"{operation} 性能报告:")
print(f"执行时间: {duration:.4f}秒")
print(f" 内存使用: 模拟数据")
@staticmethod
@contextmanager
def error_handler(operation: str, reraise: bool = True):
"""错误处理管理器"""
print(f"启动错误处理: {operation}")
try:
yield
except Exception as e:
print(f"捕获异常 in {operation}: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
# 记录错误日志
logging.error(f"操作 '{operation}' 失败: {e}")
if reraise:
print("重新抛出异常")
raise
else:
print("抑制异常")
else:
print(f"{operation} 成功完成")
def test_generator_context_managers():
"""测试基于生成器的上下文管理器"""
print("=== 基于生成器的上下文管理器测试 ===")
# 测试临时目录
print("1. 临时目录测试:")
with GeneratorContextManagers.temporary_directory("my_temp_") as temp_dir:
print(f"在临时目录中工作: {temp_dir}")
# 创建一些文件
test_file = os.path.join(temp_dir, "test.txt")
with open(test_file, 'w') as f:
f.write("临时文件内容")
print(f"创建文件: {test_file}")
# 测试数据库事务
print("\n2. 数据库事务测试:")
try:
with GeneratorContextManagers.database_transaction() as txn_id:
print(f"执行业务逻辑 (事务ID: {txn_id})")
# 模拟业务操作
time.sleep(0.1)
# raise Exception("业务逻辑异常") # 取消注释测试异常情况
except Exception as e:
print(f"事务处理异常: {e}")
# 测试性能监控
print("\n3. 性能监控测试:")
with GeneratorContextManagers.performance_monitor("数据分析") as monitor:
print(f"执行数据分析...")
time.sleep(0.2) # 模拟耗时操作
print(f"分析开始时间: {monitor['start_time']}")
# 测试错误处理
print("\n4. 错误处理测试:")
# 抑制异常
with GeneratorContextManagers.error_handler("测试操作1", reraise=False):
print("执行可能出错的操作...")
raise ValueError("模拟错误")
print("程序继续执行...")
# 重新抛出异常
try:
with GeneratorContextManagers.error_handler("测试操作2", reraise=True):
print("执行另一个可能出错的操作...")
raise RuntimeError("另一个模拟错误")
except RuntimeError as e:
print(f"外部捕获异常: {e}")
test_generator_context_managers()
基于类的上下文管理器: 通过实现__enter__和__exit__方法,定义资源的获取和释放逻辑。
支持异常处理,__exit__方法接收异常信息,可选择是否抑制异常。
适合管理复杂状态和多步骤资源操作。
典型示例: 1) 计时器上下文管理器:自动记录代码块执行时间。2) 线程安全锁管理器:安全获取和释放线程锁,支持超时。3)资源池管理器:管理有限资源的获取和释放。
基于生成器的上下文管理器:利用contextlib.contextmanager装饰器,将生成器函数转换为上下文管理器。通过yield分隔资源获取和释放代码,yield之前为进入上下文的操作,之后为退出上下文的清理。
典型示例:1)临时目录管理器:创建并自动删除临时目录。2)数据库事务管理器:模拟事务的开始、提交与回滚。3)性能监控管理器:自动统计代码块执行时间。4)错误处理管理器:捕获并处理代码块中的异常。
| 场景类型 | 推荐实现方式 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 复杂资源管理 | 基于类的上下文管理器 | 支持状态维护和多步骤操作 |
| 简单资源管理 | 基于生成器的上下文管理器 | 代码简洁,快速实现 |
| 需要异常处理 | 两者均可 | 生成器方式更简洁 |
| 需要多线程支持 | 基于类的上下文管理器 | 更灵活的锁和状态管理 |
异步上下文管理器
import asyncio,time
import aiohttp
import aiofiles
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
from typing import AsyncGenerator
class AsyncContextManagerBasics:
"""异步上下文管理器基础"""
class AsyncTimerManager:
"""异步计时器管理器"""
def __init__(self, operation: str):
self.operation = operation
self.start_time = None
self.end_time = None
async def __aenter__(self):
print(f"异步开始计时: {self.operation}")
self.start_time = time.time()
return self
async def __aexit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.end_time = time.time()
duration = self.end_time - self.start_time
if exc_type is None:
print(f"{self.operation} 异步完成,耗时: {duration:.4f}秒")
else:
print(f"{self.operation} 异步异常,耗时: {duration:.4f}秒")
return False
class AsyncResourceManager:
"""异步资源管理器"""
def __init__(self, resource_name: str):
self.resource_name = resource_name
self.resource = None
async def __aenter__(self):
print(f"异步获取资源: {self.resource_name}")
# 模拟异步资源获取
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
self.resource = f"AsyncResource-{self.resource_name}"
print(f"资源获取成功: {self.resource}")
return self.resource
async def __aexit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
print(f"异步释放资源: {self.resource}")
# 模拟异步资源释放
await asyncio.sleep(0.05)
self.resource = None
print(f"资源释放完成")
return False
async def test_async_context_manager_basics():
print("=== 异步上下文管理器基础测试 ===")
# 测试异步计时器
print("1. 异步计时器测试:")
async with AsyncContextManagerBasics.AsyncTimerManager("异步操作") as timer:
print("执行异步操作...")
