Minimum Sum
Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1152 Accepted Submission(s): 263
Problem Description
You are given N positive integers, denoted as x0, x1 ... xN-1. Then give you some intervals [l, r]. For each interval, you need to find a number x to make
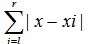 as small as possible!
as small as possible!
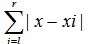 as small as possible!
as small as possible!
Input
The first line is an integer T (T <= 10), indicating the number of test cases. For each test case, an integer N (1 <= N <= 100,000) comes first. Then comes N positive integers x (1 <= x <= 1,000, 000,000) in the next line. Finally, comes an integer Q (1 <= Q <= 100,000), indicting there are Q queries. Each query consists of two integers l, r (0 <= l <= r < N), meaning the interval you should deal with.
Output
For the k-th test case, first output “Case #k:” in a separate line. Then output Q lines, each line is the minimum value of
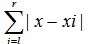 . Output a blank line after every test case.
. Output a blank line after every test case.
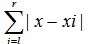 . Output a blank line after every test case.
. Output a blank line after every test case.
Sample Input
2 5 3 6 2 2 4 2 1 4 0 2 2 7 7 2 0 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case #1: 6 4 Case #2: 0 0
Author
standy
Source
这个不同于POJ的Kth Number,比它要注意的几点是:
1、它的数值序列式允许重复的,因此需要解决
2、需要统计和
解题思路:这一题很久一前就见过,不过不会做。因为当时不会划分树,我们可以很容易的看出找到中位数,在统计中位数两边的和即可
这里我们统计总和和一边的和,拿总的减去一边便是另一边。这里我颠覆来原来看似简洁的写法,原来那个边界考虑的很多,容易糊涂
这里为了简单改写为另一种写法,就是行布朗当的把从一开始的所有和均统计出来,我们从一开始,0号元素为0,那么就不会影响结果。
所有区间的统计均是末减初
(前提是先序遍历,你懂得),这样统计某一区间时,直接减即可。
第一种写法代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100002;
const int MAX_depth = 32;
int val[MAX_depth][MAX];
int a[MAX_depth][MAX];
long long sum[MAX_depth][MAX];
int s[MAX];
void Build(int l, int r, int depth) {
if (l == r) {
sum[depth][l] = val[depth][l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
int same = mid - l + 1;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
if (val[depth][i] < s[mid]) {
same--;
}
}
int lc = l;
int rc = mid + 1;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
if (i == l) {
sum[depth][i] = val[depth][i];
} else {
sum[depth][i] = sum[depth][i - 1] + val[depth][i];
}
if ((val[depth][i] < s[mid]) || (val[depth][i] == s[mid] && same > 0)) {
if (val[depth][i] == s[mid]) same--;
if (i == l) {
a[depth][i] = 1;
} else {
a[depth][i] = a[depth][i - 1] + 1;
}
val[depth + 1][lc++] = val[depth][i];
} else {
if (i == l) {
a[depth][i] = 0;
} else {
a[depth][i] = a[depth][i - 1];
}
val[depth + 1][rc++] = val[depth][i];
}
}
Build(l, mid, depth + 1);
Build(mid + 1, r, depth + 1);
}
long long total;
int pre_same;
int Search(int s, int e, int l, int r, int k, int depth) {
if (l == r) {
return val[depth][l];
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
int So = a[depth][s - 1];
if (s == l) {
So = 0;
}
int x = a[depth][e] - So;
if (x >= k) {
return Search(l + So, l + a[depth][e] - 1, l, mid, k, depth + 1);
} else {
pre_same += x;
if (a[depth][e] > 0) {
total += sum[depth + 1][l + a[depth][e] - 1];
if (So > 0) {
total -= sum[depth + 1][l + So - 1];
}
}
return Search(mid + 1 + s - l - So, mid + 1 + e - l - a[depth][e], mid + 1, r, k - x, depth + 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for (int k1 = 1; k1 <= T; k1++) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &val[0][i]);
s[i] = val[0][i];
}
sort(s + 1, s + n + 1);
Build(1, n, 0);
int s, e;
scanf("%d", &m);
printf("Case #%d:\n", k1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &s, &e);
s++, e++;
int k = (e - s + 2) / 2;
total = 0;
pre_same = 0;
long long x = Search(s, e, 1, n, k, 0);
long long All = sum[0][e];
if (s > 1) {
All -= sum[0][s - 1];
}
long long result = pre_same * x - total + All - total - (e - s + 1 -pre_same) * x;
cout<<result<<endl;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
第二种写法:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_depth = 33;
const int MAX = 100010;
int to_left[MAX_depth][MAX];
int val[MAX_depth][MAX];
long long sum[MAX_depth][MAX];
int s[MAX];
long long sum1[MAX];
/*明白了思想,其实没必要每段都算,其实是给自己制造麻烦,累加即可*/
void Build(int left, int right, int depth) {
if (left == right)return;
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
int same = mid - left + 1;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if (val[depth][i] < s[mid]) {
same--;
}
}
int lc = left, rc = mid + 1;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if ((val[depth][i] < s[mid]) || (val[depth][i] == s[mid] && same > 0)) {
