例如:假设有两个主题,主题1有4个相关网页,主题2有5个相关网页。某系统对于主题1检索出4个相关网页,其rank分别为1, 2, 4, 7;对于主题2检索出3个相关网页,其rank分别为1,3,5。对于主题1,平均准确率为(1/1+2/2+3/4+4/7)/4=0.83。对于主题 2,平均准确率为(1/1+2/3+3/5+0+0)/5=0.45。则MAP= (0.83+0.45)/2=0.64。”
MRR是把标准答案在被评价系统给出结果中的排序取倒数作为它的准确度,再对所有的问题取平均。
Wiki
Precision and recall are single-value metrics based on the whole list of documents returned by the system. For systems that return a ranked sequence of documents, it is desirable to also consider the order in which the returned documents are presented. Average precision emphasizes ranking relevant documents higher. It is the average of precisions computed at the point of each of the relevant documents in the ranked sequence:
where r is the rank, N the number retrieved, rel() a binary function on the relevance of a given rank, and P(r) precision at a given cut-off rank:
This metric is also sometimes referred to geometrically as the area under the Precision-Recall curve.
Note that the denominator (number of relevant documents) is the number of relevant documents in the entire collection, so that the metric reflects performance over all relevant documents, regardless of a retrieval cutoff. See:.
^ Turpin, Andrew; Scholer, Falk (2006). "User performance versus precision measures for simple search tasks". Proceedings of the 29th Annual international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in information Retrieval_r(Seattle, Washington, USA, August 06-11, 2006) (New York, NY: ACM): 11–18. doi:10.1145/1148170.1148176
转自: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_662234020100pozd.html








 本文深入解析了MAP(Mean Average Precision)和MRR(Mean Reciprocal Rank)在信息检索领域的核心概念及计算方法。通过具体实例,展示了如何评估系统在返回相关文档上的性能,特别是强调了排名相关文档的重要性。文章还讨论了这两个指标在不同场景下的应用,为读者提供了一种全面评估信息检索系统效能的视角。
本文深入解析了MAP(Mean Average Precision)和MRR(Mean Reciprocal Rank)在信息检索领域的核心概念及计算方法。通过具体实例,展示了如何评估系统在返回相关文档上的性能,特别是强调了排名相关文档的重要性。文章还讨论了这两个指标在不同场景下的应用,为读者提供了一种全面评估信息检索系统效能的视角。

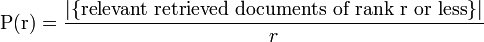
















 6214
6214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








