If you work a lot in the command line, you probably keep more than one Terminal window open at once. However, instead of having separate windows, you can condense all your Terminal sessions onto one window using tabs.
如果您在命令行中进行了大量工作,则可能一次打开多个“终端”窗口。 但是,您可以使用选项卡将所有终端会话浓缩为一个窗口,而不是使用单独的窗口。
We’ll show you how to open multiple Terminal sessions as tabs in Ubuntu.
我们将向您展示如何在Ubuntu中将多个终端会话作为选项卡打开。
To begin, open a Terminal window and select “Preferences” from the “Terminal” menu. The menu bar may either be on the title bar of the Terminal window or on the top panel on the desktop, depending on whether global menus are enabled in Ubuntu.
首先,打开一个终端窗口,然后从“终端”菜单中选择“首选项”。 菜单栏可能位于“终端”窗口的标题栏上,也可能位于桌面的顶部面板上,具体取决于是否在Ubuntu 中启用了全局菜单 。
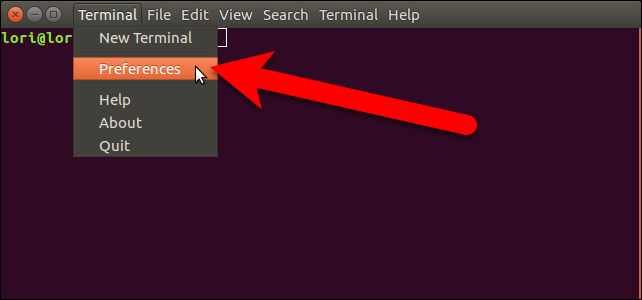
On the Preferences dialog box, make sure the General tab is active. Then, select “Tab” from the “Open new terminals in” drop-down list.
在“首选项”对话框中,确保“常规”选项卡处于活动状态。 然后,从“打开新终端”下拉列表中选择“制表符”。
Click “Close” to accept the change and close the Preferences dialog box.
单击“关闭”接受更改,然后关闭“首选项”对话框。

