🐕给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
说明:
必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
尽量减少操作次数。
🐇思路一:双指针
slow指针一开始在0位置、fast指针在1位置
slow总是停到 数为0的位置 fast总是停到 数不为0的位置 且 在slow之后
此时如果两个指针都不越界 ,交换两个指针对应的值,都自增
上代码
public static void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length < 2) {
return;
}
int slow = 0;
int fast = 1;
while(slow != fast && slow < nums.length && fast < nums.length) {
while(slow < nums.length && nums[slow] != 0) {
slow ++;
}
//此时slow 要不是在 数为0的位置 要不就是在末尾
while(fast < nums.length && (fast <= slow || nums[fast] == 0)) {
fast ++;
}
//此时fast 要不是在 数不为0的位置 要不就是在末尾
if(slow < nums.length && fast < nums.length) {
if(slow == fast ) {
break;
}else {
nums[slow] = nums[slow] ^ nums[fast];
nums[fast] = nums[slow] ^ nums[fast];
nums[slow] = nums[slow] ^ nums[fast];
slow++;
fast++;
}
}
}
}
虽然能过但还是挺麻的
🐇思路二:
遍历数组 把 不等于0 的顺序排在前面,最后如果index不越界 把index后面的数归零
上代码
public static void moveZeroes2(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
}
int index = 0;
//遍历数组 把 不等于0 的顺序排在前面
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] != 0) {
nums[index++] = nums[i];
}
}
//最后如果index不越界 把index后面的数归零
while(index < nums.length) {
nums[index++] = 0;
}
}
🐇思路三:
双指针的思路解决
指针j是一直往后移动的,如果指向的值不等于0才对他进行操作。
而 index 统计的是前面 0 的个数,我们可以把 j-index 看做另一个指针
它是指向前面第一个0的位置,然后我们让j指向的值和j-index指向的值交换
上代码
public static void moveZeroes3(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
}
int index = 0;//用来记录 值为0 的个数
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i]==0) {//当为0 index自增
index++;
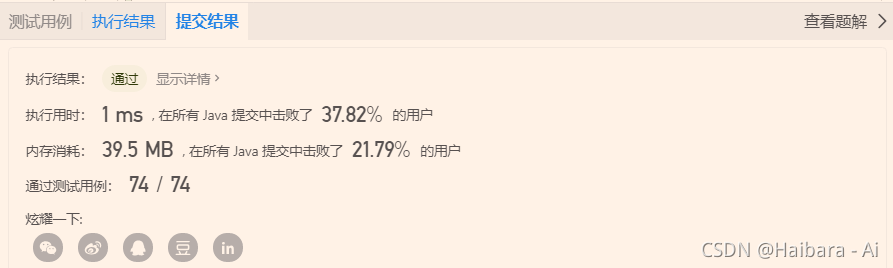
}else if(index != 0){//不为0 开始替换 i-index就是第一个为0的位置
nums[i-index] = nums[i];
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
}






















 815
815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








