核心概念
- 约定大于配置 -> 零配置
- 依赖即配置
网上有一个总结非常好的图
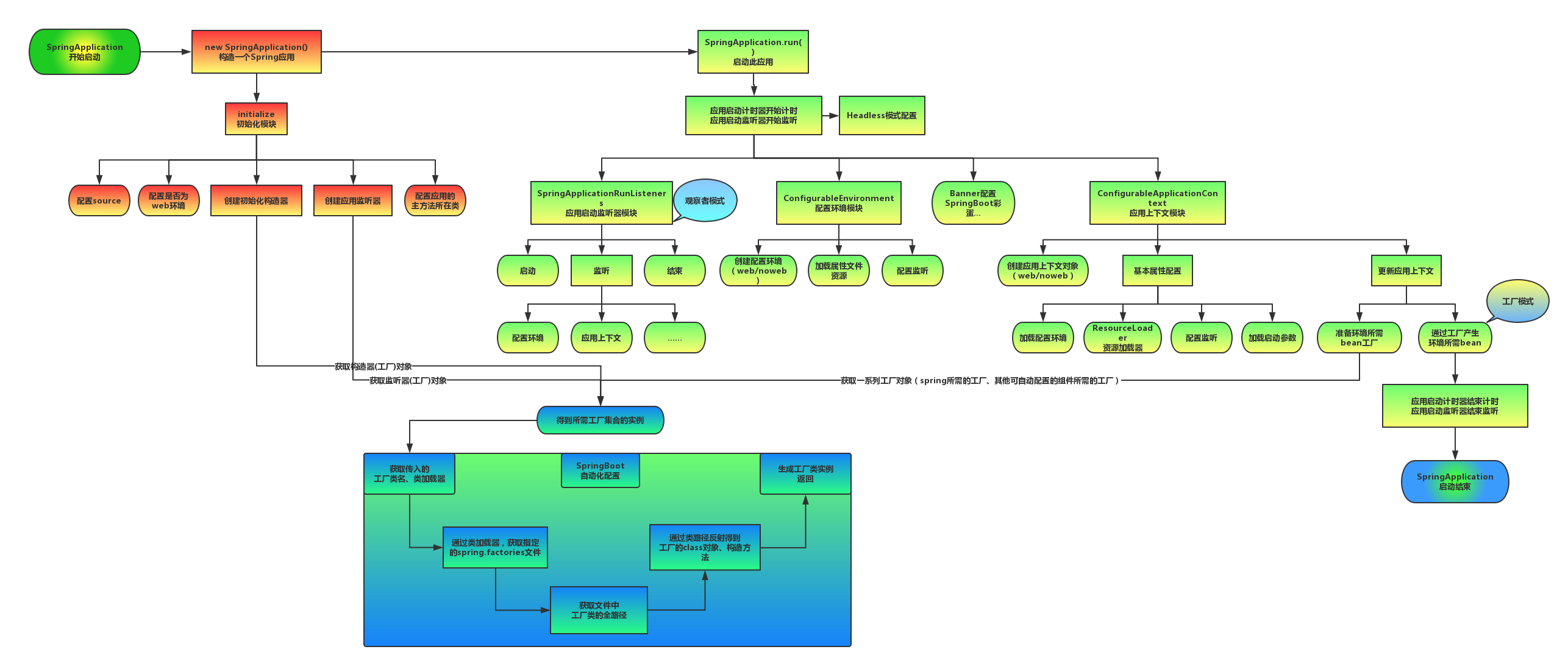
启动区别
jar包和war包启动区别
jar包:执行SpringBootApplication的run方法,启动IOC容器,然后创建嵌入式Servlet容器
war包: 先是启动Servlet服务器,服务器启动会根据规范回掉(springBootServletInitizer),然后启动IOC容器
启动流程
每个SpringBoot程序都有一个主入口,也就是main方法,main里面调用SpringApplication.run()启动。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//StopWatch一个用于记录人物开始和结束时间的类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
//创造了应用监听器,并开始监听过程
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//配置SpringBoot的应用环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//打印Banner(就是启动的那个图案,如果你信佛,可以自定义个如来佛祖打在启动控制台)
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//初始化容器
context = createApplicationContext();
//错误分析机制,只有在抛出异常时才会用到。
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//调用((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh(); 对于web工程启动tomcat
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
//是否打印启动信息日志,可以通过SpringApplicationBuilder进行设置。
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
自动配置
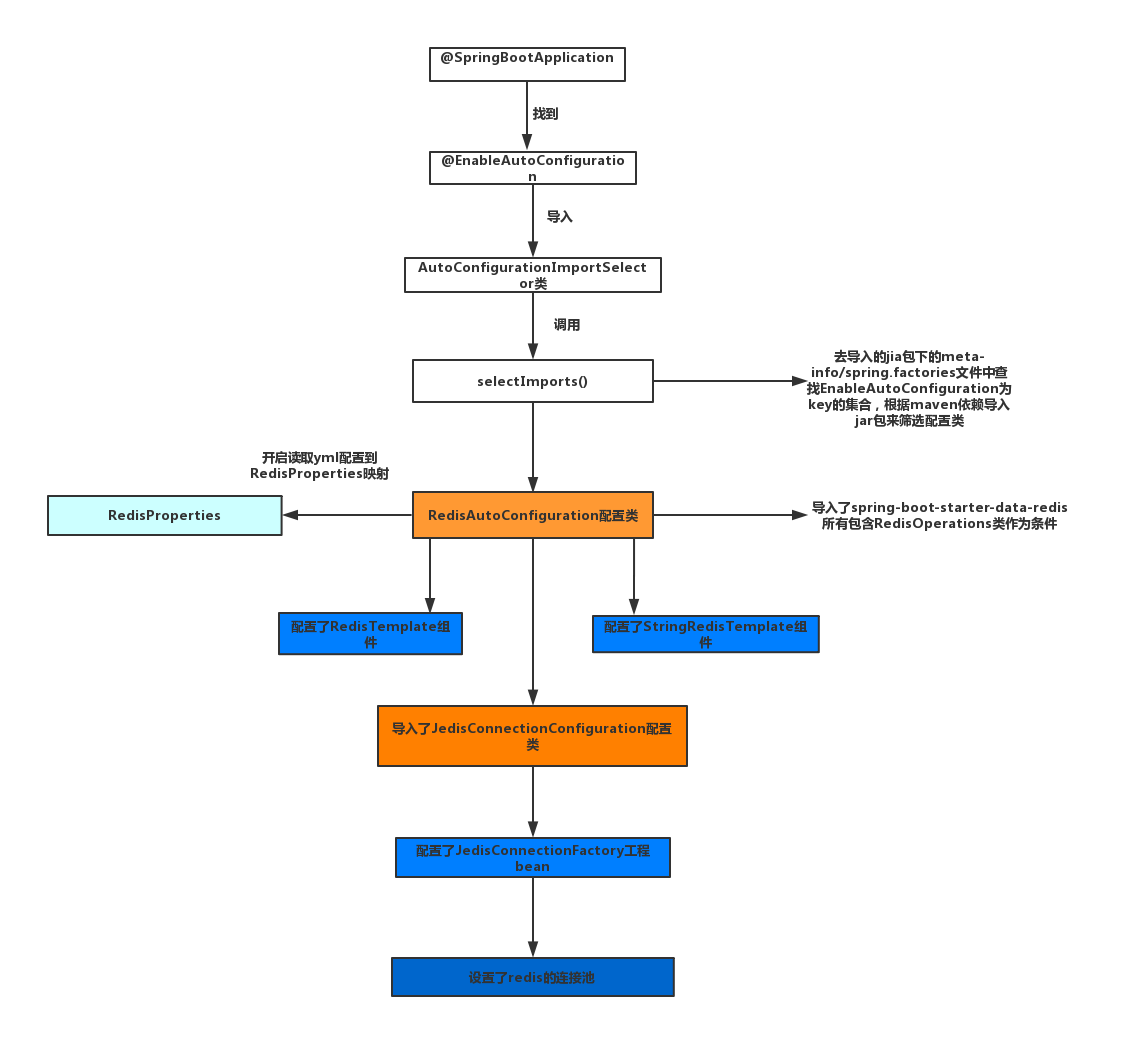
spring.fatories的文件例子如下
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.sg.config.SwaggerConfig
这个类可以是第三方的,也可以是自己写的,这样就可以让spring-boot找到这个类
起步依赖
spring-boot-starter-web包自动帮我们引入了web模块开发需要的相关jar包,
mybatis-spring-boot-starter帮我们引入了dao开发相关的jar包。
spring-boot-starter-xxx是官方提供的starter,xxx-spring-boot-starter是第三方提供的starter。
以mybatis为例,在上面的截图中,我们发下mybatis-spring-boot-starter这个包帮我们引入了mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包,如下图:
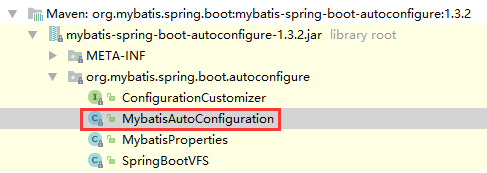
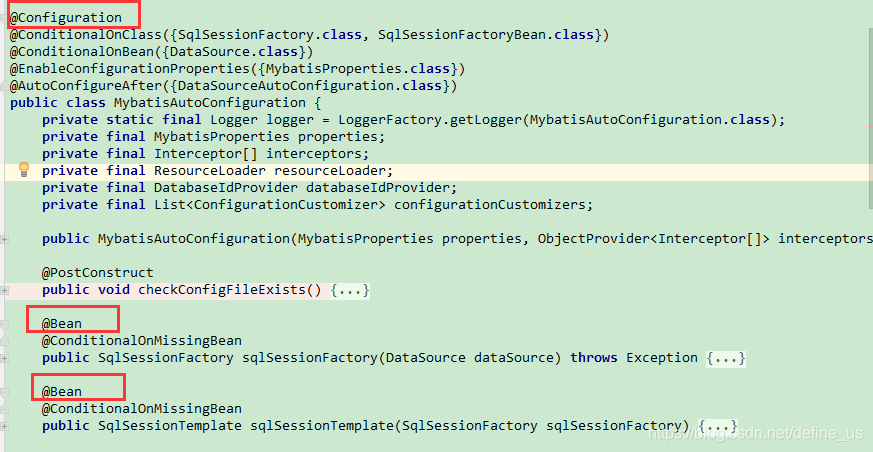
下面是spring-boot-autoconfigure这个jar中spring.factories文件部分内容,其中有一个key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的值定义了需要自动配置的bean,通过读取这个配置获取一组@Configuration类。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
