.
标记类为Attr,这个类中将对第一和第二阶段未标记的如Statement和Expression进行标记,作用如下:
进行语义合法性的检查和进行逻辑判断,如:
(1)变量的类型是否匹配
(2)变量在使用前是否已经初始化
(3)能够推导出泛型方法的参数类型
(4)字符串常量的合并
其中还有其它的一些辅助类来完成一些检查:
(1)Check 检查变量类型是否正确,如二元操作符两边的操作数的类型是否匹配,方法返回的类型是否与接收的引用值类型匹配等
(2)Resolve 主要检查变量、方法或者类的访问是否合法、变量是否有静态变量、变量是否已经初始化等
(3)ConstanceFold 常量折叠。
了解下Attr中的方法。
Type attribTree(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment, int protoKind, Type protoType, String errKey) {
// 保存之前的环境
Environment<AttrContext> prevEnv = this.env;
int prevPkind = this.protoKind;
Type prevPt = this.protoType;
String prevErrKey = this.errorKey;
try {
// 创造自己的环境
this.env = environment;
this.protoKind = protoKind;
this.protoType = protoType;
this.errorKey = errKey;
jcTree.accept(this);
if (jcTree == breakTree){
throw new BreakAttr(environment);
}
return result;
} catch (CompletionFailure ex) {
jcTree.type = symbolTable.errType;
return check.completionError(jcTree.position(), ex);
} finally {
// 还原之前的环境
this.env = prevEnv;
this.protoKind = prevPkind;
this.protoType = prevPt;
this.errorKey = prevErrKey;
}
}
替换Attr中的几个属性,如下:
/** Visitor argument: the current env.
*/
Environment<AttrContext> env;
/** Visitor argument: the currently expected proto-kind.
*/
int protoKind;
/** Visitor argument: the currently expected proto-type.
*/
Type protoType;
/** Visitor argument: the error key to be generated when a type error occurs
*/
String errorKey;
/** Visitor result: the computed type.
*/
Type result;
这个方法主要由以下的两个方法调用,如下:
/** Visitor method: attribute a tree, catching any completion failure
* exceptions. Return the tree's type.
*
* @param jcTree The tree to be visited.
* @param environment The environment visitor argument.
* @param protoKind The protokind visitor argument. protoKind 为Symbol的类型Kinds
* @param protoType The prototype visitor argument. prototype为Type的类型TypeTags
*/
Type attribTree(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment, int protoKind, Type protoType) {
return attribTree(jcTree, environment, protoKind, protoType, "incompatible.types"); // 不兼容的类型
}
public Type attribExpression(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment, Type protoType, String key) {
Type temp = null;
if(protoType.typeTag != ERROR){
temp = protoType;
}else{
temp = Type.noType;
}
return attribTree(jcTree, environment, _VAL_12, temp , key);
}
如上两个方法由下面这几个方法调用,主要是attribStatement(),attribType()与attribExpression(),如下:
/** Derived visitor method: attribute an expression tree.
*/
public Type attribExpression(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment, Type protoType) {
Type temp = null;
if(protoType.typeTag != ERROR){
temp = protoType;
}else{
temp = Type.noType;
}
return attribTree(jcTree, environment, _VAL_12, temp); // String a = "a".toString()
}
/** Derived visitor method: attribute an expression tree with
* no constraints on the computed type.
*/
Type attribExpression(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment) {
return attribTree(jcTree, environment, _VAL_12, Type.noType); // "a".toString();
}
/** Derived visitor method: attribute a type tree.
*/
Type attribType(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment) {
Type result = attribTree(jcTree, environment, _TYP_2, Type.noType); // 类型参数相关
return result;
}
/** Derived visitor method: attribute a statement or definition tree.
*/
public Type attribStatement(JCTree jcTree, Environment<AttrContext> environment) {
return attribTree(jcTree, environment, _NIL_0, Type.noType); // "a".toString()
}
重点关注调用方法时为方法参数protoKind与protoType指定的值。
举例来说变量的类型是否匹配是如何检查的,如下:
package m20170409;
public class TestA<T> {
public Integer x(){
return new Integer(2);
}
public void test(int a){
Integer x = x().toString(); // 声明与初始化类型不匹配
}
}
主要看代码Integer x = x().toString();的JCVariableDeclaration语法节点。
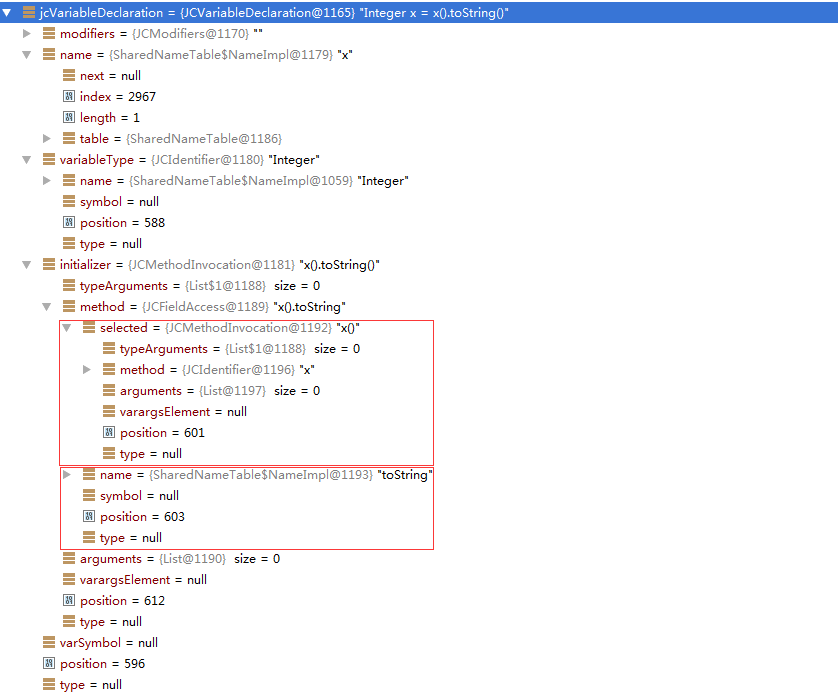
首先看对variableType属性的处理,这个节点是JCIdentifier类型,调用如下方法来标记:
attribTree(jcTree, environment, _TYP_2, Type.noType);
进一步调用了visitIdentifier()方法来处理,如下:




 本文深入探讨了Java编译器中的Attr类及其方法在语义合法性检查和逻辑判断中的应用,包括变量类型匹配、初始化状态验证及泛型方法参数类型的推导。同时,介绍了Attr类如何通过检查变量类型、方法访问合法性以及常量折叠等功能,确保代码的正确性和效率。
本文深入探讨了Java编译器中的Attr类及其方法在语义合法性检查和逻辑判断中的应用,包括变量类型匹配、初始化状态验证及泛型方法参数类型的推导。同时,介绍了Attr类如何通过检查变量类型、方法访问合法性以及常量折叠等功能,确保代码的正确性和效率。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








