Preliminary
-
The bias can also be viewed as the weight of another input component that is always set to 1
-
z=∑iwixiz=\sum_{i} w_{i} x_{i}z=∑iwixi
-
What we learn: The …parameters… of the network
-
Learning the network: Determining the values of these parameters such that the network computes the desired function
-
How to learn a network?
- W^=argminW∫Xdiv(f(X;W),g(X))d \widehat{\boldsymbol{W}}=\underset{W}{\operatorname{argmin}} \int_{X} \operatorname{div}(f(X ; W), g(X)) d W=Wargmin∫Xdiv(f(X;W),g(X))d
- div() is a divergence function thet goes to zero when f(X;W)=g(X)f(X ; W)=g(X)f(X;W)=g(X)
-
But in practice g(x)g(x)g(x) will not have such specification
- Sample g(x)g(x)g(x): just gather training data
Learning
Simple perceptron
do For i=1..Ntraini = 1.. N_{train}i=1..Ntrain
O(xi)=sign(WTXi)O(x_i) = sign(W^TX_i)O(xi)=sign(WTXi)
if O(xi)≠yiO(x_i) \neq y_iO(xi)=yi
W=W+YiXiW = W+Y_iX_iW=W+YiXi
until no more classification errors
A more complex problem
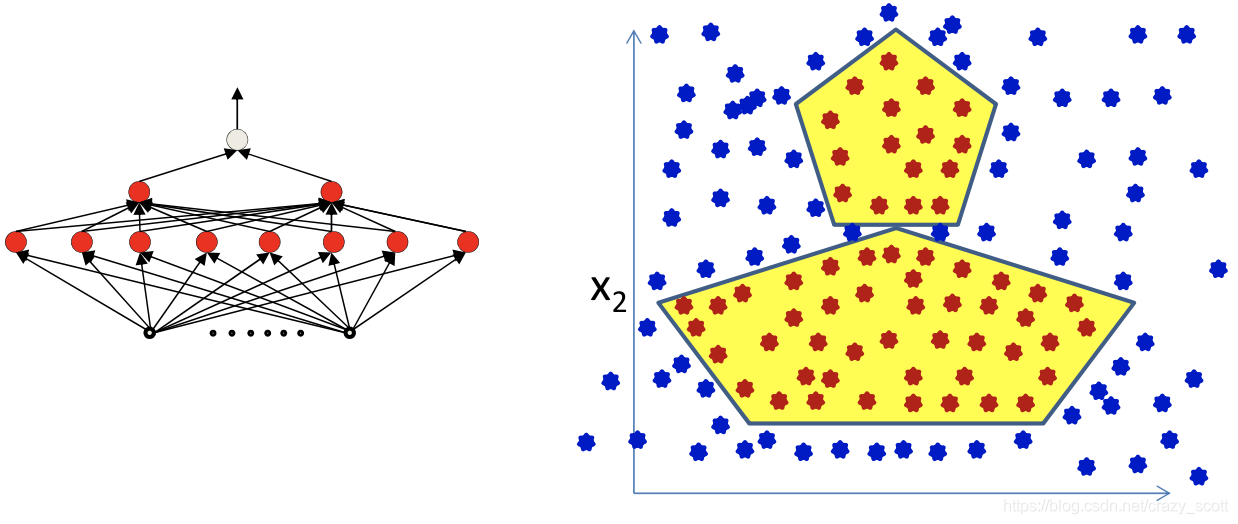
- This can be perfectly represented using an MLP
- But perveptron algorithm require linearly separated labels to be learned in lower-level neurons
- An exponential search over inputs
- So we need differentiable function to compute the change in the output for …small… changes in either the input or the weights
Empirical Risk Minimization
Assuming XXX is a random variable:
W^=argminW∫Xdiv(f(X;W),g(X))P(X)dX=argminWE[div(f(X;W),g(X))]
\begin{aligned}
\widehat{\boldsymbol{W}}=& \underset{W}{\operatorname{argmin}} \int_{X} \operatorname{div}(f(X ; W), g(X)) P(X) d X \\
&=\underset{W}{\operatorname{argmin}} E[\operatorname{div}(f(X ; W), g(X))]
\end{aligned}
W=Wargmin∫Xdiv(f(X;W),g(X))P(X)dX=WargminE[div(f(X;W),g(X))]
Sample g(X)g(X)g(X), where di=g(Xi)+noised_{i}=g\left(X_{i}\right)+ noisedi=g(Xi)+noise, estimate function from the samples
The empirical estimate of the expected error is the average error over the samples
E[div(f(X;W),g(X))]≈1N∑i=1Ndiv(f(Xi;W),di)
E[\operatorname{div}(f(X ; W), g(X))] \approx \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \operatorname{div}\left(f\left(X_{i} ; W\right), d_{i}\right)
E[div(f(X;W),g(X))]≈N1i=1∑Ndiv(f(Xi;W),di)
Empirical average error (Empirical Risk) on all training data
Loss(W)=1N∑idiv(f(Xi;W),di)
\operatorname{Loss}(W)=\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i} \operatorname{div}\left(f\left(X_{i} ; W\right), d_{i}\right)
Loss(W)=N1i∑div(f(Xi;W),di)
Estimate the parameters to minimize the empirical estimate of expected error
W^=argminWLoss(W)
\widehat{\boldsymbol{W}}=\underset{W}{\operatorname{argmin}} \operatorname{Loss}(W)
W=WargminLoss(W)
Problem statement
-
Given a training set of input-output pairs
(X1,d1),(X2,d2),…,(XN,dN) \left(\boldsymbol{X}_{1}, \boldsymbol{d}_{1}\right),\left(\boldsymbol{X}_{2}, \boldsymbol{d}_{2}\right), \ldots,\left(\boldsymbol{X}_{N}, \boldsymbol{d}_{N}\right) (X1,d1),(X2,d2),…,(XN,dN)
- Minimize the following function
Loss(W)=1N∑idiv(f(Xi;W),di) \operatorname{Loss}(W)=\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i} \operatorname{div}\left(f\left(X_{i} ; W\right), d_{i}\right) Loss(W)=N1i∑div(f(Xi;W),di)
- This is problem of function minimization
- An instance of optimization





 本文探讨了神经网络的基本概念,包括偏置项的作用、权重更新规则及最小化经验风险的策略。通过解析感知器算法和多层感知器,阐述了如何通过训练数据集调整网络参数,实现对复杂问题的解决。
本文探讨了神经网络的基本概念,包括偏置项的作用、权重更新规则及最小化经验风险的策略。通过解析感知器算法和多层感知器,阐述了如何通过训练数据集调整网络参数,实现对复杂问题的解决。

















 309
309

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








