📑 摘要
本文旨在为中国开发者,特别是 AI 应用开发者,提供一份全面的 Docker 镜像加速与优化指南。通过详细讲解 Docker 镜像加速器的配置方法、最佳实践、常见问题及解决方案,帮助开发者提升镜像拉取速度,优化开发效率。文章结合实际应用场景,提供丰富的实践案例和代码示例,确保内容通俗易懂且实用性强。
思维导图:Docker 镜像加速知识体系
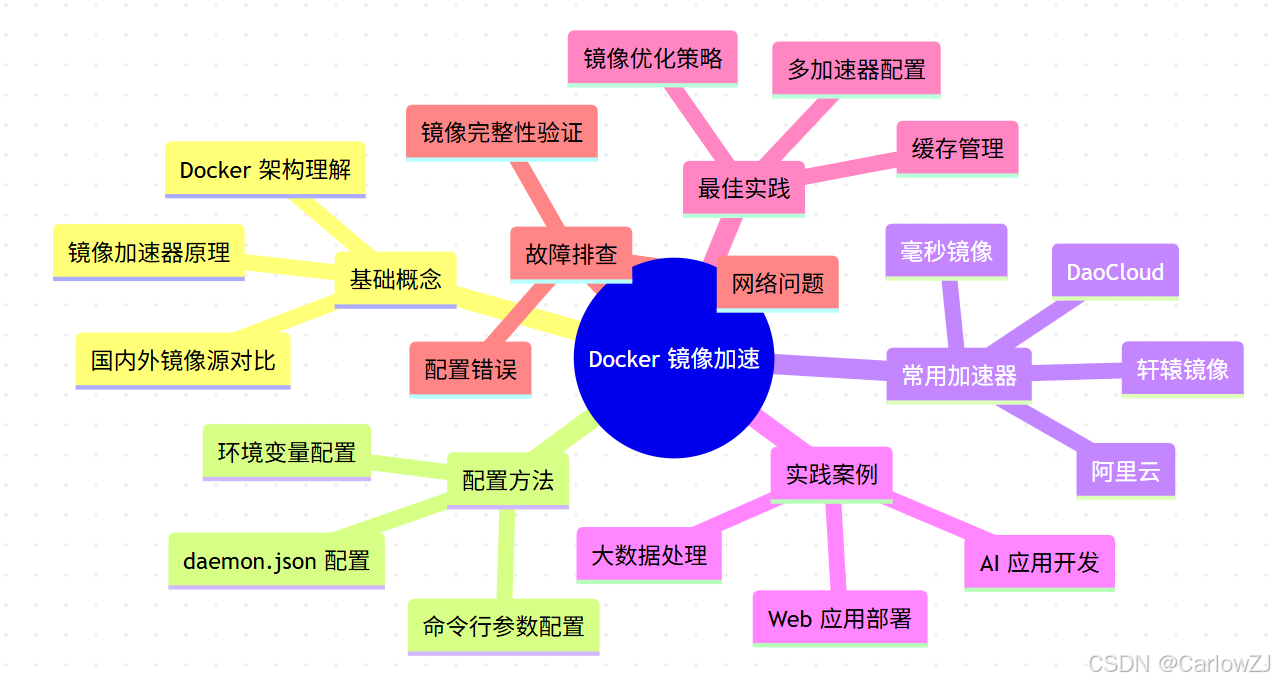
mindmap
root((Docker 镜像加速))
基础概念
镜像加速器原理
国内外镜像源对比
Docker 架构理解
配置方法
daemon.json 配置
命令行参数配置
环境变量配置
常用加速器
轩辕镜像
毫秒镜像
DaoCloud
阿里云
实践案例
AI 应用开发
Web 应用部署
大数据处理
最佳实践
多加速器配置
镜像优化策略
缓存管理
故障排查
网络问题
配置错误
镜像完整性验证
第一章:引言 - 为什么需要 Docker 镜像加速
在现代软件开发中,Docker 已成为不可或缺的工具,尤其是在 AI 应用开发中。然而,由于默认的 Docker Hub 服务器位于国外,国内开发者在拉取镜像时常常面临速度慢甚至失败的问题。
特别是在 AI 开发领域,常见的 TensorFlow、PyTorch 等框架的官方镜像通常体积庞大(往往超过1GB),在没有加速器的情况下,拉取这些镜像可能需要数十分钟甚至更长时间,严重影响开发效率。
💡 AI 场景痛点:PyTorch/TensorFlow 镜像动辄数 GB,未加速时拉取耗时 30+ 分钟,加速后仅需 2-5 分钟。
第二章:Docker 镜像加速器简介 - 技术原理与选型
Docker 镜像加速器是通过在国内部署的服务器缓存 Docker Hub 上的镜像,从而减少从国外服务器拉取镜像的时间。当用户请求一个镜像时,加速器会首先检查本地是否有缓存,如果有则直接返回,否则从 Docker Hub 拉取后再返回给用户并缓存。
2.1 常用国内镜像加速器
以下是一些常用的国内镜像加速器,按稳定性排序:
| 加速器名称 | 地址 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 轩辕镜像 | https://docker.xuanyuan.me | 稳定性高,缓存更新及时 |
| 毫秒镜像 | https://docker.1ms.run | 速度快,支持多种镜像 |
| DaoCloud | https://docker.m.daocloud.io | 老牌服务商,可靠性好 |
| 阿里云 | https://<your_id>.mirror.aliyuncs.com | 需注册,企业级服务 |
| 腾讯云 | https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com | 需注册,华南地区速度快 |
2.2 镜像加速器架构图
第三章:配置 Docker 镜像加速器 - 详细步骤
配置 Docker 镜像加速器非常简单,只需修改 /etc/docker/daemon.json 文件并重启 Docker 服务即可。
3.1 Linux 系统配置
步骤 1:编辑 /etc/docker/daemon.json
sudo nano /etc/docker/daemon.json
步骤 2:添加镜像加速器地址
{
"registry-mirrors": [
"https://docker.xuanyuan.me",
"https://docker.1ms.run",
"https://docker.m.daocloud.io",
"https://hub.rat.dev",
"https://dockercf.jsdelivr.fyi"
]
}
步骤 3:重启 Docker 服务
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
验证配置是否生效
docker info | grep -A 5 "Registry Mirrors"
输出示例:
Registry Mirrors:
https://docker.xuanyuan.me/
https://docker.1ms.run/
https://docker.m.daocloud.io/
https://hub.rat.dev/
https://dockercf.jsdelivr.fyi/
3.2 Windows 系统配置
