
pc 上运行line
With a Windows computer there are several maintenance tasks you should run on a regular basis, though most of us forget. Here’s how to automate the most important maintenance tasks in XP, Vista & Windows 7 and keep your PC running like new.
对于Windows计算机,您应该定期执行几项维护任务,尽管我们大多数人都忘记了。 这是在XP,Vista和Windows 7中自动执行最重要的维护任务,并使PC像新设备一样运行的方法。
We’ll take a look at automating some of the most common tasks, and while it takes a bit of time to set each one up, once you do you’ll have peace of mind knowing your system is clean and up to date.
我们将看一下如何自动化一些最常见的任务,并且设置每个任务都需要一些时间,但是一旦您完成设置,您就可以放心地知道系统是最新的。
自动清理硬盘 (Automate Cleaning Up Your Hard Drive)
If you want to make sure you have plenty of space on your hard drive, and get rid of old files you no longer need, you can schedule Disk Cleanup to run in Windows 7 or Vista, which gets rid of plenty of temporary files and other stuff that doesn’t need to be around anymore.
如果要确保硬盘驱动器上有足够的空间并清除不再需要的旧文件,可以安排磁盘清理在Windows 7或Vista中运行 ,从而清除大量的临时文件和其他文件。不再需要的东西。
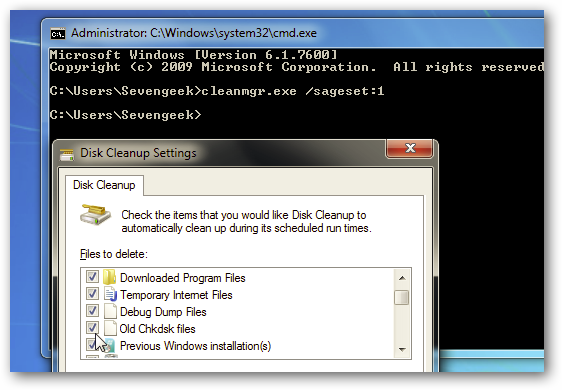
You can setup Disk Cleanup in XP as well as a Scheduled Task. The process is easy following the Scheduled Task Wizard in XP.
您可以在XP中以及“计划任务”中设置“磁盘清理”。 按照XP中的“ 计划任务向导”,此过程很容易。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[15-36-45] sshot-2010-10-03-[15-36-45]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/55f8d8d5ef7d9d109b67491a87cb7b4a.png)
If you really want to keep your system automated, however, you can setup the freeware CCleaner tool to automatically run every night, which will clean up more than just the regular temporary files—CCleaner can even clear out your browser history, applications caches, and more.
但是,如果您确实想使系统保持自动化,则可以将免费软件CCleaner工具设置为每晚自动运行 ,这不仅可以清理常规的临时文件,还可以清理您的浏览器历史记录,应用程序缓存和更多。

Note: you’ll want to make sure that you don’t select any toolbars during CCleaner installation, or get the slim download from the optional downloads section.
注意:您需要确保在CCleaner安装过程中不要选择任何工具栏,或者从可选下载部分中获取苗条下载。
自动化备份以确保数据安全 (Automate Backups to Keep Your Data Secure)
The most important task Windows users need to do is make sure your data is backed up—that way, no matter what happens to your PC, you can always get to your files, even from another PC. If your PC is completely dead, you’ll be able to restore those files onto your new computer and get right back to whatever you were doing.
Windows用户要做的最重要的任务是确保备份数据-这样一来,无论您的PC发生什么情况,您都可以始终从其他PC上获取文件。 如果您的PC完全没电了,您将能够将这些文件还原到新计算机上,并恢复到所做的一切。
Local Backups
本地备份
Windows 7 includes an easy-to-use, wizard-driven Backup & Restore utility in all versions, which includes creating a system image. For more on which files to backup, check out The Geek’s guide to What Files you Should Backup on Your Windows PC.
Windows 7在所有版本中都包含一个易于使用,向导驱动的“ 备份和还原”实用程序 ,其中包括创建系统映像 。 有关要备份哪些文件的更多信息,请参阅《 The Geek's Guide》(《极客指南》), 有关在Windows PC上应备份哪些文件 。
![sshot-2010-09-30-[15-44-13] sshot-2010-09-30-[15-44-13]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/3ac1c34db63fae3eec414147445d2ab9.png)
The Backup & Restore utility included in Windows 7 allows you to set a schedule from daily, weekly, or monthly. The choice is up to you, but if you backup on a regular basis, you’ll be glad you did.
