稍微下拉,左端目录栏检索命令
查看目录下文件 ls
ls [-a -l -h] [路径] -a(全部) -l(细节) -h(大小)
ls
ls /
ls -a
ls -l
ls -h
ls -alh
ls -l -h -a
ls -lah /
切换目录 cd
cd [路径] change directory
. 当前目录 .. 上一级目录 ~ HOME目录
cd /
cd
cd ..
cd ~
cd ~/Desktop 等价于 cd /home/itheima/Desktop
cd ../..
cd Desktop
cd ./Desktop
cd ../test/hello.txt打印当前路径 pwd
pwd print work deirectory
pwd创建目录(文件夹) mkdir
mkdir [-p] Linux路径 make directory
-p 创建不存在的父目录,适用于创建连续多层级的目录
ls
mkdir itheima
ls
mkdir /home/itheima/test
ls
mkdir ./test2
ls
mkdir ~/test4
ls
mkdir -p itcast/good/666
cd itcast/good/666
pwd
问:Centos里,/root和/home/itheima有什么区别,为什么/root下无法用mkdir创建目录,而/home/itheima可以?
答
在CentOS系统中,/root 和 /home/itheima 都是目录路径,但在系统中的用途有所不同。
/root 目录是Linux系统中超级用户(root用户)的主目录,也就是root用户的家目录。这个目录只有超级用户才有写权限,普通用户无法在该目录下创建新的文件夹或文件。
/home/itheima 目录是普通用户 "itheima" 的主目录,这个目录是用来存储普通用户的个人数据的,包括文档、图片、视频等等。普通用户可以在该目录下创建新的文件夹或文件,但是无法更改其他用户的主目录。
因此,/root 和 /home/itheima 的权限和用途是不同的。对于/root目录,只有超级用户才能访问和操作;而对于/home/itheima目录,则是普通用户的专属目录,普通用户对其有写权限
创建文件 touch
touch Linux路径
ls
touch test.txt
ls查看文件内容 cat
cat Linux路径
ls
cat test.txt
more Linux路径
more支持翻页,文件内容过多,可以一页页展示
复制文件 cp
cp [-r] 参数1 参数2 copy
-r 复制文件夹使用,表示递归
参数1 Linux路径 被复制的文件
参数2 Linux路径 复制到的文件
ls
cp test.txt test2.txt
cat test2.txt
cp -r itheima itheima2
ls移动文件 mv
mv 参数1 参数2 move
参数1 Linux路径 被移动的文件(夹)
参数2 Linux路径 移动到的地方 如果目标不存在,则进行改名,确保存在
ls
mv test.txt Desktop
ls Desktop
mv test2.txt test3.txt
ls
ls
mv test2 Desktop
ls Desktop删除文件 rm
rm [-r -f] 参数1 参数2 ... 参数N remove
同cp,-r 用于删除文件夹
-f 表示 force,强制删除(不弹出提示确认信息)
-- 普通用户删除内容不会弹出提示,只有root管理员用户删除内容会提示
-- 所以普通用户用不到 -f 选项
参数1 ~ N 表示要删除的路径,空格分隔
ls
rm test3.txt
(y确认 n取消)
ls
ls
rm -r test3
ls
rm -r test4 itheima itheima2 itcast
ls
rm 命令支持 * 表示通配符
test* 表示test开头的内容
*test 表示test结尾的内容
*test* 表示任何包含test的内容
ls
rm -r test*
ls
touch 1test
touch 2test
touch 3test
rm -f *test
ls
touch 1test2
touch 2test3
touch 3test4
ls
rm -f *test*
ls通过 su - root
查找命令所在文件 which
Linux命令,本质就是二进制可执行程序,类似Windows的.exe文件。
which 命令
which cd
which pwd
which ...查找指定文件 find
(1)find 起始路径 -name "被查找文件名"
find / -name "test"
find / -name "test*"
find / -name "*test"
find / -name "*test*"(2)find 起始路径 -size +/- n[kMG]
+ / - 表示大于 / 小于
n 表示大小的数字
kMG 表示大小的单位,k表示kb,M表示MB,G表示GB
find / -size -1k
find / -size +1G