在 Windows 系统中,可以通过 Docker Desktop 进行配置:
- 打开 Docker Desktop
- 进入 Settings → Docker Engine
- 在配置文件中添加 registry-mirrors 配置:
{
"registry-mirrors": [
"https://docker.xuanyuan.me",
"https://docker.1ms.run",
"https://docker.m.daocloud.io"
]
}
- 点击 Apply & Restart 重启 Docker
3.3 macOS 系统配置
在 macOS 系统中,同样通过 Docker Desktop 进行配置:
- 打开 Docker Desktop
- 进入 Preferences → Docker Engine
- 添加 registry-mirrors 配置
- 点击 Apply & Restart 重启 Docker
第四章:实践案例 - AI 应用开发中的镜像加速
在 AI 应用开发中,经常需要拉取大型镜像,如 TensorFlow、PyTorch 等。使用镜像加速器可以显著提升拉取速度。
4.1 Python 脚本自动化拉取镜像
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
docker_image_puller.py
Docker 镜像拉取工具,支持自动重试和多加速器切换
"""
import subprocess
import time
import sys
from typing import List, Optional
class DockerImagePuller:
"""
Docker 镜像拉取器
"""
def __init__(self, mirrors: List[str] = None):
"""
初始化镜像拉取器
Args:
mirrors (List[str]): 镜像加速器列表
"""
self.mirrors = mirrors or [
"docker.xuanyuan.me",
"docker.1ms.run",
"docker.m.daocloud.io",
"hub.rat.dev"
]
def check_docker_installed(self) -> bool:
"""
检查 Docker 是否已安装
Returns:
bool: 是否已安装
"""
try:
result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "--version"],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
check=True
)
print(f"✅ Docker 已安装: {result.stdout.strip()}")
return True
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, FileNotFoundError):
print("❌ Docker 未安装或未正确配置")
return False
def pull_image_with_mirror(self, image_name: str, mirror: str) -> bool:
"""
使用指定镜像加速器拉取镜像
Args:
image_name (str): 原始镜像名称
mirror (str): 镜像加速器地址
Returns:
bool: 是否拉取成功
"""
# 构造加速镜像名称
if image_name.startswith("docker.io/"):
accelerated_image = image_name.replace("docker.io/", f"{mirror}/", 1)
elif "/" not in image_name or "." not in image_name.split("/")[0]:
# 官方镜像,如 nginx, ubuntu 等
accelerated_image = f"{mirror}/library/{image_name}"
else:
# 已经是完整路径的镜像
accelerated_image = image_name.replace(image_name.split("/")[0], mirror, 1)
print(f"🔄 正在使用加速器 {mirror} 拉取镜像: {accelerated_image}")