Windows 7中包含的“备份和还原”实用程序使您可以设置每天,每周或每月的时间表。 选择取决于您,但是如果您定期进行备份,您会很高兴的。
![sshot-2010-09-30-[15-44-59] sshot-2010-09-30-[15-44-59]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/82b313ce5e7bea58361cdb875076386c.png)
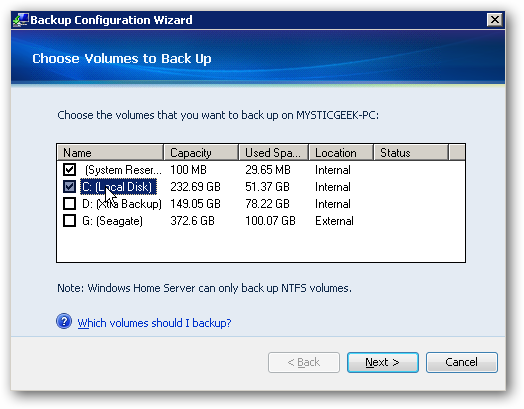
If you have Windows Home Server, backing up your computers is very easy to configure and automate. You can set it to backup on a regular schedule and also have WHS wake up your machine to back it up at night.
如果您有Windows Home Server,则备份和配置计算机非常容易 。 您可以将其设置为定期备份,也可以让WHS唤醒计算机以在晚上进行备份。
Online Backup Services
在线备份服务
If you want to be really thorough with in your backup strategy, having redundant backups onsite and offsite is a good thing. There’s plenty of commercial backup services, like Mozy and Carbonite. They both work the same way, pushing your data up to their servers and making it available for download from another PC, or allowing you to restore individual files that you might have deleted.
如果您想在备份策略中做到周全,那么在现场和非现场进行冗余备份是一件好事。 有很多商业备份服务,例如Mozy和Carbonite 。 它们的工作方式相同,将数据推送到其服务器上并可以从另一台PC下载,或者允许您还原可能已删除的单个文件。

自动进行磁盘碎片整理,以使驱动器保持平稳运行 (Automate Disk Defrag to Keep Your Drive Running Smooth)
The cool thing with Vista and Windows 7 is that Disk Defragmenter is scheduled to run by default at 1 AM every Wednesday, so it’s something you no longer have to deal with. You can customize the defragmenter schedule if you want, but there’s probably no reason to change it.
Vista和Windows 7的好处是,默认情况下,磁盘碎片整理程序计划在每个星期三的凌晨1点运行,因此您无需再处理此问题。 您可以根据需要自定义碎片整理程序时间表 ,但是可能没有理由对其进行更改。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[16-00-35] sshot-2010-10-03-[16-00-35]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/188dcb4a39aae32b0e2502a0989d645a.png)
If you’re still on Windows XP you can get the same feature by creating your own Windows 7 style auto defrag using Task Scheduler. There’s no reason to have to remember to do it manually, and really no reason to waste money on a commercial defrag utility that does it automatically when you can set it up yourself.
如果您仍在使用Windows XP,则可以通过使用Task Scheduler 创建自己的Windows 7样式自动碎片整理功能来获得相同的功能。 没有理由要记住手动进行操作,也没有理由浪费金钱在可以自行设置的自动碎片整理实用程序上。
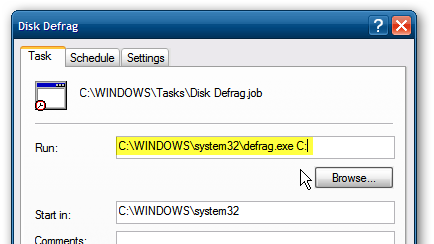
If you’ve got multiple hard drives in your XP machine, you can also setup a batch file that will defragment multiple hard drives at once.
如果您的XP机器中有多个硬盘驱动器,则还可以设置一个批处理文件,该文件将立即对多个硬盘驱动器进行碎片整理 。
自动检查磁盘 (Automate Disk Checking)
The chkdsk.exe utility in Windows allows you to scan your hard drive for errors and fix them as well, and this task can be automated with the command-line and Task Scheduler as well, though it’s going to require rebooting your PC in order for it to work, so it’s probably best to just trigger this one manually every so often.
Windows中的chkdsk.exe实用程序允许您扫描硬盘驱动器中的错误并进行修复,该任务也可以通过命令行和Task Scheduler自动执行,尽管这将需要重新引导PC才能解决。它可以正常工作,因此最好是每隔一段时间手动触发一次。
If you do want to schedule it to run automatically, you can simply create a new Task Scheduler job that runs chkdsk.exe with the parameters from our guide to check disk.
