Anton is growing a tree in his garden. In case you forgot, the tree is a connected acyclic undirected graph.
There are n vertices in the tree, each of them is painted black or white. Anton doesn't like multicolored trees, so he wants to change the tree such that all vertices have the same color (black or white).
To change the colors Anton can use only operations of one type. We denote it aspaint(v), where v is some vertex of the tree. This operation changes the color of all verticesu such that all vertices on the shortest path fromv to u have the same color (includingv and u). For example, consider the tree
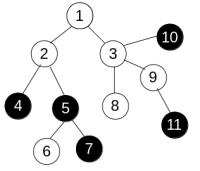
and apply operation paint(3) to get the following:
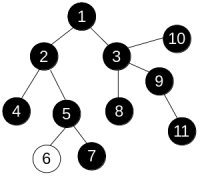
Anton is interested in the minimum number of operation he needs to perform in order to make the colors of all vertices equal.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers colori (0 ≤ colori ≤ 1) — colors of the vertices.colori = 0 means that thei-th vertex is initially painted white, whilecolori = 1 means it's initially painted black.
Then follow n - 1 line, each of them contains a pair of integersui andvi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) — indices of vertices connected by the corresponding edge. It's guaranteed that all pairs(ui, vi) are distinct, i.e. there are no multiple edges.
Print one integer — the minimum number of operations Anton has to apply in order to make all vertices of the tree black or all vertices of the tree white.
11 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 5 6 5 7 3 8 3 9 3 10 9 11
2
4 0 0 0 0 1 2 2 3 3 4
0
In the first sample, the tree is the same as on the picture. If we first apply operationpaint(3) and then apply paint(6), the tree will become completely black, so the answer is2.
In the second sample, the tree is already white, so there is no need to apply any operations and the answer is0.
好题!考察了树的直径的作用。题意中的paint(v)就是把所有的与v同色的并从这个点到v不经过其他颜色的点都涂成一种颜色,包括v;
这样缩点是必然的,用dfs缩点后重构树(可证:重构图必然是树)
然后因为paint(v)对所有点有效,我们很容易看出树的直径/2就是答案
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=4e5+5;
int num[maxn],vis[maxn],headpre[maxn],headafter[maxn];
struct node
{
int from,to,next,v;
};
int cnt=0,edgeprenum=1,edgeafternum=1,maxnum=0,maxid;
node edgepre[maxn],edgeafter[maxn];
void addedgepre(int u,int v)
{
edgepre[edgeprenum].from=u;
edgepre[edgeprenum].to=v;
edgepre[edgeprenum].next=headpre[u];
headpre[u]=edgeprenum++;
}
void addedgeafter(int u,int v)
{
edgeafter[edgeafternum].from=u;
edgeafter[edgeafternum].to=v;
edgeafter[edgeafternum].next=headafter[u];
headafter[u]=edgeafternum++;
}
int dfs(int now)
{
vis[now]=cnt;
for(int i=headpre[now];i!=-1;i=edgepre[i].next)
{
int v=edgepre[i].to;
if(!vis[v]&&num[now]==num[v])
dfs(v);
}
}
int bfs(int now)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
queue<int>que;
que.push(now);
maxnum=0;
vis[now]=1;
while(!que.empty())
{
int u=que.front();
que.pop();
if(maxnum<vis[u])
{
maxid=u;
maxnum=vis[u];
}
for(int i=headafter[u];i!=-1;i=edgeafter[i].next)
{
int v=edgeafter[i].to;
if(!vis[v])
{
que.push(v);
vis[v]=vis[u]+1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n,a,b;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(headafter,-1,sizeof(headafter));
memset(headpre,-1,sizeof(headpre));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
addedgepre(a,b);
addedgepre(b,a);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
cnt++;
dfs(i);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<edgeprenum;i++)
{
int u=edgepre[i].from,v=edgepre[i].to;
if(vis[u]!=vis[v])
{
addedgeafter(vis[u],vis[v]);
}
}
bfs(1);
bfs(maxid);
cout<<maxnum/2<<endl;
return 0;
}







 本文探讨了一道算法题目,通过构建树形结构并利用树的直径特性来优化操作次数,实现将树中所有节点的颜色统一。文章详细介绍了问题背景、解决思路及核心代码实现。
本文探讨了一道算法题目,通过构建树形结构并利用树的直径特性来优化操作次数,实现将树中所有节点的颜色统一。文章详细介绍了问题背景、解决思路及核心代码实现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