try:
start_time = time.time()
result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "pull", accelerated_image],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=300 # 5分钟超时
)
end_time = time.time()
if result.returncode == 0:
print(f"✅ 镜像拉取成功,耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f} 秒")
# 重新标记镜像为原始名称
tag_result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "tag", accelerated_image, image_name],
capture_output=True,
text=True
)
if tag_result.returncode == 0:
print(f"🏷️ 镜像已重新标记为: {image_name}")
# 删除加速镜像标签
subprocess.run(
["docker", "rmi", accelerated_image],
capture_output=True,
text=True
)
return True
else:
print(f"❌ 镜像拉取失败: {result.stderr}")
return False
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
print("⏰ 镜像拉取超时")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 拉取过程中出现异常: {e}")
return False
def pull_image(self, image_name: str, max_retries: int = 3) -> bool:
"""
拉取镜像(自动尝试多个加速器)
Args:
image_name (str): 镜像名称
max_retries (int): 最大重试次数
Returns:
bool: 是否拉取成功
"""
print(f"🚀 开始拉取镜像: {image_name}")
# 检查 Docker 是否安装
if not self.check_docker_installed():
return False
# 尝试直接拉取(使用 daemon.json 配置的加速器)
print("🔄 尝试使用默认配置拉取...")
try:
start_time = time.time()
result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "pull", image_name],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=300
)
end_time = time.time()
if result.returncode == 0:
print(f"✅ 镜像拉取成功,耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f} 秒")
return True
else:
print(f"⚠️ 默认配置拉取失败: {result.stderr}")
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
print("⏰ 默认配置拉取超时")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 默认配置拉取异常: {e}")
# 如果默认配置失败,尝试各个加速器
for i, mirror in enumerate(self.mirrors, 1):
print(f"\n🔄 尝试第 {i} 个加速器: {mirror}")
if self.pull_image_with_mirror(image_name, mirror):
return True
# 重试机制
for retry in range(1, max_retries + 1):
print(f"🔄 第 {i} 个加速器第 {retry} 次重试...")