find / -size +100M
ls -lh /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive👆ctrl + c 强制中断搜索
过滤文件内容 grep
grep [-n] 关键字 路径
提示:当不写路径时,可用管道符左边命令所产生的内容,作为内容的输入
-n,显示被匹配内容的行号
参数,关键字,表示过滤的关键字,带有空格或其他特殊符号,一般用""包起来
参数,路径,可作为内容输入端口
finalshell,~目录下,touch test.txt
然后Centos7图形化界面中,打开home文件夹,在test.txt中添加内容👇
itheima is shabi.
itcast code is 003032cat test.txt
grep "itheima" test.txt
grep "itcast" test.txt
grep -n "code" test.txt统计内容数量 wc
wc [-c -m -l -w] 路径
提示:当不写路径时,可用管道符左边命令所产生的内容,作为内容的输入
-c bytes数量
-m 字符数量
-l 行数
-w 单词数量
参数,路径,可作为内容输入端口
wc test.txt
wc -c test.txt
wc -m test.txt
wc -l test.txt
wc -w test.txt管道符 |
shift + | 即可输出 |
管道符左边命令的结果,作为右边命令的输入
只要能产生内容输出的命令,都可以放管道符左边,作为右边命令的输入
cat test.txt | grep itheima
cat test.txt | wc -l
ls | grep test
ls /usr/bin
ls /usr/bin | grep gtf
ls -l /usr/bin | grep gtf
ls -l /usr/bin | wc -l
cat test.txt | grep itcast
cat test.txt | grep itcast | grep code
cat test.txt | grep itcast | wc -l
cat test.txt | grep itheima | wc -w输出内容 echo
echo 输出的内容
带有空格或 \ 等特殊符号,建议用 "" 包起来,防止空格后被识别为参数
echo Hello World
echo "Hello World"反引号 ` `
`` 被 `` 包围的内容,作为命令执行,而非普通字符
echo pwd
echo `pwd`重定向符 > >>
> 左侧命令结果,覆盖右侧文件
>> 左侧命令结果,追加到右侧文件
只要能产生内容的命令,都能往重定向符右侧写
ls
cat test.txt
echo "hello linux" > test.txt
cat test.txt
echo "sha bi ni shi" >> test.txt
cat test.txt
ls
ls > test.txt
cat test.txt查看文件尾部 tail
tail [-f -num] 路径
-f,表示持续跟踪,此时复制标签,新开一个centos,追加到文件的内容会实时显示,ctrl + c停止跟踪
-num,表示查看尾部多少行,默认10行,num是具体数字
ls
ls > test.txt
ls / >> test.txt
cat test.txt
tail test.txt
tail -f test.txt
(新开一个centos)----
echo "hello shabi"
----
(ctrl + c)
tail -3 test.txt
echo "我当前的工作目录是:"`pwd` > work.txt
cat work.txt
echo "我当前的工作目录是:`pwd`">> work.txt
cat work.txt
tail -f work.txt
echo "sha bi zai na li" >> work.txt
...vi / vim 编辑器
vi 路径
OR
vim 路径
文件不存在会编辑新文件,存在则编辑已有文件
Linux系统中的编辑器,类似于图形界面中的文本编辑器(比如记事本)
vim 是 vi 的加强版本,兼容 vi 所有指令,且具有 shell 程序编辑的功能,提供不同颜色字体
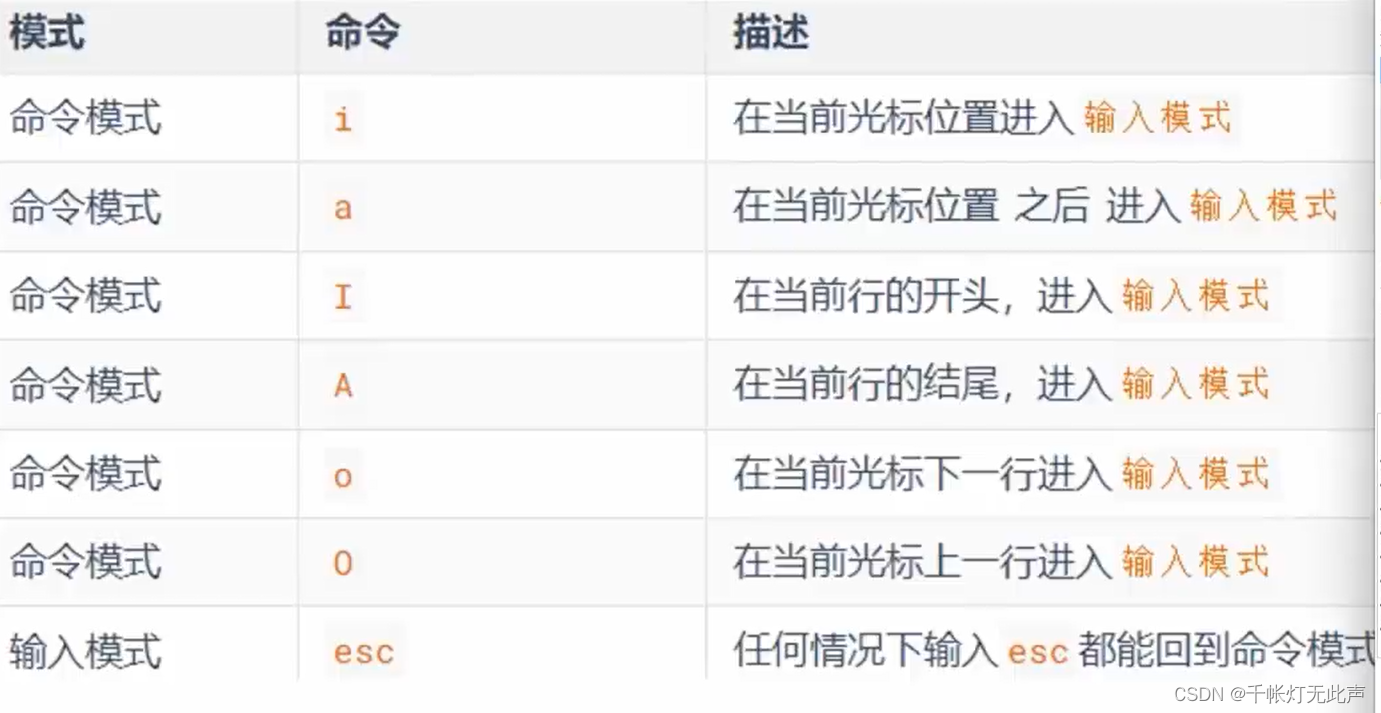
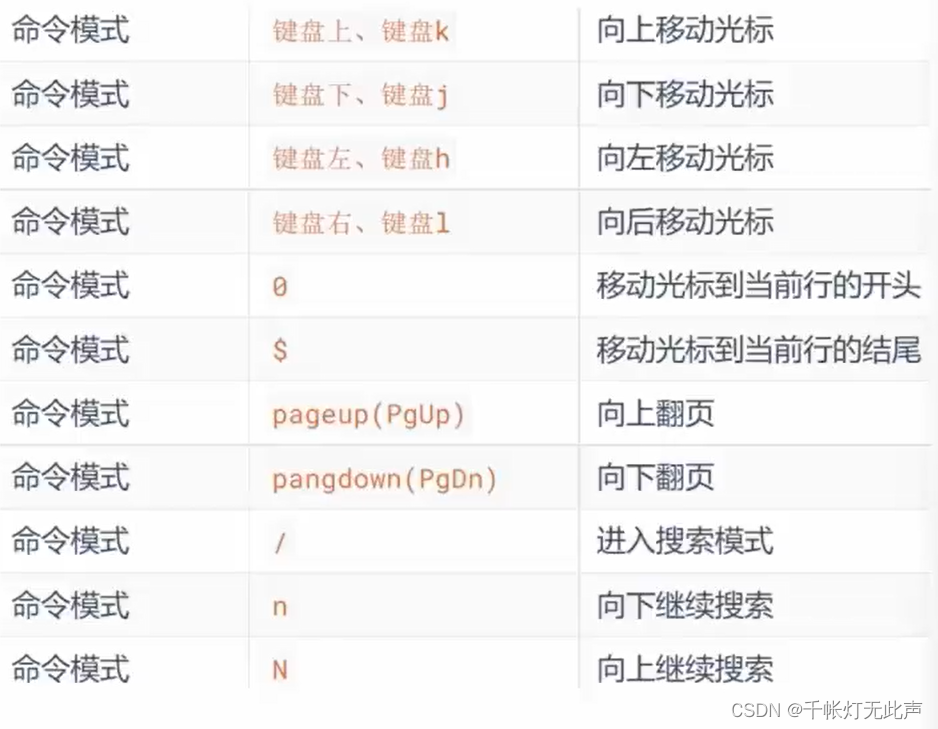
三种工作模式
(1)命令模式(Command mode)
键盘上敲的按键,作为命令,不能自由进行文本编辑(比如连按2下d删除一行)
(2)输入模式(Insert mode)
所谓的 编辑模式,插入模式,可对文本自由编辑(敲的字符串会在屏幕显示)
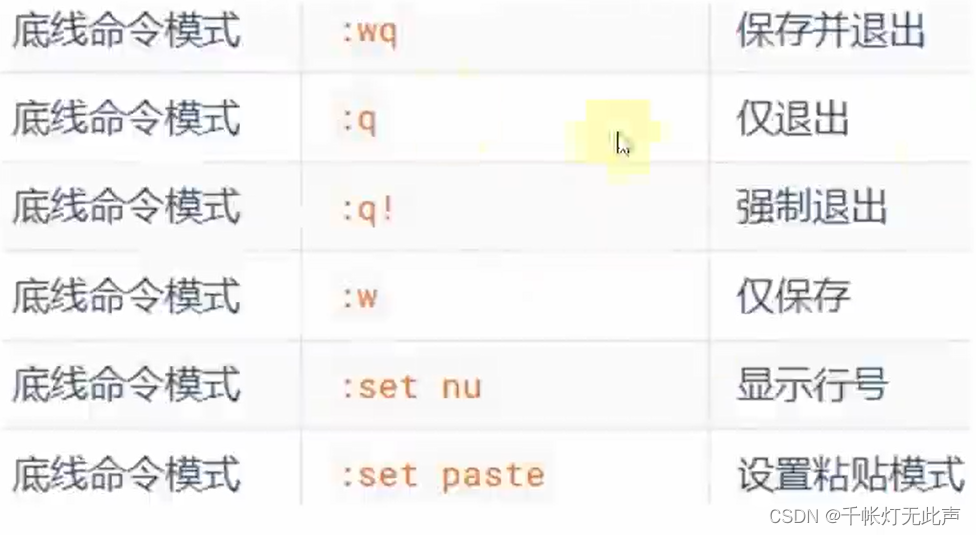
(3)底线命令模式(Last line mode)
以 : 开始,用于文件保存,退出
命令模式作为中转
vim hello.txt
进入命令模式
按 i 键进入输入模式
输入:itheima and itcast.