所有spring.factories中的文件内容org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguratio 这个key所对应的值列表会被合并
其中,使用了spring自己实现的SPI
在springboot的自动装配过程中,最终会加载META-INF/spring.factories文件,而加载的过程是由SpringFactoriesLoader加载的。从CLASSPATH下的每个Jar包中搜寻所有META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,然后将解析properties文件,找到指定名称的配置后返回。需要注意的是,其实这里不仅仅是会去ClassPath路径下查找,会扫描所有路径下的Jar包,只不过这个文件只会在Classpath下的jar包中。
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
// spring.factories文件的格式为:key=value1,value2,value3
// 从所有的jar包中找到META-INF/spring.factories文件
// 然后从文件中解析出key=factoryClass类名称的所有value值
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
// 取得资源文件的URL
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
// 遍历所有的URL
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// 根据资源文件URL解析properties文件,得到对应的一组@Configuration类
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
// 组装数据,并返回
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
SpringApplicationRunListener
这个是SpringBoot自己为Spring生态贡献的类。相当于对Spring中的ApplicationListener。
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* Called immediately when the run method has first started. Can be used for very
* early initialization.
*/
void starting();
/**
* Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the
* {@link ApplicationContext} has been created.
* @param environment the environment
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
/**
* Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but
* before sources have been loaded.
* @param context the application context
*/
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been
* refreshed.
* @param context the application context
*/
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* The context has been refreshed and the application has started but
* {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner
* ApplicationRunners} have not been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has