time.sleep(2 ** retry) # 指数退避
if self.pull_image_with_mirror(image_name, mirror):
return True
print(f"❌ 所有加速器均拉取失败: {image_name}")
return False
def batch_pull_images(self, image_list: List[str]) -> dict:
"""
批量拉取镜像
Args:
image_list (List[str]): 镜像列表
Returns:
dict: 拉取结果统计
"""
print(f"📦 开始批量拉取 {len(image_list)} 个镜像")
results = {
"success": [],
"failed": []
}
for i, image_name in enumerate(image_list, 1):
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f" [{i}/{len(image_list)}] {image_name}")
print(f"{'='*50}")
if self.pull_image(image_name):
results["success"].append(image_name)
else:
results["failed"].append(image_name)
# 输出统计结果
print(f"\n📊 批量拉取完成:")
print(f" 成功: {len(results['success'])} 个")
print(f" 失败: {len(results['failed'])} 个")
if results["failed"]:
print(f" 失败列表: {', '.join(results['failed'])}")
return results
def main():
"""
主函数 - 演示镜像拉取功能
"""
# 初始化镜像拉取器
puller = DockerImagePuller()
# 示例1: 拉取单个镜像
print("示例1: 拉取单个镜像")
puller.pull_image("nginx:latest")
print("\n" + "="*60 + "\n")
# 示例2: 批量拉取 AI 相关镜像
print("示例2: 批量拉取 AI 相关镜像")
ai_images = [
"tensorflow/tensorflow:latest",
"pytorch/pytorch:latest",
"nvidia/cuda:11.0-base",
"continuumio/anaconda3:latest"
]
# 批量拉取(实际使用时取消注释)
# results = puller.batch_pull_images(ai_images)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 注意:运行前请确保 Docker 已安装并运行
# main()
print("Docker 镜像拉取工具模块准备就绪")
4.2 AI 开发环境一键部署脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ai_env_setup.py
AI 开发环境一键部署脚本
"""
import subprocess
import sys
import time
from typing import List, Dict
class AIEnvironmentSetup:
"""
AI 开发环境一键部署工具
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化部署工具
"""
self.ai_images = {
"基础环境": [
"continuumio/anaconda3:latest",
"python:3.9-slim"
],
"深度学习框架": [
"tensorflow/tensorflow:latest",
"pytorch/pytorch:latest",
"microsoft/onnxruntime:latest"
],
"GPU支持": [
"nvidia/cuda:11.0-base",
"nvidia/cudnn:8.0-runtime-ubuntu18.04"
],
"模型服务": [
"nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:21.08-py3",
"seldonio/seldon-core-s2i-python37:1.12.0"
]
}
def check_system_resources(self) -> Dict[str, str]:
"""
检查系统资源
Returns:
Dict[str, str]: 系统资源信息
"""
resources = {}
try:
# 检查磁盘空间
df_result = subprocess.run(
["df", "-h", "/"],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
check=True
)
disk_info = df_result.stdout.split('\n')[1].split()
resources["disk_total"] = disk_info[1]
resources["disk_used"] = disk_info[2]
resources["disk_available"] = disk_info[3]
# 检查内存
free_result = subprocess.run(
["free", "-h"],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
check=True
)
mem_info = free_result.stdout.split('\n')[1].split()
resources["mem_total"] = mem_info[1]
resources["mem_used"] = mem_info[2]
resources["mem_available"] = mem_info[3]
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ 系统资源检查失败: {e}")
return resources
def setup_docker_daemon(self, mirrors: List[str]) -> bool:
"""
配置 Docker daemon
Args:
mirrors (List[str]): 镜像加速器列表
Returns:
bool: 配置是否成功
"""
daemon_config = {
"registry-mirrors": mirrors,
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "10m",
"max-file": "3"
}
}
print("🔧 正在配置 Docker daemon...")
print(f" 镜像加速器: {', '.join(mirrors)}")
try:
# 在实际环境中,这里需要写入 /etc/docker/daemon.json
# 由于权限问题,这里仅打印配置内容
import json
print(" 配置内容:")
print(json.dumps(daemon_config, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
print("💡 请手动将以上配置写入 /etc/docker/daemon.json 并重启 Docker 服务")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Docker daemon 配置失败: {e}")
return False
def pull_ai_images(self, category: str = None) -> Dict[str, list]:
"""
拉取 AI 相关镜像
Args:
category (str): 镜像分类(可选)
Returns:
Dict[str, list]: 拉取结果
"""
results = {}
# 确定要拉取的镜像类别
categories_to_pull = {category: self.ai_images[category]} if category else self.ai_images
for cat, images in categories_to_pull.items():
print(f"\n📥 拉取 {cat} 镜像...")