按 esc 键回到命令模式
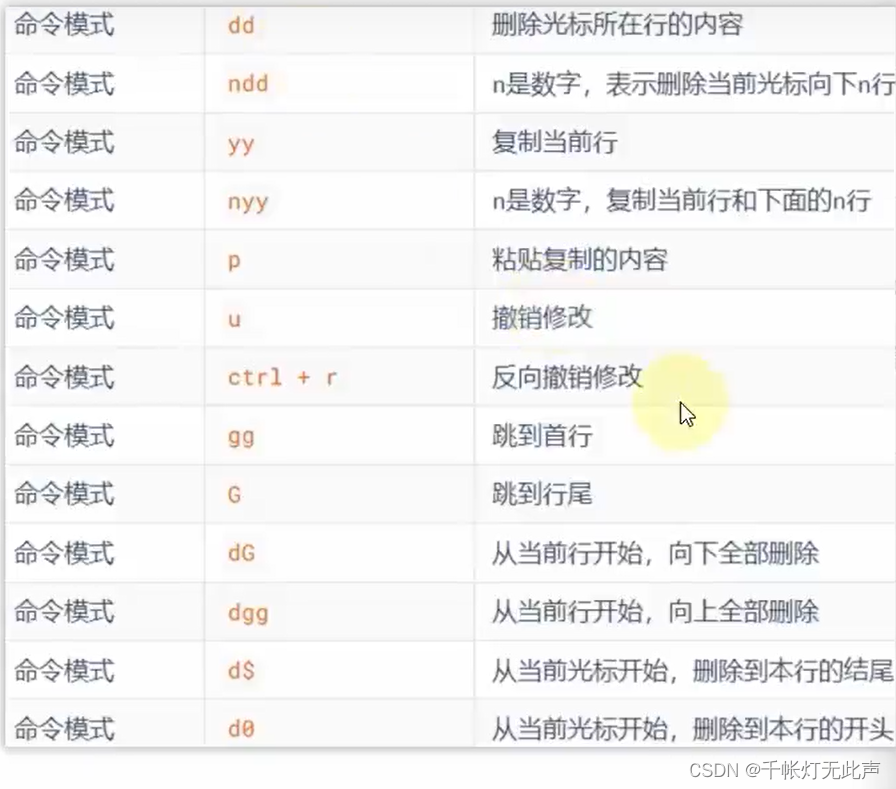
(输入模式下,通过键盘快捷键,修改文件内容)
按yyp复制多一行
按dd删除一行
按u撤销一步
命令模式下按 : 进入底线命令模式
w 保存 q 退出
:wq (回车) 保存并退出
ls
cat hello.txt(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
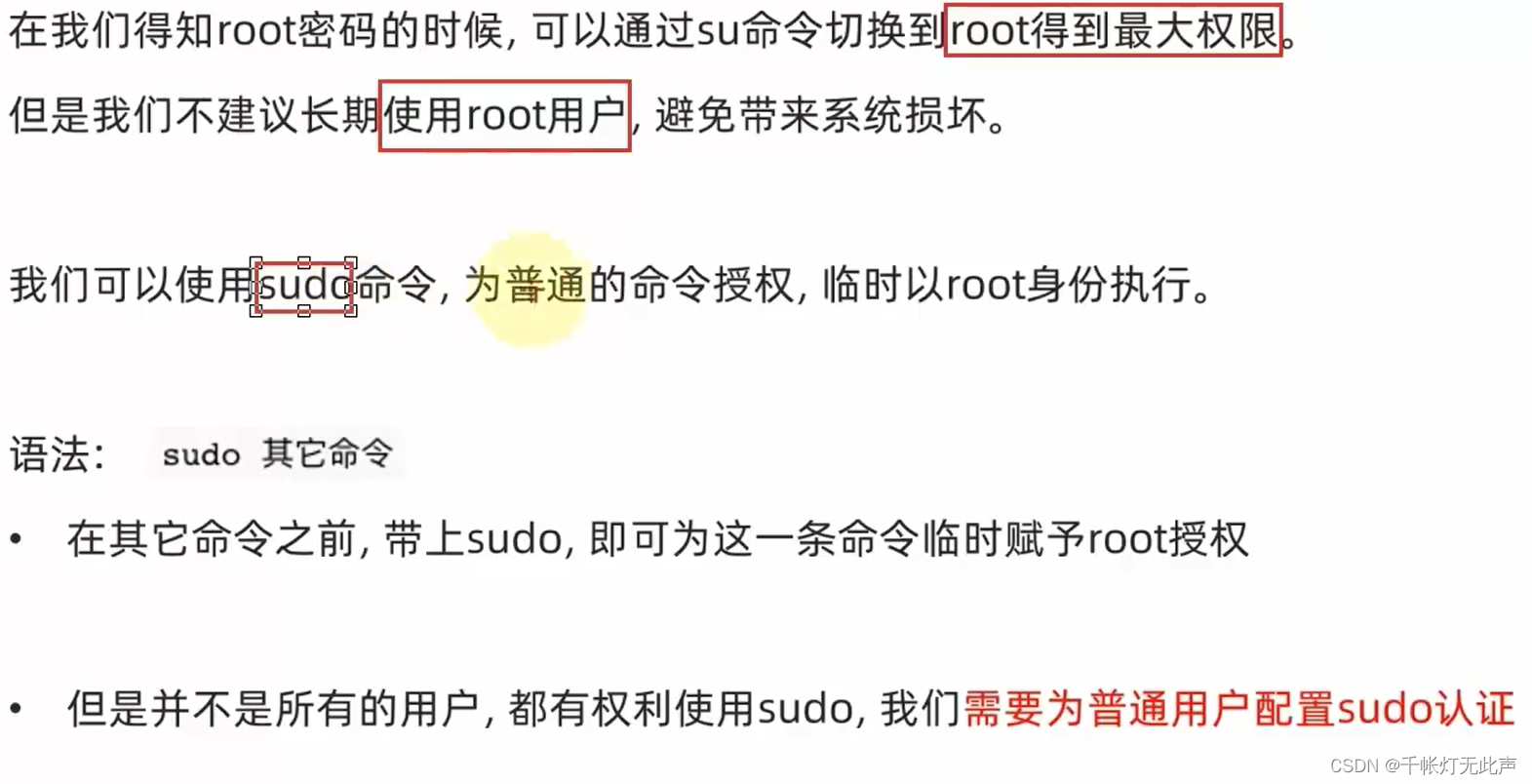
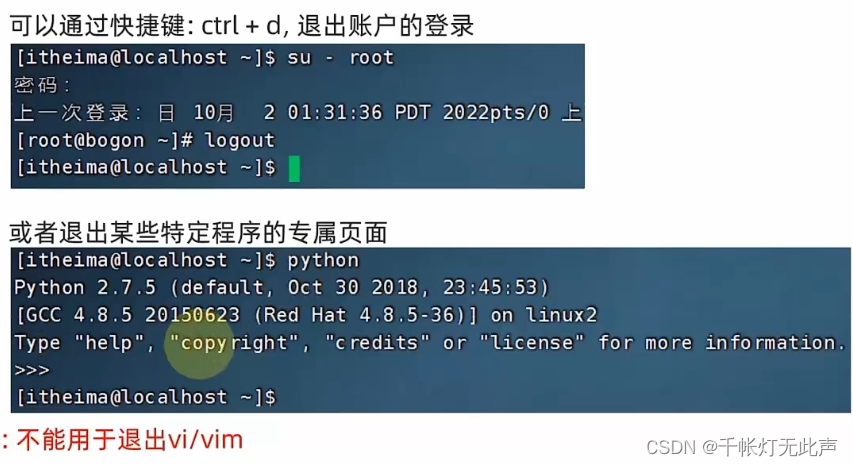
切换用户 su
su
sudo
[itheima@localhost /]$ mkdir jiujiu
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘jiujiu’: Permission denied
普通用户 itheima 的权限,只能在自己目录下创建文件夹,无法在其他目录下创建,除非切换到root权限👇
用户组 and 用户
Linux权限管控的单元,是用户级别和用户组级别
groupadd 用户组名 创建
groupdel 用户组名 删除
useradd [-g -d] 用户名 创建
-g指定组,不指定-g,则创建同名组加入
-d指定用户HOME路径,不指定则默认HOME目录在 /home/用户名
useradd test
id test
cd /home
ll
useradd test2 -g itcast -d /home/test222
su -test2
pwduserdel [-r] 用户名 删除
-r删除用户HOME目录
logout
userdel test2
cd /home
