今天学了下vuex的使用,写点记录下
首先vuex主要是一个状态管理中心,其实就是个集中更改数据的容器,让不同组件可以使用这套系统
第一步
如何在vue当中使用vuex来管理数据
首先在新建一个store.js文件src/store/store.js
在store.js当中写上

在store.js当中我们主要写四个对象
state,mutations,getters,actions
1.state 状态对象

state对象里面的属性都是存放的状态,即所谓的需要更改的数据
2.mutations 修改状态

mutations 主要是进行state中的状态更改的一些方法
3.getters 计算过滤操作,主要是对数据输出去进行再加工

4.actions 异步修改状态

actions 与mutations 最大的区别在于mutations 是进行同步状态更改,而actions 是异步
5.最后我们需要使用vuex将这些对象暴露出去

注意写法,是 new Vuex.Store({...}),不要写成vue.store
第二步,我们需要在main.js当中进行相应的配置
首先引入我们store.js文件
![]()
然后在Vue实例化中使用 store
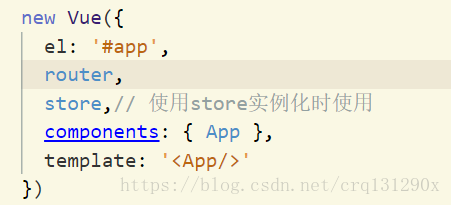
第三步,在对应的组件中去调用对应的方法和状态
注意一点:
action和mutation在组件的methods属性中进行相应的调用
state和getters则是组件在computed属性中进行调用
在这里主要写法分三种,大家可以各自选择,推荐大家用下面这种方式去调用,比较简单


这种写法的弊端在于好像分模块时会找不到对应属性,也可以采取另外两种写法
其实是采用映射的原理将store中mutations的方法映射到组件中methods中的方法当中
然后在组件中来调用
<template>
<div class="count">
{{countG}}
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<hr/>
<h3>{{countNew}}</h3>
<h3> {{ $store.state.count.count }}</h3>
<!-- $store.commit的写法 -->
<!-- $store.commit('add',10)"add是mutations中的方法名 -->
<!-- <input type="button" value="add" @click="$store.commit('add',10)">
<input type="button" value="reduce" @click="$store.commit('reduce')"> -->
<hr/>
<!-- 通过mapMutations的写法 -->
<input type="button" value="add" @click="add(5)">
<!-- <input type="button" value="add2" @click="add2"> -->
<input type="button" value="reduce" @click="reduce">
<hr/>
<input type="button" value="addAction" @click="addAction()">
<input type="button" value="reduceAction" @click="reduceAction">
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import store from '@/store/store' // ????
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
data () {
return {
msg:'Hello Vuex',
msg2:''
}
},
// methods:mapMutations(['add','reduce']),
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add','reduce']),
// add2(){
// this.count
// this.$store.state.count +=1
// }
...mapActions(['addAction','reduceAction'])
},
computed:{
// countNew(){ // 通过computed属性将vuex中的state值赋给countNew属性写法1
// return this.$store.state.count
// },
...mapState({
countNew:state => state.count.count // 传入state返回state.count ,写法2
}),
// ...mapState(["countG"]), //写法3 常用,其实就是新建一个属性countNew,用这个属性来接收store中的state中的数据
countG() {
return this.$store.getters.addC
}
},
mounted(){
console.log(this.$store.state)
console.log(this.countG)
// this.count
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// this.msg2 = this.count// computed中的函数不需要加()即可执行,写法1.2.3
// console.log(this.count)//这里的this.count其实是指computed中的count的函数执行
}
}
</script>







 本文详细介绍如何在Vue项目中运用Vuex进行状态管理,包括创建store、定义state、mutations、getters及actions,以及在组件中调用的三种方法。
本文详细介绍如何在Vue项目中运用Vuex进行状态管理,包括创建store、定义state、mutations、getters及actions,以及在组件中调用的三种方法。
















 1022
1022

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