results[cat] = {"success": [], "failed": []}
for image in images:
print(f" 正在拉取: {image}")
try:
start_time = time.time()
result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "pull", image],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=600 # 10分钟超时
)
end_time = time.time()
if result.returncode == 0:
print(f" ✅ 成功 ({end_time - start_time:.2f}s)")
results[cat]["success"].append(image)
else:
print(f" ❌ 失败: {result.stderr}")
results[cat]["failed"].append(image)
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
print(" ⏰ 超时")
results[cat]["failed"].append(image)
except Exception as e:
print(f" ❌ 异常: {e}")
results[cat]["failed"].append(image)
return results
def generate_dockerfile_templates(self) -> Dict[str, str]:
"""
生成常用的 Dockerfile 模板
Returns:
Dict[str, str]: Dockerfile 模板
"""
templates = {}
# TensorFlow 应用模板
templates["tensorflow_app"] = '''# TensorFlow 应用基础镜像
FROM tensorflow/tensorflow:latest
# 设置工作目录
WORKDIR /app
# 复制应用代码
COPY . .
# 安装依赖
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8000
# 启动应用
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
'''
# PyTorch 应用模板
templates["pytorch_app"] = '''# PyTorch 应用基础镜像
FROM pytorch/pytorch:latest
# 设置工作目录
WORKDIR /app
# 复制应用代码
COPY . .
# 安装依赖
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8000
# 启动应用
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
'''
# Jupyter Notebook 模板
templates["jupyter_notebook"] = '''# Jupyter Notebook 环境
FROM continuumio/anaconda3:latest
# 设置工作目录
WORKDIR /workspace
# 安装 Jupyter
RUN pip install jupyter
# 生成 Jupyter 配置
RUN jupyter notebook --generate-config
# 设置密码(可选)
# RUN python -c "from notebook.auth import passwd; print(passwd('your_password'))"
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8888
# 启动 Jupyter
CMD ["jupyter", "notebook", "--ip=0.0.0.0", "--allow-root", "--no-browser"]
'''
return templates
def save_templates(self, templates: Dict[str, str], output_dir: str = "./docker_templates"):
"""
保存 Dockerfile 模板到文件
Args:
templates (Dict[str, str]): 模板字典
output_dir (str): 输出目录
"""
import os
# 创建输出目录
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
for name, content in templates.items():
file_path = os.path.join(output_dir, f"Dockerfile.{name}")
try:
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(content)
print(f"✅ 模板已保存: {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 保存模板失败 {file_path}: {e}")
def run_setup(self, setup_daemon: bool = True, pull_images: bool = True):
"""
运行完整设置流程
Args:
setup_daemon (bool): 是否配置 Docker daemon
pull_images (bool): 是否拉取镜像
"""
print("🚀 开始 AI 开发环境一键部署")
print("=" * 50)
# 1. 检查系统资源
print("📋 系统资源检查")
resources = self.check_system_resources()
for key, value in resources.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
# 2. 配置 Docker daemon
if setup_daemon:
print("\n🔧 Docker daemon 配置")
mirrors = [
"https://docker.xuanyuan.me",
"https://docker.1ms.run",
"https://docker.m.daocloud.io"
]
self.setup_docker_daemon(mirrors)
# 3. 拉取 AI 镜像
if pull_images:
print("\n📥 AI 镜像拉取")
results = self.pull_ai_images()
# 输出统计结果
total_success = sum(len(r["success"]) for r in results.values())
total_failed = sum(len(r["failed"]) for r in results.values())
print(f"\n📊 拉取完成: 成功 {total_success} 个,失败 {total_failed} 个")
# 4. 生成 Dockerfile 模板
print("\n📄 生成 Dockerfile 模板")
templates = self.generate_dockerfile_templates()
self.save_templates(templates)
print(f" 已生成 {len(templates)} 个模板文件")
def main():
"""
主函数
"""
setup = AIEnvironmentSetup()
# 运行完整设置(实际使用时取消注释)
# setup.run_setup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 注意:运行前请确保 Docker 已安装并运行
# main()
print("AI 开发环境一键部署工具准备就绪")
第五章:最佳实践 - 提升效率的关键策略
5.1 多加速器配置策略
配置多个镜像加速器,确保在某个加速器不可用时,其他加速器可以作为备份。
5.2 镜像优化策略
通过多阶段构建减少镜像大小,提升拉取速度。
# 多阶段构建示例
# 构建阶段
FROM python:3.9-slim as builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --user -r requirements.txt
# 运行阶段
FROM python:3.9-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=builder /root/.local /root/.local
COPY . .