如果确实要计划它自动运行,则可以简单地创建一个新的Task Scheduler作业 ,并使用我们指南中的参数运行chkdsk.exe 来检查disk 。
Then go to the Actions tab of the job in Task Scheduler, and add another action to run after the chkdsk command, and specify shutdown as the command. This will run the chkdsk command, and then run a shutdown afterwards. Make sure to use /R as the argument so that Windows will reboot and run chkdsk, and not just shut down.
然后转到任务计划程序中作业的“操作”选项卡,并添加另一个要在chkdsk命令之后运行的操作,并指定shutdown作为该命令。 这将运行chkdsk命令,然后再运行关机。 确保使用/ R作为参数,以便Windows重新启动并运行chkdsk,而不仅仅是关闭。
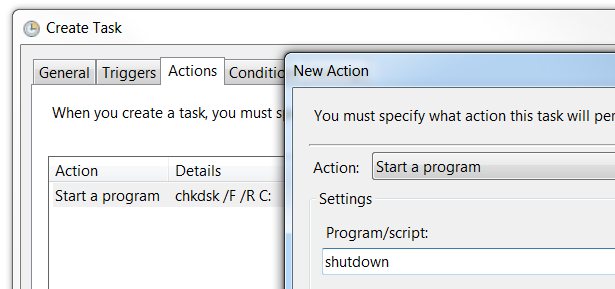
You may also want to check the box to make sure that Windows doesn’t reboot you while you’re doing something. You can head to the Conditions tab, and make it only start if the PC has been idle for a while.
您可能还需要选中该复选框,以确保Windows在执行某项操作时不会重新引导您。 您可以转到“条件”选项卡,并使其仅在PC闲置了一段时间后才能启动。
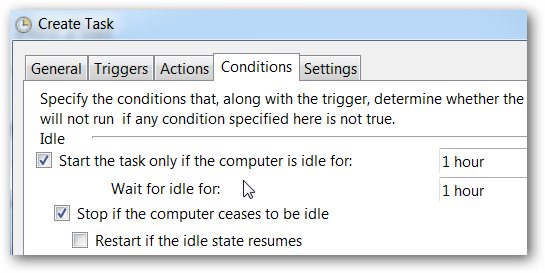
Note: Windows will automatically detect when your drive has a lot of problems and prompt you to check the disk, but that doesn’t mean running it manually is a bad idea once in a while.
注意: Windows会自动检测驱动器何时有很多问题,并提示您检查磁盘,但这并不意味着手动运行它偶尔会是个坏主意。
To manually trigger a disk check for the next time you reboot, right-click on your local drive and select Properties. Then select the Tools tab and under Error-checking, click on the Check now button.
要在下次重启时手动触发磁盘检查,请右键单击本地驱动器,然后选择“属性”。 然后选择“工具”选项卡,在“错误检查”下,单击“立即检查”按钮。
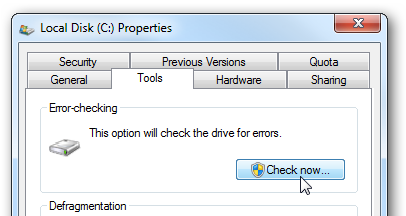
Make sure to select both Check disk options, and click Start.
确保选择两个Check disk选项,然后单击Start。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[17-53-58] sshot-2010-10-03-[17-53-58]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/1c1948cab7864dabb2e82c88b9d61a12.png)
Unfortunately it can’t start while you’re using your PC, but you can schedule it to run during next restart.
不幸的是,它在您使用PC时无法启动,但是您可以安排它在下次重新启动时运行。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[17-54-10] sshot-2010-10-03-[17-54-10]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/0e7e8110efcd6ba874d411605409d6dd.png)
The next time your machine is restarted, Check Disk will run and detect and fix errors automatically. Keep in mind this process can take quite a while depending on the size of your drive and the amount of data on it. For more, check out The Geek’s guide to Check Disk in Windows.
下次重新启动计算机时,“检查磁盘”将运行并自动检测并修复错误。 请记住,此过程可能需要花费相当长的时间,具体取决于驱动器的大小和驱动器上的数据量。 有关更多信息,请查看The Geek's Guide to Check Disk in Windows 。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[18-58-22] sshot-2010-10-03-[18-58-22]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/c899bfd749f2e33323202bd7f0bf6758.png)
自动化Windows更新以使您的PC保持补丁状态 (Automate Windows Updates to Keep Your PC Patched)
Although it should go without saying, an important task you can make run automatically is Windows Updates. You can configure Important and Recommended updates to download and install automatically, or just download and you choose which ones to install.
尽管应该说,Windows Updates是可以自动运行的重要任务。 您可以将重要更新和推荐更新配置为自动下载并安装,或者仅下载并选择要安装的更新。
For more, check out how to make Windows 7 Update display recommended and important updates.