ls
rm -rf test222
ls
userdel -r test
lsid [用户名] 查看所属组
id
useradd test3 -g itcast
su - test3
id
exit
id test3usermod -aG 用户组名 用户名 修改所属组
useradd test4
id test4
usermod -aG itcast test4
id test4getent passwd 查看所有用户
共7份信息:
用户名 : 密码(x) : 用户ID : 组ID : 描述信息(无用) : HOME目录 : 执行终端(默认bash)
getent group 查看所有用户组
共3份信息:
组名称 : 组认证(x) : 组ID
权限控制信息
修改权限 chmod chown
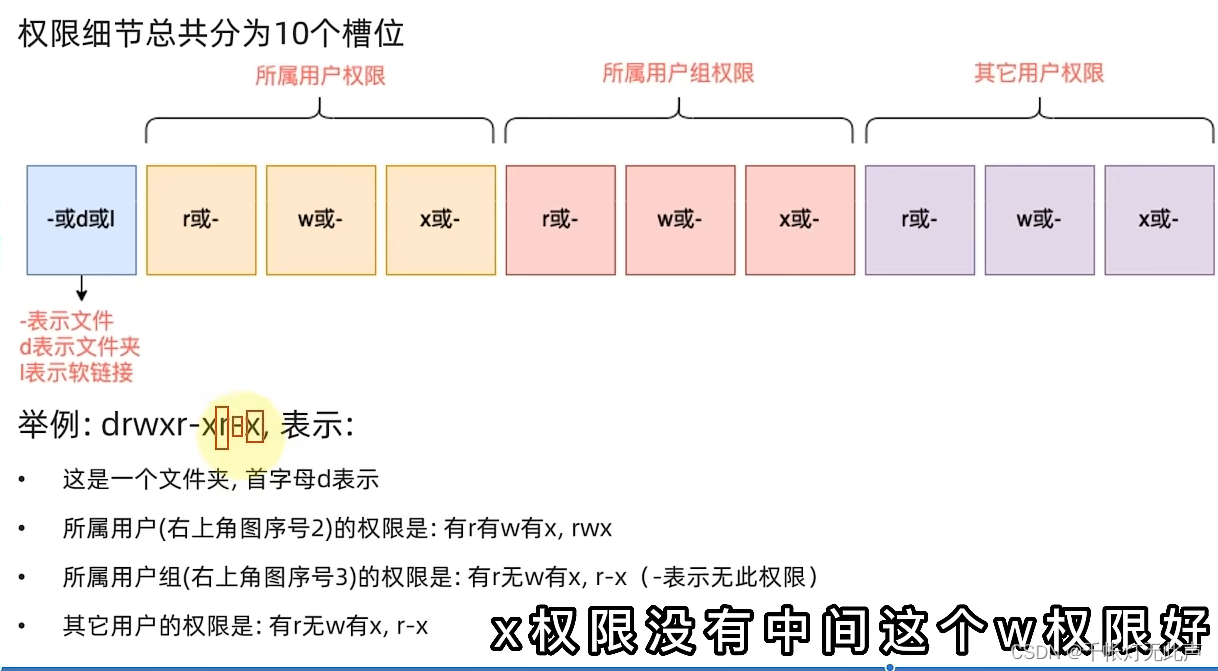
(1)chmod [-R] 权限 文件(夹)路径
-R,对文件夹内全部内容进行同样操作
ls -l
su itheima
mkdir test1
touch test1.txt
chmod u=rwx,g=r,o=w test1.txt
ls -l
mv test1.txt test1
ls test1
chmod u=r,g=w,o=x test1
ls -l
chmod -R u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx test1
ls -l
ls -l test1su itheima
touch 1.txt
ls -l
chmod 751 1.txt
ls -l(2)chown [-R] [用户][:][用户组] 文件(夹)
此命令只适用于 root
-R ,同 chmod,对文件夹内全部内容进行相同修改