await asyncio.sleep(0.2)
print("异步业务逻辑完成")
# 测试异步资源管理器
print("\n2. 异步资源管理器测试:")
async with AsyncContextManagerBasics.AsyncResourceManager("数据库连接") as resource:
print(f"使用异步资源: {resource}")
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
print("异步数据处理完成")
# 运行异步测试
asyncio.run(test_async_context_manager_basics())
class AsyncGeneratorContextManagers:
"""基于异步生成器的上下文管理器"""
@staticmethod
@asynccontextmanager
async def async_http_session(timeout: int = 30) -> AsyncGenerator[aiohttp.ClientSession, None]:
"""异步HTTP会话管理器"""
print(f"创建HTTP会话 (超时: {timeout}秒)")
timeout_config = aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=timeout)
session = aiohttp.ClientSession(timeout=timeout_config)
try:
yield session
finally:
await session.close()
print("HTTP会话已关闭")
@staticmethod
@asynccontextmanager
async def async_file_manager(filename: str, mode: str = 'r'):
"""异步文件管理器"""
print(f"异步打开文件: {filename} (模式: {mode})")
try:
async with aiofiles.open(filename, mode) as file:
yield file
except Exception as e:
print(f"文件操作异常: {e}")
raise
finally:
print(f"文件已关闭: {filename}")
@staticmethod
@asynccontextmanager
async def async_semaphore_manager(max_concurrent: int = 5):
"""异步信号量管理器"""
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent)
print(f"创建信号量 (最大并发: {max_concurrent})")
try:
async with semaphore:
print(f"获得信号量许可")
yield semaphore
finally:
print(f"释放信号量许可")
@staticmethod
@asynccontextmanager
async def async_batch_processor(batch_size: int = 10, flush_interval: float = 1.0):
"""异步批处理管理器"""
batch = []
last_flush = time.time()
print(f"启动批处理器 (批大小: {batch_size}, 刷新间隔: {flush_interval}秒)")
async def flush_batch():
nonlocal batch, last_flush
if batch:
print(f"处理批次: {len(batch)} 项")
# 模拟批处理
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
batch.clear()
last_flush = time.time()
try:
processor = {
'add': lambda item: batch.append(item),
'flush': flush_batch,
'size': lambda: len(batch)
}
yield processor
finally:
# 最终刷新
await flush_batch()
print("批处理器已关闭")
async def test_async_generator_context_managers():
"""测试异步生成器上下文管理器"""
print("=== 异步生成器上下文管理器测试 ===")
# 测试HTTP会话管理器
print("1. HTTP会话管理器测试:")
try:
async with AsyncGeneratorContextManagers.async_http_session(10) as session:
print("使用HTTP会话...")
# 这里可以进行HTTP请求
# response = await session.get('https://httpbin.org/get')
print("模拟HTTP请求完成")
except Exception as e:
print(f"HTTP会话异常: {e}")
# 测试异步文件管理器
print("\n2. 异步文件管理器测试:")
try:
# 先创建测试文件
with open('async_test.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('异步文件测试内容\n第二行内容')
async with AsyncGeneratorContextManagers.async_file_manager('async_test.txt', 'r') as file:
content = await file.read()
print(f"文件内容: {content[:50]}...")