有关更多信息,请查看如何使Windows 7 Update显示推荐的重要更新 。
![sshot-2010-10-01-[00-21-50] sshot-2010-10-01-[00-21-50]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/79d81d73a5b13c3b8356632cf3be9afa.png)
自动执行防病毒检查定义和扫描计算机 (Automate Antivirus to Check Definitions & Scan Your Computer)
Another important security task is making sure your Antivirus protection is up to date and runs automatically. Each program is different, but most provide the option to keep definition files up to date and scan automatically. For instance it’s easy to setup in our favorite Microsoft Security Essentials.
另一个重要的安全任务是确保防病毒保护是最新的并自动运行。 每个程序都不同,但是大多数程序提供了使定义文件保持最新并自动扫描的选项。 例如,可以很容易地在我们最喜欢的Microsoft Security Essentials中进行设置。
Note: of course, most anti-virus applications are set to automatically update their virus definition files, but you should double-check to make sure.
注意:当然,大多数防病毒应用程序都设置为自动更新其病毒定义文件,但是您应仔细检查以确保安全。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[21-03-45] sshot-2010-10-03-[21-03-45]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/d0675cbf7adb15692dcac36fe07583c2.png)
Anti-Spyware
反间谍软件
If you’re using another Antimalware utility to compliment your Antivirus software, make sure it’s set to find its latest definition files and scan automatically. Keep in mind though, with most of the free versions of Antispyware apps, you’ll need to purchase a license to get real-time protection, automatic updates, and scanning.
如果您使用另一个Antimalware实用程序来补充Antivirus软件,请确保已将其设置为查找其最新的定义文件并自动进行扫描。 不过请记住,使用大多数免费版本的Antispyware应用程序,您需要购买许可证才能获得实时保护,自动更新和扫描。
自动使驱动程序和第三方软件保持最新 (Automatically Keep Drivers and 3rd-Party Software Up to Date)
Another important task to automate is checking for the latest hardware driver and other app updates. There are a few good programs that will do it which we’ve previously covered such as Secunia Personal Software Inspector. It will automatically check for software updates at startup and provides continuous monitoring.
自动化的另一个重要任务是检查最新的硬件驱动程序和其他应用程序更新。 有一些很好的程序可以做到这一点,例如Secunia Personal Software Inspector ,我们以前已经介绍过。 它会在启动时自动检查软件更新,并提供连续监视。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[21-44-00] sshot-2010-10-03-[21-44-00]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/d15812af7bdcc455564457f5e515748b.png)
To automatically keep your hardware drivers up to date, try a program such as Device Doctor, Slimdrivers, or any of the other non-free utilities out there. They will complete driver scans and make sure that your drivers are updated.
要自动使您的硬件驱动程序保持最新,请尝试使用诸如Device Doctor,Slimdrivers或其他任何非免费实用程序之类的程序。 他们将完成驱动程序扫描,并确保您的驱动程序已更新。
![sshot-2010-10-03-[23-23-56] sshot-2010-10-03-[23-23-56]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/a87d03c3bc426ee35e93e6446b748f55.png)
Note: One thing to keep in mind with Device Doctor (or really any application) during installation is to skip installing the worthless Ask Toolbar.
注意:在安装过程中使用Device Doctor(或实际上是任何应用程序)要记住的一件事是跳过安装毫无用处的Ask工具栏。
This guide should definitely get you started in figuring out which maintenance tasks you want to setup to run automatically. While there certainly seems to be a lot to keep up with if you’re a Windows user, setting tasks to run automatically will free up some time so you get get to work and get things done.
该指南绝对可以帮助您确定要设置为自动运行的维护任务。 如果您是Windows用户,当然还有很多工作要做,但是将任务设置为自动运行将节省一些时间,因此您可以开始工作并完成工作。
What about you guys? What Tasks do you set up to run automatically and what methods do you use? Leave a comment below and lets us know!
你们呢? 您将哪些任务设置为自动运行,并使用了哪些方法? 在下面发表评论,让我们知道!
pc 上运行line




 本文指导如何在Windows系统中自动执行常见的维护任务,包括磁盘清理、备份、磁盘碎片整理、磁盘检查、Windows更新、防病毒扫描及软件更新,以保持系统高效稳定。
本文指导如何在Windows系统中自动执行常见的维护任务,包括磁盘清理、备份、磁盘碎片整理、磁盘检查、Windows更新、防病毒扫描及软件更新,以保持系统高效稳定。
















 1030
1030

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