# 确保用户安装的包在 PATH 中
ENV PATH=/root/.local/bin:$PATH
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
5.3 缓存管理策略
定期清理 Docker 缓存,释放磁盘空间。
# 清理未使用的镜像
docker image prune -a
# 清理构建缓存
docker builder prune -a
# 清理所有未使用的资源
docker system prune -a
5.4 镜像标签管理
合理使用镜像标签,避免使用 latest 标签在生产环境中。
第六章:常见问题与解决方案 - 故障排查指南
Q1: 为什么我的 Docker 镜像下载速度很慢?
- 原因:默认的 Docker Hub 服务器位于国外,网络连接可能不稳定。
- 解决方案:使用国内镜像加速器,如轩辕镜像、毫秒镜像等。
Q2: 如何验证 Docker 镜像的完整性?
- 方法:
- 使用
docker images命令查看镜像的 ID。 - 使用
docker inspect [镜像ID]命令查看镜像详细信息,包括其 SHA256 摘要。 - 将此摘要与官方发布的摘要进行比对。
- 使用
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
image_integrity_checker.py
Docker 镜像完整性检查工具
"""
import subprocess
import json
import hashlib
def check_image_integrity(image_name: str) -> dict:
"""
检查 Docker 镜像完整性
Args:
image_name (str): 镜像名称
Returns:
dict: 检查结果
"""
result = {
"image_name": image_name,
"exists": False,
"id": None,
"digest": None,
"size": None,
"created": None
}
try:
# 获取镜像详细信息
inspect_result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "inspect", image_name],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
check=True
)
image_info = json.loads(inspect_result.stdout)
if image_info:
result["exists"] = True
result["id"] = image_info[0].get("Id")
result["size"] = image_info[0].get("Size")
result["created"] = image_info[0].get("Created")
# 获取镜像摘要
if "RepoDigests" in image_info[0]:
result["digest"] = image_info[0]["RepoDigests"]
return result
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
result["error"] = "镜像不存在或无法访问"
return result
except Exception as e:
result["error"] = f"检查过程中出现错误: {e}"
return result
def main():
"""
主函数 - 演示镜像完整性检查
"""
# 检查镜像完整性
images_to_check = [
"nginx:latest",
"tensorflow/tensorflow:latest",
"python:3.9-slim"
]
for image in images_to_check:
print(f"🔍 检查镜像: {image}")
result = check_image_integrity(image)
if result["exists"]:
print(f" ID: {result['id'][:12]}")
print(f" 大小: {result['size']} 字节")
print(f" 创建时间: {result['created']}")
if result["digest"]:
print(f" 摘要: {result['digest']}")
else:
print(f" 错误: {result.get('error', '未知错误')}")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# main()
print("镜像完整性检查工具准备就绪")
Q3: 为什么 docker pull 失败?
- 原因:
- 网络连接问题,尤其是国内访问 Docker Hub 的稳定性较差。
- Docker Hub 镜像的名称或标签错误。
- 镜像被删除或不可用。
- 解决方案:
- 检查网络连接。
- 使用国内镜像加速器。
- 确认镜像名称和标签正确。
Q4: 如何测试镜像加速器的速度?