: 用于分隔用户和用户组
chown root 1.txt
su root
ls -l
chown root 1.txt
ls -l
chown itheima 1.txt
ls -l
chown :root 1.txt
ls -l
chown :itheima 1.txt
ls -l
chown root:root 1.txt
ls -l
chown -R root:root test1
ls -l
ls -l test1强制停止
退出/登出
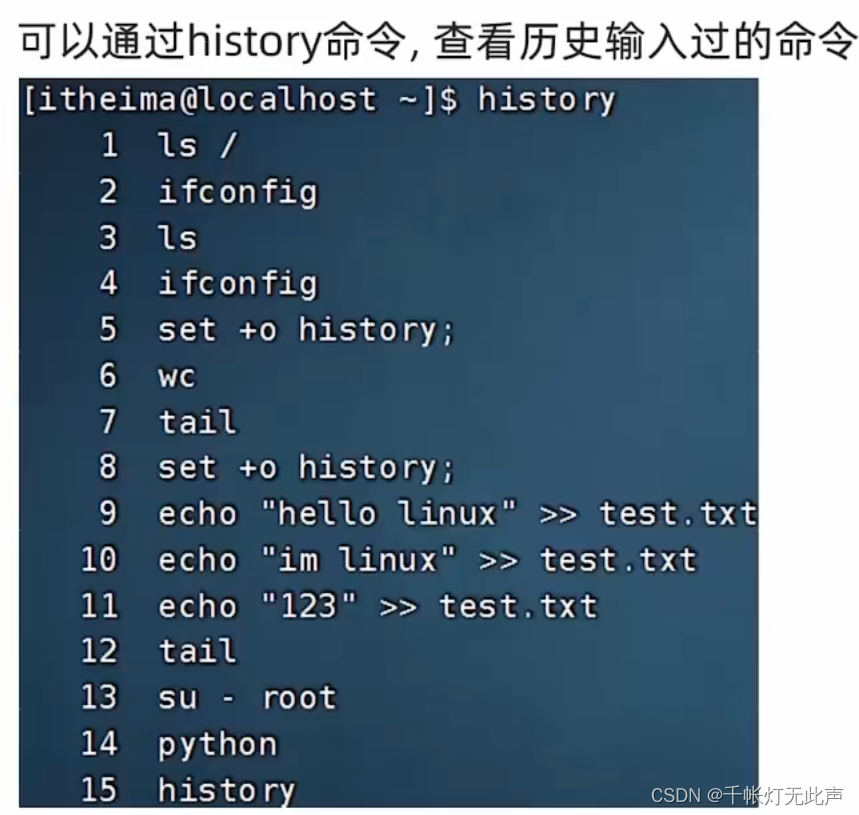
历史命令 history
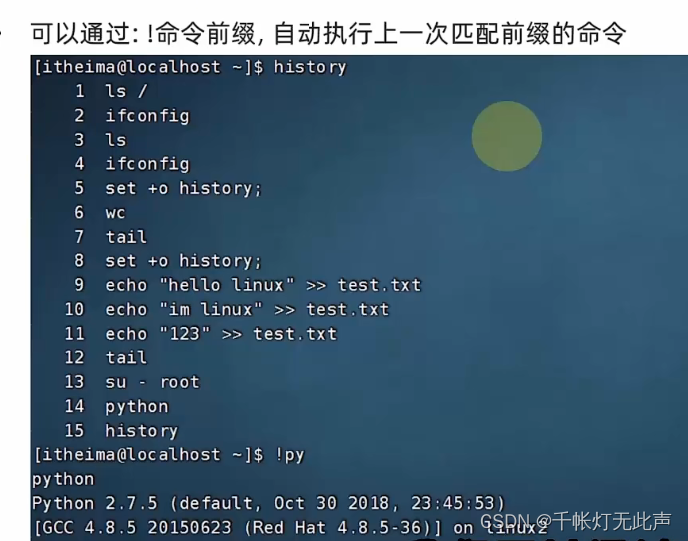
history | grep ch匹配前缀
3~5个命令之内,尽量不要太久
光标移动
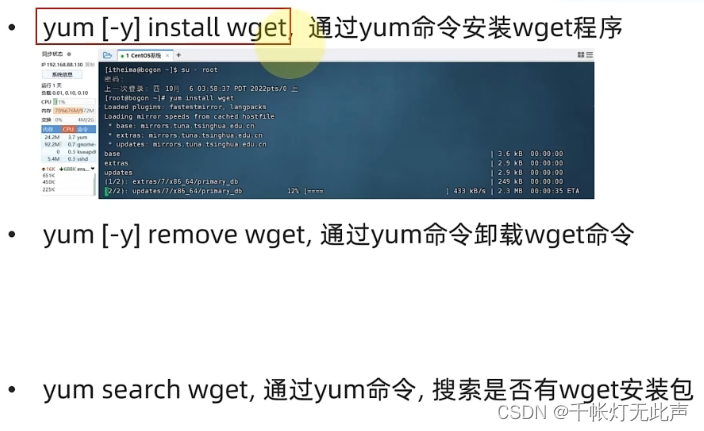
软件安装 yum
yum:RPM包软件管理器,用于自动化那幢配置Linux软件,并自动解决依赖问题。
(后缀 .rpm自动安装包)
yum [-y] [install | remove | search] 软件名称
-y ,自动确认,无需手动确认安装 或 卸载
install 安装
remove 卸载
search 搜索
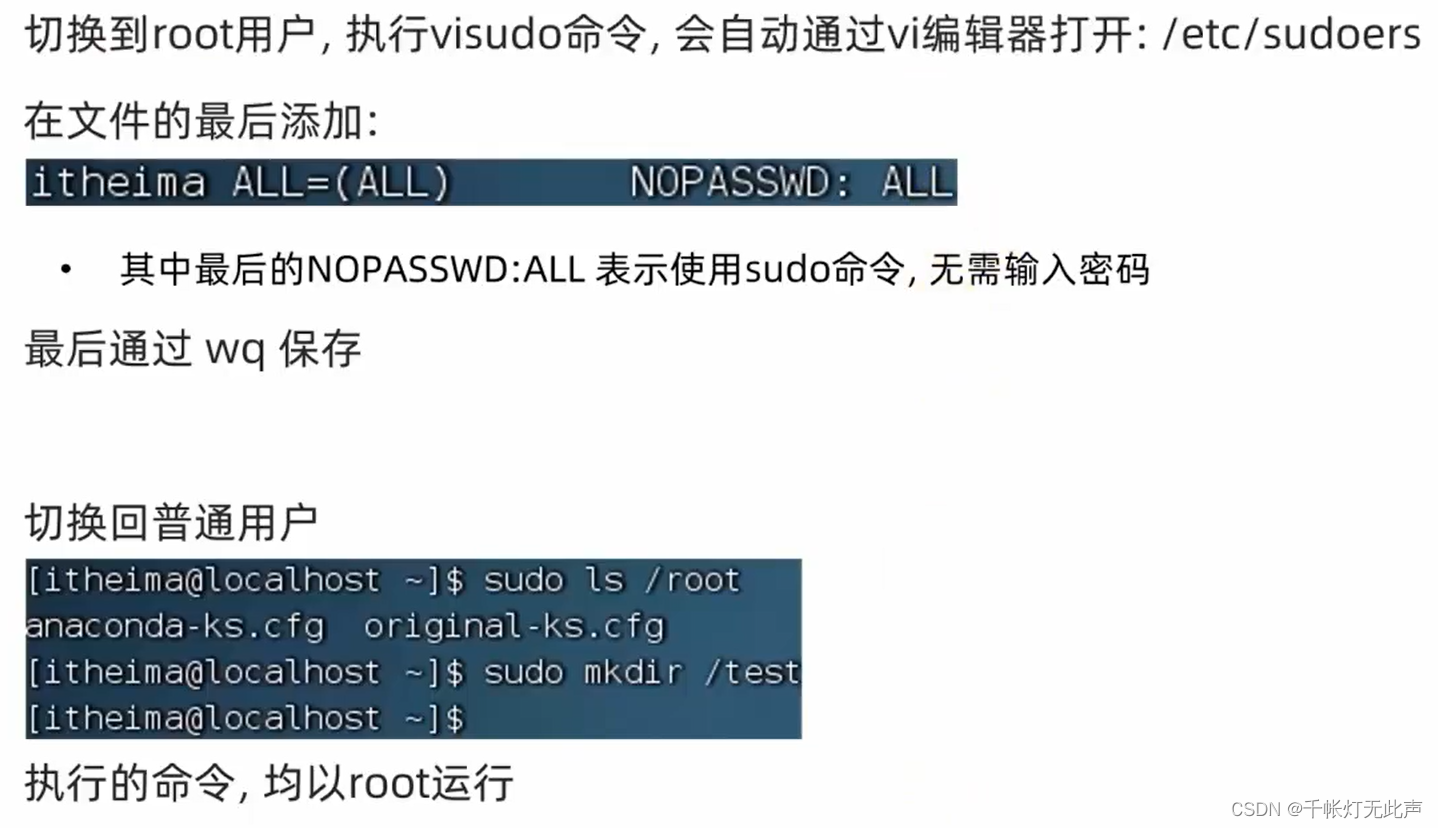
(yum需要root权限,su切换到root,或sudo提升权限)
(yum需要联网)
Ubuntu软件安装 apt
apt [-y] [install | remove | search] 软件名称
CentOS使用yum管理器,Ubuntu使用apt管理器,apt用法同yum
就是....WSL里Ubuntu,下wget,真的比虚拟机CentOS里快多了....
