引言
文件读写是JAVA程序中非常普遍的功能,也是程序员的基本功。但是否有思考过,现在实现文件读写的代码在效率上是否有提升的空间?怎样用JAVA写出高效率的文件读写程序?
传统IO的效率问题
要想写出高效率的程序,就要先了解现在的实现有什么问题。在没有进行优化IO代码的情况下,假设程序正在将文件内容复制到新文件,应用使用的是以下模型读写文件:

- 应用程序运行在用户空间,当需要读取文件时,向操作系统内核发起Read的系统调用(这是操作系统决定的,处于保护底层设备资源考虑)。然后从用户空间切换到内核空间。
- CPU向DMA控制器发起IO请求,DMA将相应数据从硬盘复制到内核空间。
- CPU将数据从内核空间复制到用户空间,数据读取完成,切换回用户空间。
- 应用程序将内存中的文件数据写到新文件,发起Write的系统调用。
- 上下文切换,CPU将数据从用户空间复制到内核空间。
- CPU向DMA发起IO请求,DMA将数据从内核空间复制到硬盘。
- 如此往复以上整个流程直到文件复制完成。
从经典IO模型可以看到,低效的原因在于:
- 用户空间与内核空间的上下文切换
- 用户空间与内核空间的数据拷贝
但次旧文件到新文件内容复制过程,就有4次上下文切换以及2次CPU参与的数据拷贝。当文件较大时时间以及资源的消耗就非常可观了。
所以我们优化的目标是减少上下文切换以及CPU参与的数据复制,做到这个,IO效率就能提升了。实现这个目标的方法就是使用零拷贝技术
零拷贝(ZERO-COPY)
零拷贝就是一种避免 CPU 将数据从一块存储拷贝到另外一块存储的技术。针对操作系统中的设备驱动程序、文件系统以及网络协议堆栈而出现的各种零拷贝技术极大地提升了特定应用程序的性能,并且使得这些应用程序可以更加有效地利用系统资源。这种性能的提升就是通过在数据拷贝进行的同时,允许 CPU 执行其他的任务来实现的。
所以,所谓的零拷贝,指的就是CPU的零拷贝。零拷贝技术的实现方式主要有mmap(内存映射),sendfile以及splice。这些系统调用指的是Linux系统,不同的操作系统支持度不同。
MMAP就是将用户的虚拟地址空间映射到内核的数据地址空间,从而避免用户空间和内核空间的数据复制。sendfile用于将文件发送到socket的场景,比如经典的下载文件场景,就可以通过sendfile系统调用实现高效的文件下载。与sendfile类似,但splice用于文件之间的传输。
MMAP
将文件读写改成MMAP模型,省去了用户空间和内核空间的CPU复制过程。数据通过内存映射的方式共享。

MMAP读文件
 MMAP写文件
MMAP写文件
Sendfile/Splice
Sendfile 或者 Splice的模型,数据的复制直接在内核区完成,系统调用过程最多只有一次CPU复制。减少了两次上下文切换,一次CPU复制。

JAVA代码实现
JAVA对零拷贝的支持位于NIO包内。NIO包就是为了提升JAVA IO的性能而出现的。下面是一些代码实现的例子,并且比较普通读写与零拷贝读写间的性能差异。
- 普通方式读取大文件
@Test
public void normalRead() throws IOException {
AtomicLong bytesCount = new AtomicLong();
Files.lines(new File("D:\\tmp\\many_integers.txt").toPath()).forEach(
line -> {
bytesCount.addAndGet(line.getBytes().length + 1);
}
);
System.out.printf("total bytes:%d\n",bytesCount.longValue());
}
耗时:51 sec 824 ms
- MMAP读取大文件
@Test
public void readLargeFile() throws Exception {
File file = new File("D:\\tmp\\many_integers.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(file.toPath(), StandardOpenOption.READ);
long position = 0;
final long DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 100 * 1024 * 1024;
long totalBytes = 0;
long size = fileChannel.size();
while (size > 0) {
long buffSize = Math.min(size, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, position, buffSize);
size -= buffSize;
position += buffSize;
totalBytes += mappedByteBuffer.limit();
((DirectBuffer) mappedByteBuffer).cleaner().clean();
}
fileChannel.close();
System.out.printf("total bytes:%d\n", totalBytes);
}
耗时:9 ms