if (val[depth][i] == s[mid])same--;
val[depth + 1][lc++] = val[depth][i];
to_left[depth][i] = to_left[depth][i - 1] + 1;
sum[depth][i] = sum[depth][i - 1] + val[depth][i];
} else {
val[depth + 1][rc++] = val[depth][i];
to_left[depth][i] = to_left[depth][i - 1];
sum[depth][i] = sum[depth][i - 1];
}
}
Build(left, mid, depth + 1);
Build(mid + 1, right, depth + 1);
}
long long left_sum;
int lnum;
int Search(int start, int end, int left, int right, int k, int depth) {
if (left == right) return val[depth][left];
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
int s = to_left[depth][start - 1] - to_left[depth][left - 1];
int e = to_left[depth][end] - to_left[depth][left - 1];
int x = to_left[depth][end] - to_left[depth][start - 1];
int rs = start - left - s; /*[left,start-1]*/
int re = end - left + 1 - e; /*[left,end]*/
if (x >= k) {
return Search(left + s, left + e - 1, left, mid, k, depth + 1);
} else {
lnum += x;
left_sum += sum[depth][end] - sum[depth][start - 1];
return Search(mid + 1 + rs, mid + 1 + re - 1, mid + 1, right, k - x, depth + 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
int T;
while (scanf("%d", &T) != EOF) {
for (int cas = 1; cas <= T; cas++) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < 33; i++) {
sum[i][0] = 0;
to_left[i][0] = 0;
}
sum1[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &val[0][i]);
s[i] = val[0][i];
sum1[i] = sum1[i - 1] + s[i];
}
sort(s + 1, s + n + 1);
Build(1, n, 0);
scanf("%d", &m);
printf("Case #%d:\n", cas);
int s, e;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &s, &e);
s++;
e++;
lnum = 0;
left_sum = 0;
int k = (e - s) / 2 + 1;
long long x = Search(s, e, 1, n, k, 0);
long long all = sum1[e] - sum1[s - 1];
long long res = lnum * x - left_sum + all - left_sum - (e - s + 1 - lnum) * x;
cout<<res<<endl;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_depth = 33;
const int MAX = 100010;
int to_left[MAX_depth][MAX];
int val[MAX_depth][MAX];
long long sum[MAX_depth][MAX];
int s[MAX];
long long sum1[MAX];
/*明白了思想,其实没必要每段都算,其实是给自己制造麻烦,累加即可*/
void Build(int left, int right, int depth) {
if (left == right)return;
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
int same = mid - left + 1;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if (val[depth][i] < s[mid]) {
same--;
}
}
int lc = left, rc = mid + 1;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if ((val[depth][i] < s[mid]) || (val[depth][i] == s[mid] && same > 0)) {
if (val[depth][i] == s[mid])same--;
val[depth + 1][lc++] = val[depth][i];
to_left[depth][i] = to_left[depth][i - 1] + 1;
sum[depth][i] = sum[depth][i - 1] + val[depth][i];
} else {
val[depth + 1][rc++] = val[depth][i];
to_left[depth][i] = to_left[depth][i - 1];
sum[depth][i] = sum[depth][i - 1];
}
}
Build(left, mid, depth + 1);
Build(mid + 1, right, depth + 1);
}
long long left_sum;
int lnum;
int Search(int start, int end, int left, int right, int k, int depth) {
if (left == right) return val[depth][left];
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
int s = to_left[depth][start - 1] - to_left[depth][left - 1];
int e = to_left[depth][end] - to_left[depth][left - 1];
int x = to_left[depth][end] - to_left[depth][start - 1];
int rs = start - left - s; /*[left,start-1]*/
int re = end - left + 1 - e; /*[left,end]*/
if (x >= k) {
return Search(left + s, left + e - 1, left, mid, k, depth + 1);
} else {
lnum += x;
left_sum += sum[depth][end] - sum[depth][start - 1];
return Search(mid + 1 + rs, mid + 1 + re - 1, mid + 1, right, k - x, depth + 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
int T;
while (scanf("%d", &T) != EOF) {
for (int cas = 1; cas <= T; cas++) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < 33; i++) {
sum[i][0] = 0;
to_left[i][0] = 0;
}
sum1[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &val[0][i]);
s[i] = val[0][i];
sum1[i] = sum1[i - 1] + s[i];
}
sort(s + 1, s + n + 1);
Build(1, n, 0);
scanf("%d", &m);
printf("Case #%d:\n", cas);
int s, e;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &s, &e);
s++;
e++;
lnum = 0;
left_sum = 0;
int k = (e - s) / 2 + 1;
long long x = Search(s, e, 1, n, k, 0);
long long all = sum1[e] - sum1[s - 1];
long long res = lnum * x - left_sum + all - left_sum - (e - s + 1 - lnum) * x;
cout<<res<<endl;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}








 本文介绍了一种通过划分树寻找给定区间内能使区间最小和达到最小子序列的方法。通过两个不同实现方式的代码示例详细讲解了算法的构建过程及查询操作。
本文介绍了一种通过划分树寻找给定区间内能使区间最小和达到最小子序列的方法。通过两个不同实现方式的代码示例详细讲解了算法的构建过程及查询操作。
















 1023
1023

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