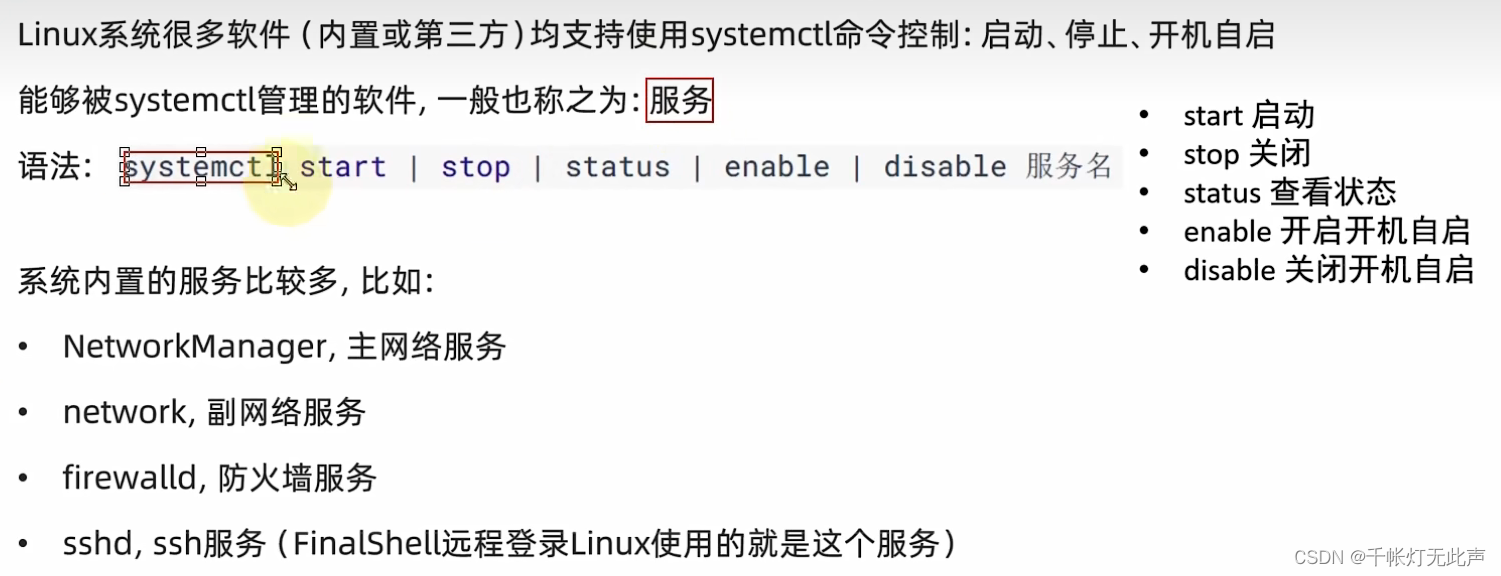
systemctl命令
systemctl start | stop | status | enable | disable 服务名
Linux系统很多软件(内置第三方),支持systemctl命令启动
控制系统内置的服务
systemctl status firewalld
systemctl start firewalld
systemctl enable firewalld
创建软连接 ln
ln -s 参数1 参数2
系统中创建软连接,将文件(夹)链接到其他位置
类似Windows系统中的快捷方式
-s ,创建软连接
参数1,被链接的
参数2,链接目的地
cd /etc
ls
pwd
cd
ls
ln -s /etc/yum.conf ~/yum.conf
ls -l
cd /etc
ls
ln -s /etc/yum ~/yum
ls -l
cat /etc/yum.conf
cat yum.conf
cd /etc/yum
ls -l
cd
cd yum
ls查看时间 date
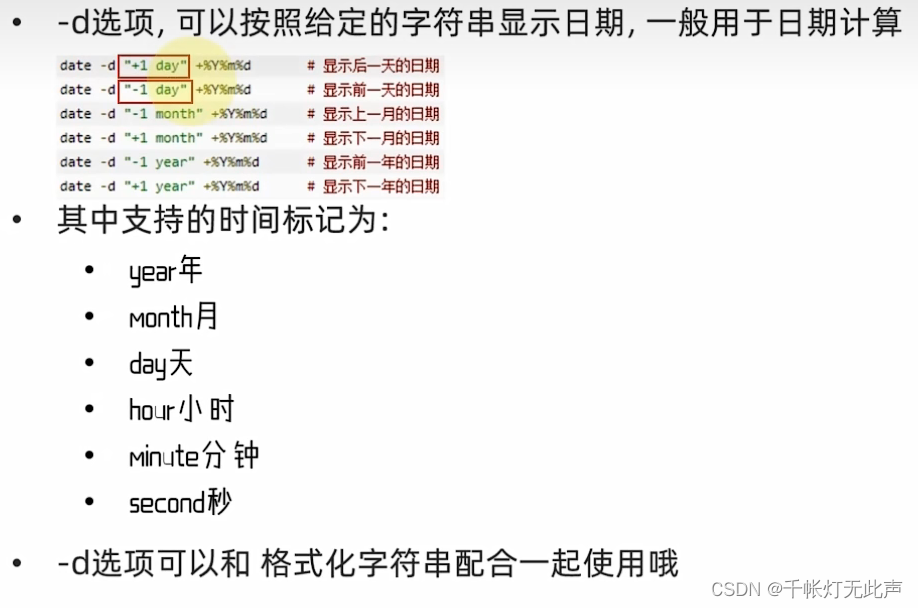
date [-d] [+格式化字符串]
date命令,查看系统时间
-d ,按照给定字符串显示日期,用于日期计算
%Y 年
%y 年份后2位数字(00...99)
%M 月份(01...12)
%d 日(01...31)
%H 小时(00...23)
%M 分钟(00...59)
%S 秒(00...60)
%s 自1970-01-01 00:00:00到现在的秒数
su itheima
date
date +%Y-%m-%d
date +%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"date -d "+1 day"
date -d "+1 day" +%Y%m%d
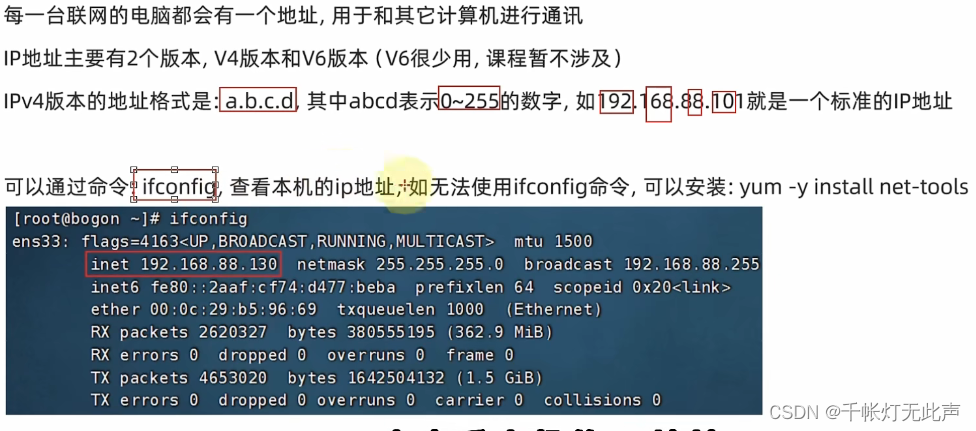
date -d "-1 week" +%Y/%m/%d查看ip地址 ifconfig
ifconfig
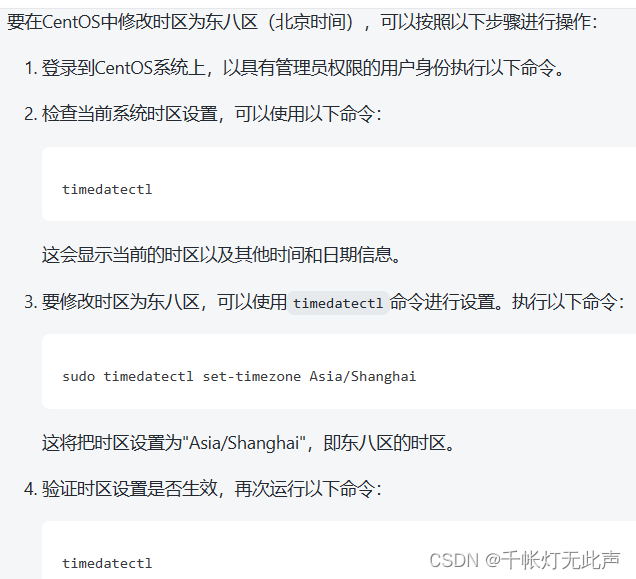
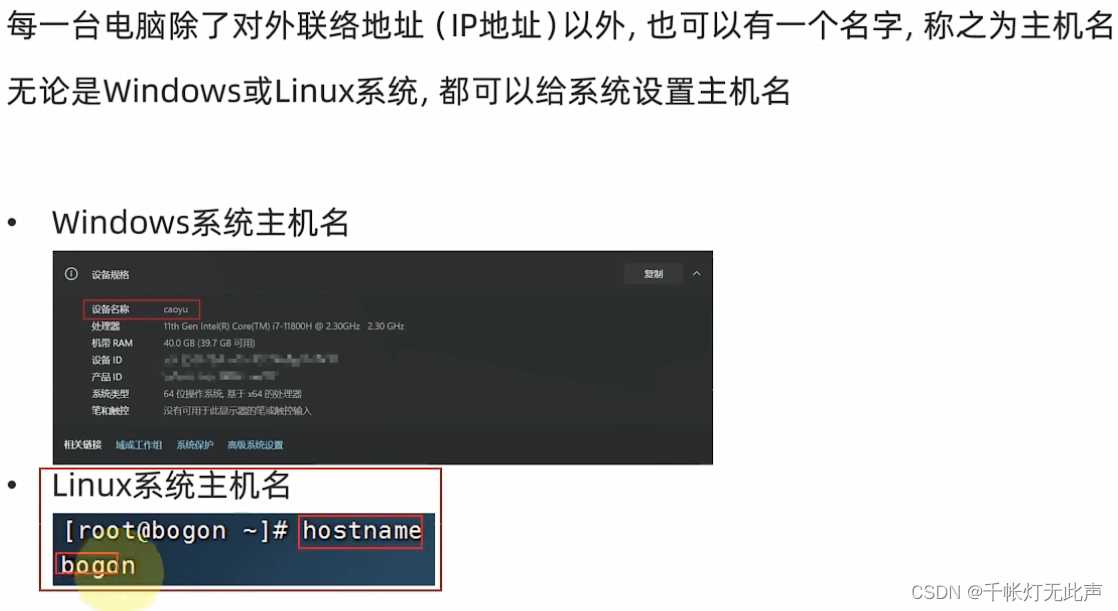
修改主机名
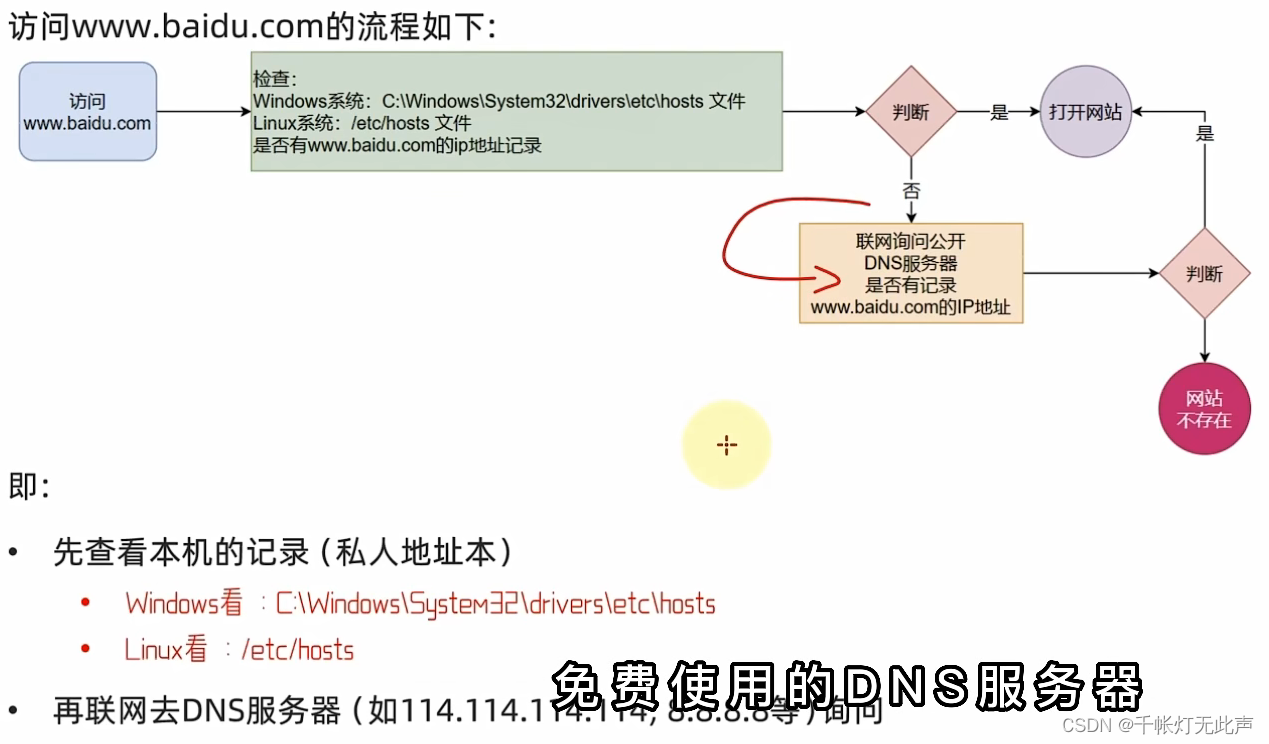
域名解析
通过,配置主机名与 ip 地址的映射关系,不用再记那么长的域名和 ip地址
管理员打开记事本,hosts文件的位置, 在最后添加
192.168....130 centos保存即可
Linux固定 ip 地址
第四章-07-配置Linux固定IP地址_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
检查联通 ping