- 普通方式写入大文件
@Test
public void writeManyIntegerNormal() throws Exception {
File f = new File("D:\\tmp\\many_integers_normal.txt");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = Files.newBufferedWriter(f.toPath());
int cnt = 0;
while (++cnt <= 300000000) {
bufferedWriter.write("Hello World\n");
}
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
}
耗时:1 min 2 sec

- MMAP写入大文件
@Test
public void writeManyIntegers() {
File f = new File("D:\\tmp\\many_integers.txt");
f.delete();
try {
f.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("D:\\tmp\\many_integers.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ)) {
long position = 0L;
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, position, 100 * 1024 * 1024);
byte[] bytes = "Hello World\n".getBytes();
long bytesCnt = 0l;
int cnt = 0;
while (++cnt <= 300000000) {
if (mappedByteBuffer.limit() - mappedByteBuffer.position() < bytes.length) {
mappedByteBuffer.flip();
position += mappedByteBuffer.limit();
// unMapBuffer(mappedByteBuffer, fileChannel.getClass());
((DirectBuffer) mappedByteBuffer).cleaner().clean();
mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, position, 100 * 1024 * 1024);
}
mappedByteBuffer.put(bytes);
bytesCnt += bytes.length;
}
// unMapBuffer(mappedByteBuffer, fileChannel.getClass());
((DirectBuffer) mappedByteBuffer).cleaner().clean();
fileChannel.truncate(bytesCnt);
} catch (
IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
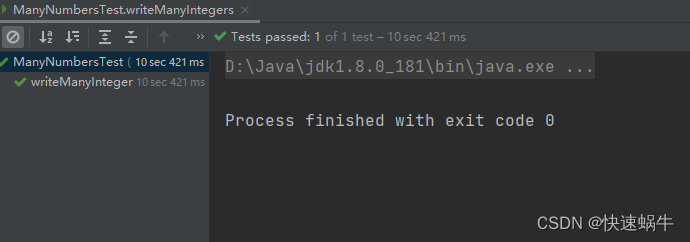
耗时:10 sec 421 ms
- JAVA通过transferTo/transferFrom 获得sendfile或者splice的支持。请注意这个依赖于具体的操作系统是否支持,如果不支持则最终可以退化为普通的文件读写。
下面是用相关的API进行大文件的分割和合拼的例子
文件分割:
@Test
public void testSplit() throws Exception{
File file = new File("D:\\tmp\\many_integers.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(file.toPath(), StandardOpenOption.READ);
long position = 0;
final long DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
long size = fileChannel.size();
for(int i=0;size>0;i++){
long buffSize = Math.min(size, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
FileChannel open = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(String.format("D:\\tmp\\split1\\part_%s.txt", i)), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.WRITE);
fileChannel.transferTo(position,buffSize,open);
open.close();
size -= buffSize;
position += buffSize;
}
fileChannel.close();
}
文件合拼:
@Test
public void testMerge(){
try(FileChannel open = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("D:\\tmp\\split1\\merge\\merge.txt"), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.APPEND)){
long position=0;
for(File file : new File("D:\\tmp\\split1").listFiles()){
if(file.isFile()){
FileChannel srcChannel = FileChannel.open(file.toPath(), StandardOpenOption.READ);
long size = srcChannel.size();
open.transferFrom(srcChannel,position,size);
srcChannel.close();
position+=size;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}





 本文探讨了JAVA程序中文件读写的传统IO效率问题,提出通过零拷贝技术(如MMAP、sendfile和splice)降低上下文切换和CPU参与的数据复制,展示了使用NIO包下的零拷贝方法提升文件操作性能的实例和对比普通读写方式的时间节省。
本文探讨了JAVA程序中文件读写的传统IO效率问题,提出通过零拷贝技术(如MMAP、sendfile和splice)降低上下文切换和CPU参与的数据复制,展示了使用NIO包下的零拷贝方法提升文件操作性能的实例和对比普通读写方式的时间节省。
















 593
593