# 清理测试文件
os.remove('async_test.txt')
except Exception as e:
print(f"文件操作异常: {e}")
# 测试信号量管理器
print("\n3. 信号量管理器测试:")
async def worker(worker_id: int):
async with AsyncGeneratorContextManagers.async_semaphore_manager(2) as sem:
print(f"工作者 {worker_id} 开始工作")
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
print(f"工作者 {worker_id} 完成工作")
# 启动多个异步任务
tasks = [worker(i) for i in range(5)]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# 测试批处理管理器
print("\n4. 批处理管理器测试:")
async with AsyncGeneratorContextManagers.async_batch_processor(3, 0.5) as processor:
for i in range(8):
processor['add'](f"item-{i}")
print(f" 添加项目: item-{i} (当前批大小: {processor['size']()})")
if processor['size']() >= 3:
await processor['flush']()
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
# 运行异步测试
asyncio.run(test_async_generator_context_managers())基于类的异步上下文管理器:实现__aenter__和__aexit__异步方法,支持async with语法。
适合管理异步资源的获取和释放,如异步计时器、异步连接等。支持异常检测和处理,保证资源正确释放。
典型示例:1)异步计时器管理器:记录异步代码块的执行时间。2)异步资源管理器:模拟异步资源的获取和释放过程。
基于异步生成器的上下文管理器:利用contextlib.asynccontextmanager装饰器,将异步生成器函数转换为异步上下文管理器。通过yield分隔资源获取和释放代码,简化异步上下文管理器的编写。
适合简洁的异步资源管理和流程控制。
典型示例:1)异步HTTP会话管理器:管理aiohttp.ClientSession的生命周期。2)异步文件管理器:异步打开和关闭文件。3)异步信号量管理器:控制异步任务的并发数。4)异步批处理管理器:实现批量数据处理和定时刷新。
实战项目:数据库连接池管理器
import sqlite3
import threading
import queue
import time
from typing import Dict, Any
import logging
from contextlib import contextmanager
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s')
class DatabaseConnectionPool:
"""数据库连接池管理器"""
def __init__(self,
database_url: str,
min_connections: int = 2,
max_connections: int = 10,
connection_timeout: float = 30.0,
idle_timeout: float = 300.0):
"""
初始化连接池
Args:
database_url: 数据库连接URL
min_connections: 最小连接数
max_connections: 最大连接数
connection_timeout: 获取连接超时时间(秒)
idle_timeout: 连接空闲超时时间(秒)
"""
self.database_url = database_url
self.min_connections = min_connections
self.max_connections = max_connections
self.connection_timeout = connection_timeout
self.idle_timeout = idle_timeout
# 连接池队列
self._pool = queue.Queue(maxsize=max_connections)
self._all_connections: Dict[int, Dict[str, Any]] = {}
self._pool_lock = threading.RLock()
# 统计信息
self._stats = {
'created_connections': 0,
'active_connections': 0,
'pool_hits': 0,
'pool_misses': 0,
'timeouts': 0,
'errors': 0
}
# 初始化最小连接数
self._initialize_pool()
# 启动清理线程
self._cleanup_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._cleanup_idle_connections, daemon=True)
self._cleanup_thread.start()
logging.info(f"数据库连接池初始化完成: {self.database_url}")
def _create_connection(self) -> sqlite3.Connection:
"""创建新的数据库连接"""
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.database_url, check_same_thread=False)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row # 使结果可以按列名访问
with self._pool_lock:
self._stats['created_connections'] += 1
conn_id = id(conn)
self._all_connections[conn_id] = {
'connection': conn,
'created_at': time.time(),
'last_used': time.time(),
'in_use': False
}
logging.debug(f"创建新连接: {conn_id}")
return conn
except Exception as e:
with self._pool_lock:
self._stats['errors'] += 1
logging.error(f"创建连接失败: {e}")
raise
def _initialize_pool(self):
"""初始化连接池,创建最小连接数"""
for _ in range(self.min_connections):
try:
conn = self._create_connection()
self._pool.put(conn, block=False)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"初始化连接池失败: {e}")
break
def _cleanup_idle_connections(self):
"""清理空闲连接的后台线程"""
while True:
try:
time.sleep(60) # 每分钟检查一次
current_time = time.time()
with self._pool_lock:
idle_connections = []
