用于回顾数据结构与算法时刷题的一些经验记录
(链表题目最好自己动手画一画,可以较为清晰地知道指针的处理)
文章目录
-
-
-
- [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- [92. 反转链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/)
- 160. [相交链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
- [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
- [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
- [86. 分隔链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list/)
- [83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/)
- [82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/)
- [19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
- [138. 复制带随机指针的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
- [2. 两数相加](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/)
- [148. 排序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/)
-
-
链表的结构体定义:
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {
}
* };
*/
206. 反转链表
给定一个链表的头节点,将其反转,并输出新的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
分析:
迭代法:
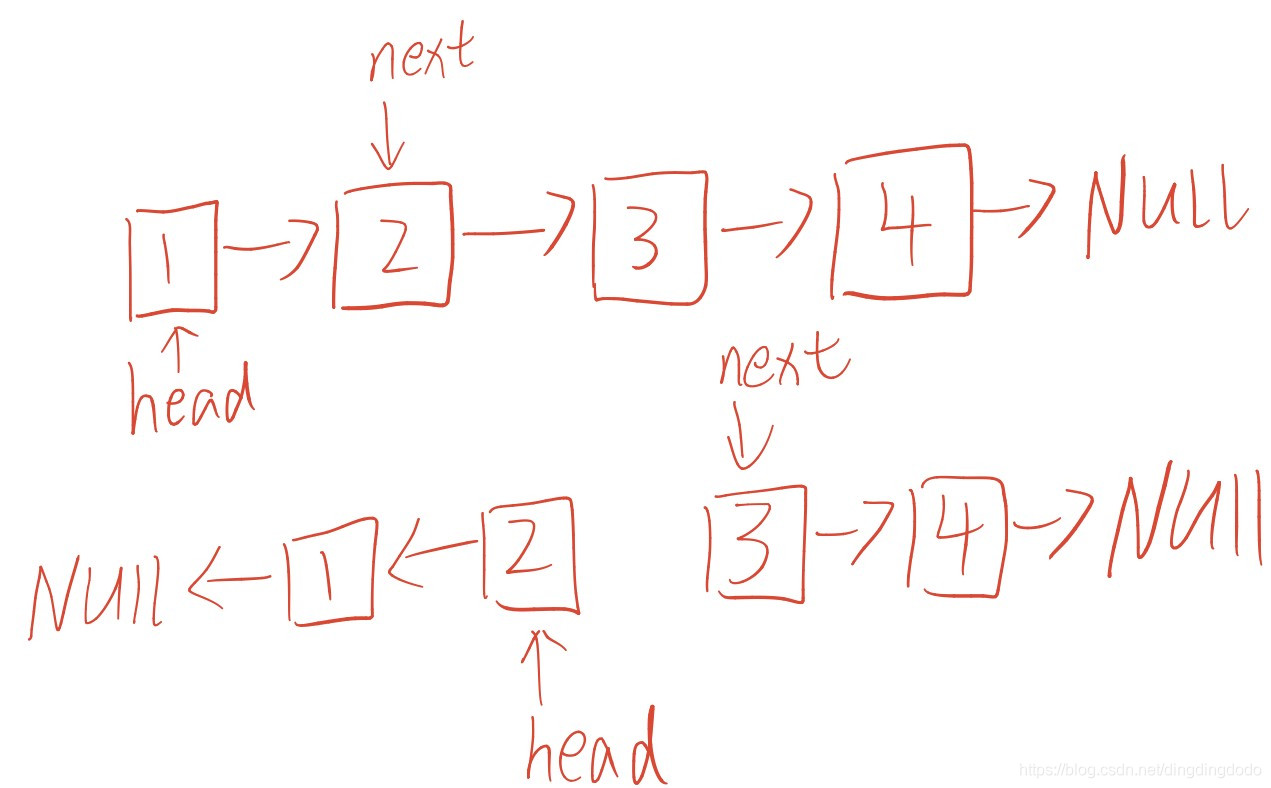
如果头节点为NULL或者为单节点,则返回头节点即可
如果头节点的next不为NULL,则进行迭代
-
(目的是让当前头节点的下一个节点指向头节点,在此基础上不断令next向后迭代即可)
-
这个过程需要创建新的指针保存next的中间值
-
mid=next_node//保存中间值 next_node=next_node->next//向后迭代next_node mid->next=head; //令后一个节点指向head head=newhead; //迭代head
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
return head; //链表为空或者只有一个节点,则返回自身即可
else
{
ListNode* mid=NULL;
ListNode* next_node=head->next;
head->next=NULL;
while(next_node!=NULL)
{
mid=next_node;
next_node=next_node->next;
mid->next=head;
head=mid;
}
return head;
}
}
};
复杂度分析: 时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 空间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O (1) O(1)
递归法:
- 迭代终止:如果head是NULL或者单节点,则返回自身即可
- 否则执行迭代:
- 令 newhead 赋值为 对head之后链表反转的结果