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
mirror_speed_tester.py
Docker 镜像加速器速度测试工具
"""
import subprocess
import time
from typing import List, Dict
class MirrorSpeedTester:
"""
镜像加速器速度测试器
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化测试器
"""
self.test_images = [
"nginx:alpine", # 小型镜像
"python:3.9-slim", # 中型镜像
"tensorflow/tensorflow:latest" # 大型镜像
]
self.mirrors = [
"docker.xuanyuan.me",
"docker.1ms.run",
"docker.m.daocloud.io",
"hub.rat.dev"
]
def test_mirror_speed(self, image_name: str, mirror: str = None) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""
测试镜像拉取速度
Args:
image_name (str): 镜像名称
mirror (str): 镜像加速器地址
Returns:
Dict[str, any]: 测试结果
"""
# 构造镜像名称
if mirror:
if image_name.startswith("docker.io/"):
test_image = image_name.replace("docker.io/", f"{mirror}/", 1)
elif "/" not in image_name or "." not in image_name.split("/")[0]:
test_image = f"{mirror}/library/{image_name}"
else:
test_image = image_name.replace(image_name.split("/")[0], mirror, 1)
else:
test_image = image_name
result = {
"image": image_name,
"mirror": mirror or "default",
"test_image": test_image,
"success": False,
"duration": None,
"error": None
}
try:
# 删除可能存在的镜像
subprocess.run(
["docker", "rmi", "-f", test_image],
capture_output=True,
text=True
)
# 开始计时并拉取镜像
start_time = time.time()
pull_result = subprocess.run(
["docker", "pull", test_image],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=300 # 5分钟超时
)
end_time = time.time()
if pull_result.returncode == 0:
result["success"] = True
result["duration"] = end_time - start_time
print(f"✅ {test_image}: {result['duration']:.2f} 秒")
else:
result["error"] = pull_result.stderr
print(f"❌ {test_image}: 失败 - {pull_result.stderr}")
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
result["error"] = "超时"
print(f"⏰ {test_image}: 超时")
except Exception as e:
result["error"] = str(e)
print(f"❌ {test_image}: 异常 - {e}")
finally:
# 清理测试镜像
subprocess.run(
["docker", "rmi", "-f", test_image],
capture_output=True,
text=True
)
return result
def run_speed_test(self):
"""
运行速度测试
"""
print("🏁 开始 Docker 镜像加速器速度测试")
print("=" * 60)
results = []
for image in self.test_images:
print(f"\n🚀 测试镜像: {image}")
print("-" * 40)
# 测试默认配置
default_result = self.test_mirror_speed(image)
results.append(default_result)
# 测试各加速器
for mirror in self.mirrors:
mirror_result = self.test_mirror_speed(image, mirror)
results.append(mirror_result)
# 输出测试结果汇总
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("📊 测试结果汇总")
print("=" * 60)
# 按镜像分组显示结果
for image in self.test_images:
print(f"\n📦 镜像: {image}")
print("-" * 30)
image_results = [r for r in results if r["image"] == image]
# 按耗时排序
image_results.sort(key=lambda x: x["duration"] or float('inf'))
for i, result in enumerate(image_results, 1):
status = "✅" if result["success"] else "❌"
duration = f"{result['duration']:.2f}s" if result["duration"] else "失败"
print(f" {i:2d}. {status} {result['mirror']:<20} {duration}")
def main():
"""
主函数
"""
tester = MirrorSpeedTester()
# tester.run_speed_test()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 注意:运行测试会消耗网络流量和时间
# main()
print("镜像加速器速度测试工具准备就绪")
第七章:扩展阅读 - 深入学习资源
7.1 推荐文档
7.2 相关工具
- Docker Compose: 用于定义和运行多容器 Docker 应用程序
- Docker Swarm: Docker 原生集群管理和编排工具
- Kubernetes: 容器编排平台
7.3 最佳实践文章
Docker 镜像加速实施计划甘特图
镜像拉取速度对比饼图
Docker 镜像拉取时序图
🏁 总结
本文详细介绍了 Docker 镜像加速器的配置方法、最佳实践、常见问题及解决方案。通过配置国内镜像加速器,可以显著提升镜像拉取速度,优化开发效率。关键要点总结:
- 加速器选型:选择稳定可靠的国内镜像加速器,如轩辕镜像、毫秒镜像等
- 多加速器配置:配置多个镜像加速器以提高可用性
- 自动化工具:使用 Python 脚本自动化镜像拉取和管理
- 镜像优化:通过多阶段构建等方式优化镜像大小
- 故障排查:掌握常见问题的诊断和解决方法
实践是检验真理的唯一标准,立即动手 为你的 Docker 环境配置镜像加速器吧!






















 5909
5909

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