To open a new Terminal session on a new tab, select “New Terminal” from the “Terminal” menu.
要在新选项卡上打开新的终端会话,请从“终端”菜单中选择“新终端”。
A second Terminal session is opened on a new tab and the original session is also available on a tab. The name on the tab includes the current directory you’re in on that tab.
在新选项卡上打开第二个终端会话,并且在选项卡上也可以使用原始会话。 选项卡上的名称包括您在该选项卡上的当前目录。
NOTE: Even when the Open new terminals in option is set to Tab, pressing Ctrl+Alt+T opens a new Terminal session in a new window, not a new tab.
注意:即使将“在以下位置打开新终端”选项设置为“选项卡”,按Ctrl + Alt + T也会在新窗口而不是新选项卡中打开新的终端会话。
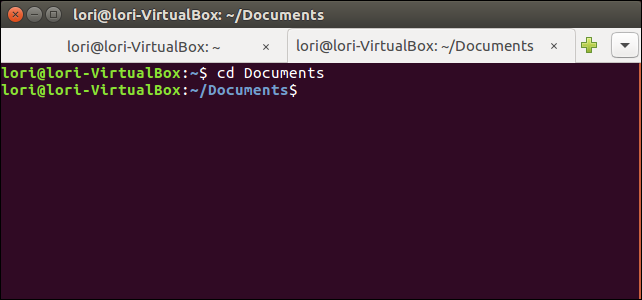
Once you have two sessions open, you can open additional sessions using plus button to the right of the tabs.
打开两个会话后,可以使用选项卡右侧的加号按钮打开其他会话。
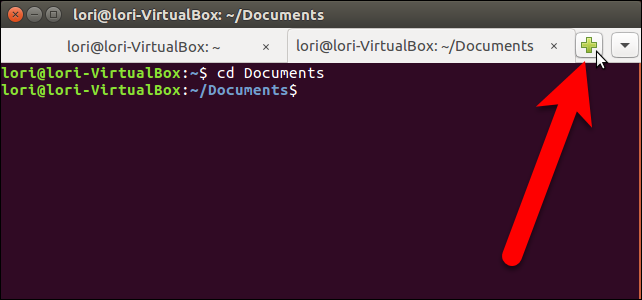
When you add a new tab, whether it be through the Terminal menu or using the plus button, the new session is open to the same directory you were in on the tab that was currently active at that time.
当您添加新选项卡时,无论是通过“终端”菜单还是使用加号按钮,新会话都将打开到您当时处于活动状态的选项卡上的同一目录。
There are several ways to switch among tabs. You can click on a tab to activate it, of course. You can also use the down arrow button on the far right to select the session you want or press Alt+1, Alt+2, etc. on your keyboard to jump to a specific tab. The tabs are numbered from the left, starting at 1.
有几种在选项卡之间切换的方法。 当然,您可以单击选项卡将其激活。 您也可以使用最右边的向下箭头按钮选择所需的会话,或按键盘上的Alt + 1,Alt + 2等以跳到特定选项卡。 这些选项卡从左侧开始编号,从1开始。
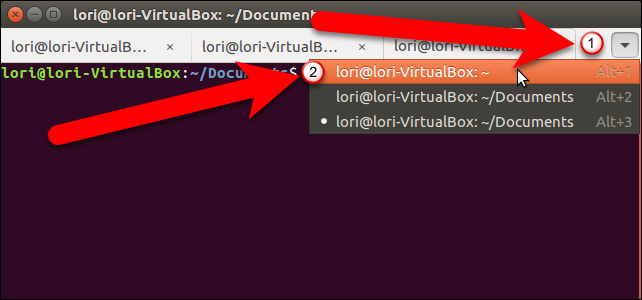
If you want change the order of the tabs, you can click on a tab and drag it to another location on the tab bar. When you move tabs, they’re renumbered, so using the Alt+1, Alt+2 keyboard shortcuts to switch among the tabs will account for the new tab order. For example, if you move the third tab to the second position, Alt+2 would then activate what used to be the third tab.
如果要更改选项卡的顺序,可以单击选项卡并将其拖动到选项卡栏上的其他位置。 移动选项卡时,它们会重新编号,因此使用Alt + 1,Alt + 2键盘快捷键在各选项卡之间切换将说明新的选项卡顺序。 例如,如果将第三个选项卡移动到第二个位置,则Alt + 2将激活以前的第三个选项卡。
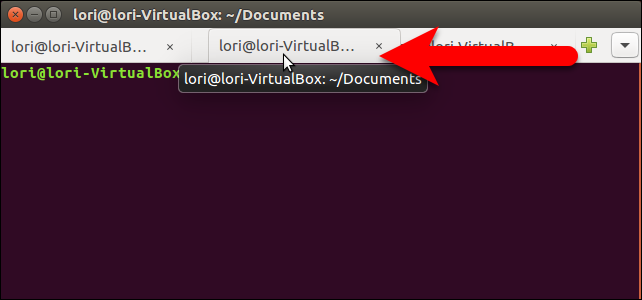
To close a tab, click the “X” button on the right side of the tab.
要关闭选项卡,请单击选项卡右侧的“ X”按钮。
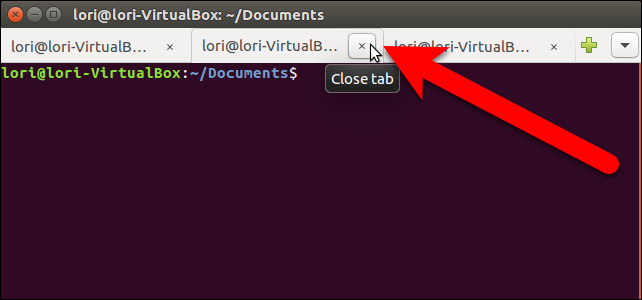
You can also move and close tabs by right-clicking on a tab and selecting an option from the popup menu.
您还可以通过右键单击选项卡并从弹出菜单中选择一个选项来移动和关闭选项卡。
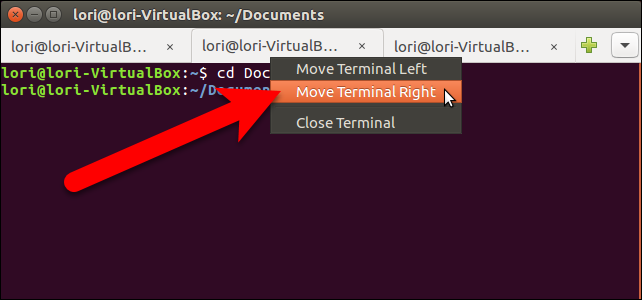
To close the Terminal window, and all the tabs, click the “X” button in the upper-left corner of the window.
要关闭“终端”窗口和所有选项卡,请单击窗口左上角的“ X”按钮。
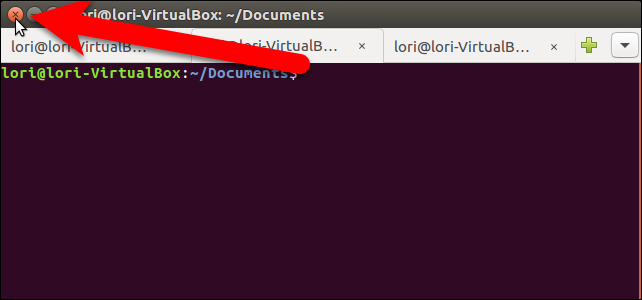
The tabs are not saved when you close the Terminal window. However, the Open new terminals in setting is preserved and you can open multiple sessions on tabs the next time you open a Terminal window.
关闭“终端”窗口时,不会保存这些选项卡。 但是,将保留“在以下位置打开新终端”设置,并且下次打开“终端”窗口时,可以在选项卡上打开多个会话。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/267348/how-to-add-tabs-to-ubuntus-terminal/




 本文介绍如何在Ubuntu系统中使用选项卡功能管理多个终端会话,包括设置、切换、移动和关闭选项卡的方法。
本文介绍如何在Ubuntu系统中使用选项卡功能管理多个终端会话,包括设置、切换、移动和关闭选项卡的方法。
















 587
587

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