* been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and
* {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* Called when a failure occurs when running the application.
* @param context the application context or {@code null} if a failure occurred before
* the context was created
* @param exception the failure
* @since 2.0.0
*/
void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception);
}
SpringApplicationRunListener 接口的作用主要就是在springboot 启动初始化的过程中可以通过SpringApplicationRunListener接口回调来让用户在启动的各个流程中可以加入自己的逻辑。可以SpringBoot的源代码在启动流程中详细查看这些listener被触发的时间。请参考参考文献1。
prepareEnvironment
SpringApplication在初始化时,有如下,需要判断本工程是不是WEB工程。方法就是查看是否拥有Web工程所需要的所有的类。
private boolean deduceWebEnvironment() {
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
然后,根据这个判断准备当前的运行环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
if (isWebEnvironment(environment) && !this.webEnvironment) {
environment = convertToStandardEnvironment(environment);
}
return environment;
}
createApplicationContext
简单来说就是创建应用上下文。
根据SpringApplication的webApplicationType来实例化对应的上下文
- 如果webApplicationType的值是SERVLET,那么实例化AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 如果是REACTIVE则实例化AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext(响应式编程,后续再看)。此时程序一般是不依赖SpringMVC,而是Spring WebFlux。
- 如果既不是SERVLET、也不是REACTIVE,那么则是默认情况(也就是我们所说的非web应用),实例化AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
参考文献
【1】https://www.jianshu.com/p/308534c60b11





 本文深入解析SpringBoot的启动流程,包括约定大于配置的原则、启动方式的区别、自动配置的机制以及关键类SpringApplicationRunListener的作用。同时,介绍了如何通过spring.factories文件实现自动配置,以及SpringBoot如何判断并准备Web环境。
本文深入解析SpringBoot的启动流程,包括约定大于配置的原则、启动方式的区别、自动配置的机制以及关键类SpringApplicationRunListener的作用。同时,介绍了如何通过spring.factories文件实现自动配置,以及SpringBoot如何判断并准备Web环境。
















 580
580

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