for conn_id, conn_info in list(self._all_connections.items()):
if (not conn_info['in_use'] and
current_time - conn_info['last_used'] > self.idle_timeout):
idle_connections.append(conn_id)
# 关闭空闲连接(保持最小连接数)
active_count = len(self._all_connections) - len(idle_connections)
can_close = max(0, active_count - self.min_connections)
for conn_id in idle_connections[:can_close]:
conn_info = self._all_connections.pop(conn_id)
try:
conn_info['connection'].close()
logging.debug(f"关闭空闲连接: {conn_id}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"关闭连接失败: {e}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"清理线程异常: {e}")
@contextmanager
def get_connection(self) -> sqlite3.Connection:
"""
获取连接的上下文管理器
使用示例:
with pool.get_connection() as conn:
# 使用conn执行数据库操作
"""
conn = None
try:
# 尝试从连接池获取连接
conn = self._pool.get(block=True, timeout=self.connection_timeout)
conn_id = id(conn)
with self._pool_lock:
self._stats['pool_hits'] += 1
self._all_connections[conn_id]['in_use'] = True
self._all_connections[conn_id]['last_used'] = time.time()
logging.debug(f"连接池命中: {conn_id}")
yield conn
except queue.Empty:
with self._pool_lock:
self._stats['timeouts'] += 1
logging.error("获取连接超时")
raise TimeoutError("获取数据库连接超时")
except Exception as e:
with self._pool_lock:
self._stats['errors'] += 1
logging.error(f"获取连接异常: {e}")
raise
else:
# 连接正常使用完毕后归还连接池
if conn:
with self._pool_lock:
conn_id = id(conn)
self._all_connections[conn_id]['in_use'] = False
self._all_connections[conn_id]['last_used'] = time.time()
try:
self._pool.put(conn, block=False)
logging.debug(f"连接归还池: {conn_id}")
except queue.Full:
# 连接池已满,关闭连接
with self._pool_lock:
self._all_connections.pop(conn_id, None)
try:
conn.close()
logging.debug(f"连接池满,关闭连接: {conn_id}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"关闭连接失败: {e}")
finally:
# 如果异常发生且conn未归还,确保连接状态正确
if conn:
with self._pool_lock:
conn_id = id(conn)
if conn_id in self._all_connections:
self._all_connections[conn_id]['in_use'] = False
self._all_connections[conn_id]['last_used'] = time.time()
def get_stats(self) -> Dict[str, int]:
"""获取连接池统计信息"""
with self._pool_lock:
stats_copy = self._stats.copy()
stats_copy['current_pool_size'] = self._pool.qsize()
stats_copy['total_connections'] = len(self._all_connections)
return stats_copy
# 测试示例
def test_database_connection_pool():
pool = DatabaseConnectionPool('test.db', min_connections=2, max_connections=5, connection_timeout=5, idle_timeout=120)
def worker(thread_id: int):
try:
with pool.get_connection() as conn:
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, value TEXT)")
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO test (value) VALUES (?)", (f"Thread-{thread_id}",))
conn.commit()
logging.info(f"线程 {thread_id} 插入数据成功")
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"线程 {thread_id} 操作异常: {e}")
threads = []
for i in range(8):
t = threading.Thread(target=worker, args=(i,))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
stats = pool.get_stats()
logging.info(f"连接池状态: {stats}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_database_connection_pool()
连接池初始化
创建最小连接数的连接,放入线程安全的queue.Queue中。维护所有连接的状态信息,包括创建时间、最后使用时间、是否正在使用。
线程安全:
使用threading.RLock保护连接状态和统计信息的访问。连接池队列本身是线程安全的。
连接获取与归还:
通过上下文管理器get_connection安全获取和归还连接。支持超时等待,超时抛出异常。归还连接时更新状态,若连接池已满则关闭连接。
空闲连接清理:
后台守护线程定时检查空闲连接,关闭超过空闲超时的连接,保持最小连接数。防止资源浪费
异常处理:
捕获连接创建、获取、关闭过程中的异常,保证连接池稳定。统计异常次数,方便监控。
统计信息:
记录创建连接数、活跃连接数、命中次数、超时次数等指标。提供接口获取当前连接池状态
实际使用示例:
多线程模拟数据库操作,测试连接池的并发性能和稳定性。





















 1677
1677

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