- 则head的next应当是翻转后链表的尾,因此令head->next->next等于head,即实现了将head加入反转链表的操作
- 则此时的head为新的翻转后的尾,令其next=NULL即可
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL) return head;
else
{
ListNode* newhead=NULL;
newhead=reverseList(head->next); //这意味这已经将除了head之后节点的已经反转
head->next->next=head; //故需要令让head->next的next指向head实现head的反转
head->next=NULL; //将head的next置空
return newhead;
}
}
};
92. 反转链表 II
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
分析:这个问题较之前的问题难度有了增加,因为要反转部分链表,故考虑因素会增多。
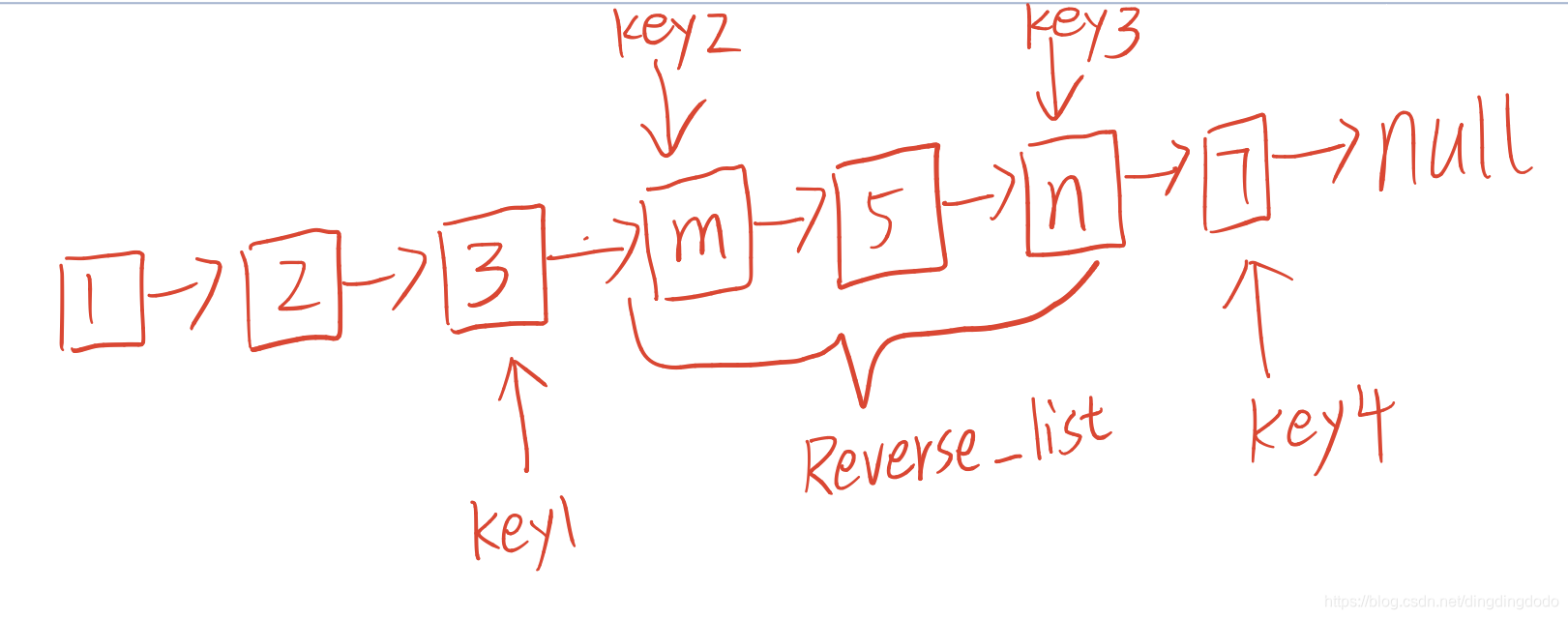
将大致链表画出,我们可以知道,将 m − > . . . − > n m->...->n m−>...−>n 进行反转,需要确定一些重要信息
- key1 :反转部分链表的前一个节点,之后需要将其next指向反转后的链表
- key2 :反转部分链表的头节点,既需要确定其进行反转,也需要在反转后令其指向之后节点
- key3 :反转部分链表的尾节点,确定出反转的范围,同时反转后将key1部分指向key3
- key4 :反转部分链表的后一个节点,需要将反转后的链表尾部连接
因此,总体思路分为三部分:
-
找到所需要的重要信息
-
将需要反转的部分链表进行反转,并进行链接
-
返回处理后的链表的头节点(注意:如果原始头节点参与了反转,则返回节点将不是原始头节点,故需要分情况考虑)
class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL) return head; int length=n-m+1; //需要逆置的节点数量 ListNode* key1=NULL; ListNode* result=head; //作为结果,之后如果特殊情况,将修改 while(head!=NULL&&(--m)) //确定出key1的位置,如果key1为NULL,也说明了头节点参与了逆置 { key1=head; head=head->next; } ListNode* key2=head; //确定key2位置 ListNode* newhead=NULL; //用于逆置的辅助 ListNode* key3=NULL; ListNode* next_node=head->next; //用于逆置的辅助 while(head!=NULL&&(--length)) //完成逆置 { newhead=next_node; next_node=next_node->next; newhead->next=head; head=newhead; } key3=head; //确定key3的位置 ListNode* key4=next_node; //确定key4的位置 //此时已经知道了关键的4个位置,因此根据key1的情况分情况进行连接 if





 这篇博客详细解析了LeetCode中涉及链表的多个经典题目,包括206. 反转链表、92. 反转链表 II、160. 相交链表、141. 环形链表等,讲解了迭代法和递归法等解题思路,涉及链表操作、链表结构的理解及复杂度分析。
这篇博客详细解析了LeetCode中涉及链表的多个经典题目,包括206. 反转链表、92. 反转链表 II、160. 相交链表、141. 环形链表等,讲解了迭代法和递归法等解题思路,涉及链表操作、链表结构的理解及复杂度分析。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