ping [-c num] ip或主机名
-c ,检查次数,不用 -c 会无限次持续检查
ping baidu.com
ping -c 2 baidu.com
ping -c 3 39.156.66.10
ping 192.168.88.5下载网络文件 wget curl
(1)wget [-b] url
-b ,后天下载,并将日志写入当前工作目录的 wget-log 文件
url ,下载链接
yum install wget
wget http://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.0/hadoop-3.3.0.tar.gz
ctrl c
ls
rm -f hadoop-3.3.0.tar.gz
ls
(2)发起网络请求
curl [-O] url
curl url 类似打开网页
-O ,用于下载文件,url是下载链接时,可以保存文件
url ,发起请求的网络地址
curl cip.cc
curl python.itheima.com
curl -O http://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.0/hadoop-3.3.0.tar.gz查看端口占用情况
(ip 只能确定计算机,通过 端口 才能确定要交互的程序)
nmap ip地址
yum -y install nmap
nmap 127.0.0.1netstat -anp | grep 端口号 (查看指定端口占用情况)
yum -y install net-tools
netstat -anp
netstat -anp | grep 22
netstat -anp | grep 111
netstat -anp | grep 580
netstat -anp | grep 761
netstat -anp | grep 12345查看进程 ps
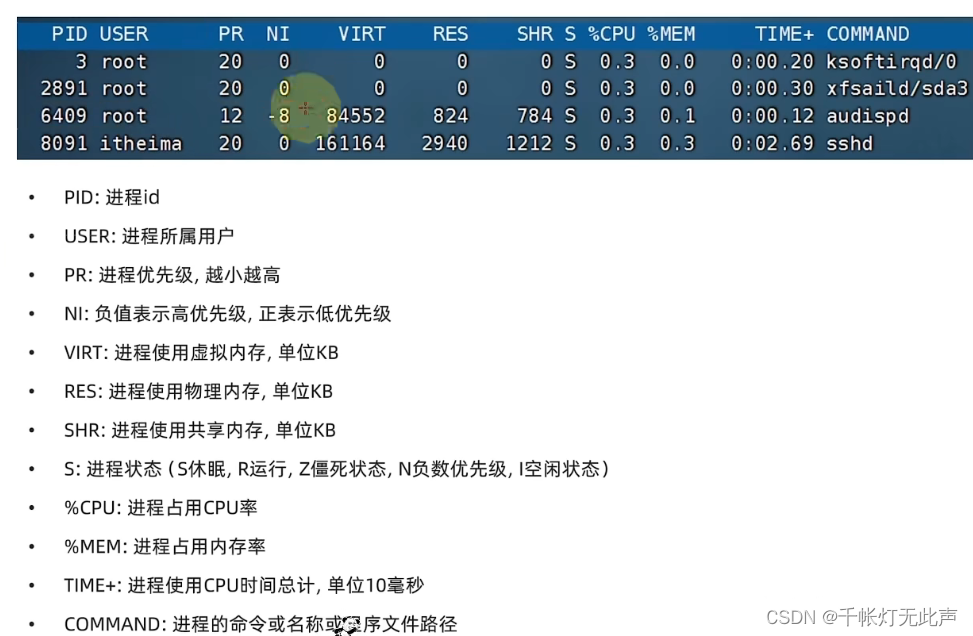
ps [-e -f]
-e ,显示全部
-f ,格式化形式显示
ps -ef ,列出全部进程全部信息
两个终端
tail
ps -ef | grep tail关闭进程 kill
kill [-9] 进程ID
-9 ,强制关闭进程,是否关闭要看进程自身的处理机制
ps -ef | grep tail
kill -9 23906
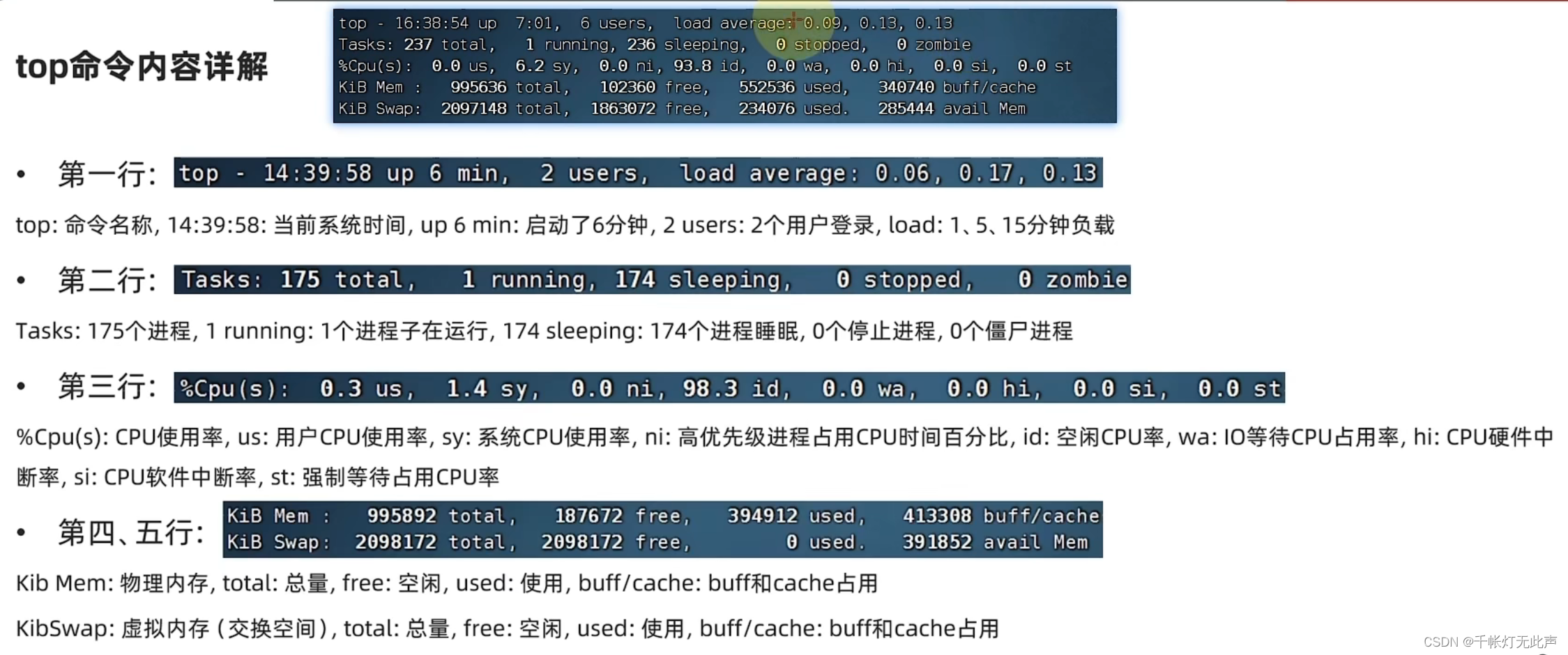
ps -ef | grep tail查看系统资源占用 top
top
查看CPU,内存占用,类似Windows任务管理器
默认3秒刷新1次,ctrl + c 或 直接 q 退出
top -p 1
top -p 2
top -d 3
top -c
top -n 3
top -b -n 3 > 1.txt
more 1.txt
top -i
top -u itheima磁盘信息
(1)df [-h]
-h ,更人性化的单位
(2)iostat [-x] [num1] [num2]
-x ,显示更多信息
num1 ,数字,刷新间隔;num2,数字,刷新次数
yum install sysstat
iostat
iostat -x
iostat 3 3
iostat -x 1网络状态监控
sar -n DEV num1 num2
-n ,查看网络,DEV 表示查看网络接口
num1,刷新间隔;num2,刷新次数
sar -n DEV
sar -n DEV 3 3环境变量
比较危险,不要乱搞
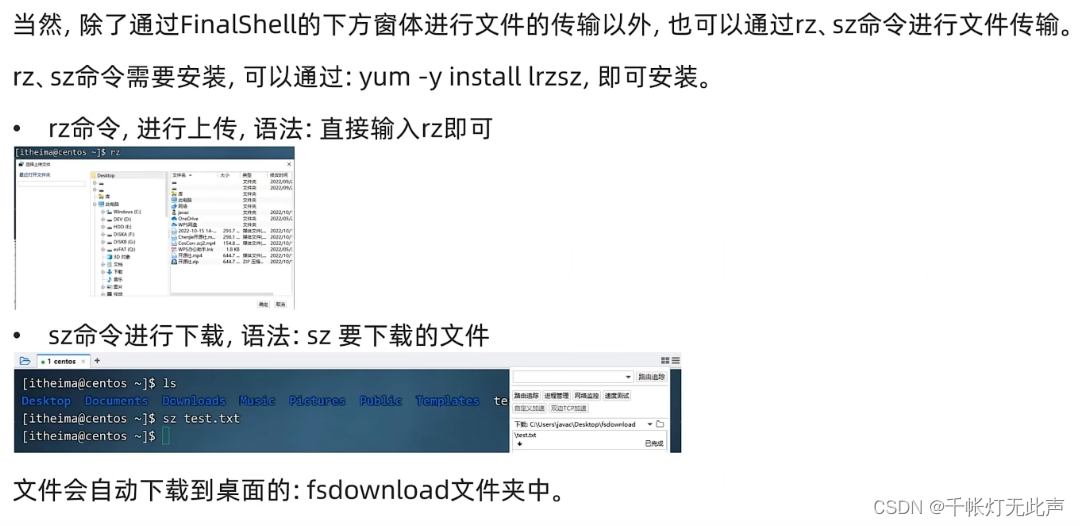
文件下载上传 rz sz
大文件最好拖拽,不要用rz,rz较慢
压缩与解压
(1)tar 命令压缩
tar [-c -v -x -f -z -C] 参数1 参数2 ... 参数N
-c ,创建压缩文件,用于压缩模式
-v ,显示过程,查看进度
-x ,解压模式
-f ,要创建 / 解压的文件,-f 必须放最后
-z ,gzip模式,不使用就是普通的 tarball 格式
-C ,解压目的地,用于解压模式
touch 2.txt
touch 3.txt
ls -lh
tar -cvf test.tar 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
ls -lh
tar -zcvf test.tar.gz 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
ls -lh
rm -f 1.txt 2.txt 3.txtgzip显示 5 k(压缩效果),tarball显示 120 k(简单打包)
(2)tar 命令解压
tar -xvf test.tar
ls -lh
rm -f 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
tar -zxvf test.tar.gz
ls
mkdir test
ls
tar -zxvf test.tar.gz -C test/
cd test
ls(3)zip
zip [-r] 参数1 ... 参数N
-r ,被压缩的包含文件夹,类似 rm, cp 等命令的 -r
解压时,有同名内容会被替换





 本文详细介绍了Linux系统中的基本命令,如目录切换、文件操作、权限管理、软件安装、网络测试、进程查看和资源监控等,帮助读者理解Linux的核心操作和权限结构。
本文详细介绍了Linux系统中的基本命令,如目录切换、文件操作、权限管理、软件安装、网络测试、进程查看和资源监控等,帮助读者理解Linux的核心操作和权限结构。









































 5847
5847

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










