参考网址 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/xuezhisdc/article/details/54634080
Eigen中的求解Ax=b问题,应该采用什么方法, 才能较快的实现出来呢? 主要结果是这样的:
Eigen中有一些求解稀疏系数矩阵的线性方程组。由于稀疏矩阵的特殊的表示方式,因此获得较好的性能需要格外注意。查看《Eigen教程3 - 稀疏矩阵操作》,了解更多有关稀疏矩阵的内容。本文列出了Eigen中的稀疏求解器。同时也介绍了所有线性求解器的共同步骤。用户可以根据矩阵的性质,准确度的要求,来调整求解步骤,以提升代码的性能。注意:没有必要深入了解这些步骤后面隐藏的内容。
本文最后一部分列出了一个基准例程,可以用于窥探所有的求解器的性能。

稀疏求解器的列表
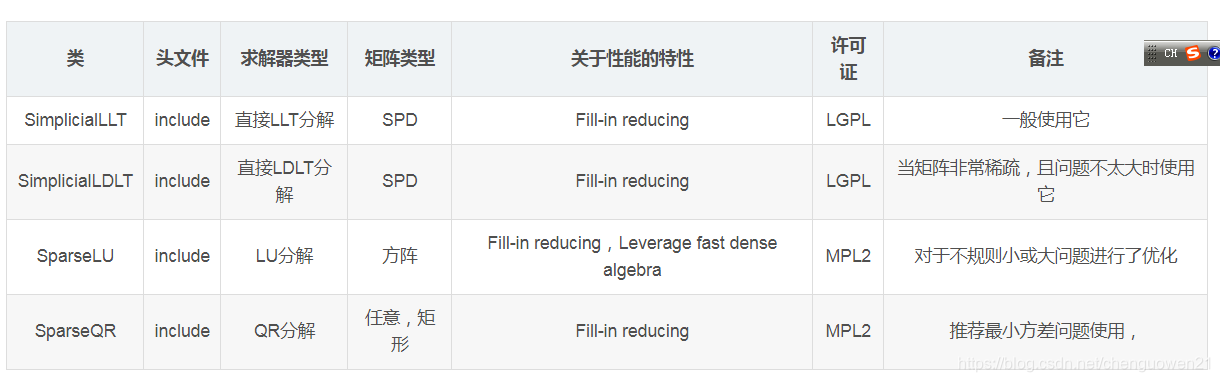
Eigen提供了一系列的内建求解器和封装了一些外部求解器库。
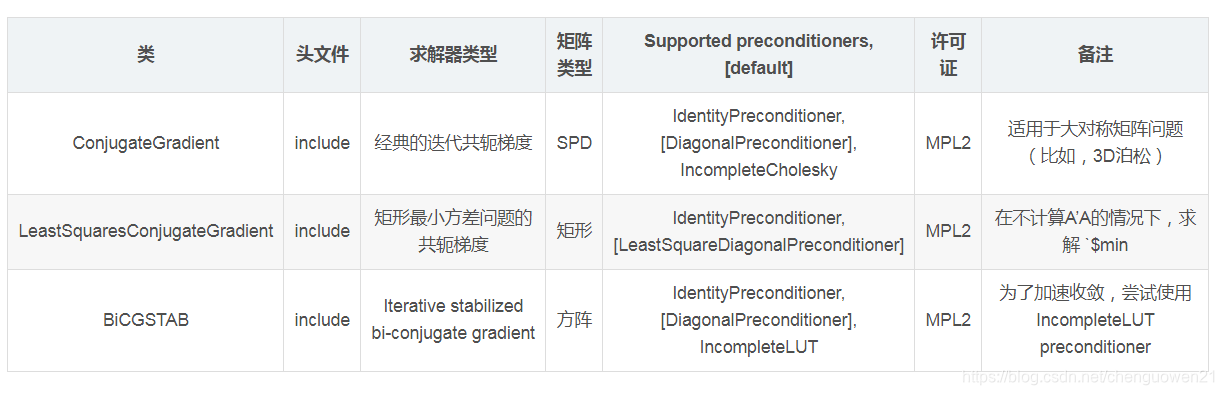
内建的直接求解器
* 说明:此处的SPD (symmetric positive definite) 表示对称正定。
用Auto最快 将Tolerance设置的大一些 是更好的。
#include <Eigen/Sparse> //system solving and Eigen::SparseMatrix
#include <ctime> //measure time to execute
#include <unsupported/Eigen/SparseExtra> //loadMarket
// Use typedefs instead of using if c++11 is not supported by your compiler
using SpMatrix = Eigen::SparseMatrix<double>;
using Matrix = Eigen::MatrixXd;
int main() {
// Use multi-threading. If you don't have OpenMP on your system
// it will simply use 1 thread and it will not crash. So do not worry about
// that.
Eigen::initParallel();
Eigen::setNbThreads(6);
// Load system matrices
SpMatrix A, B;
Eigen::loadMarket(A, "/home/iason/Desktop/Thesis/build/A.mtx");
Eigen::loadMarket(B, "/home/iason/Desktop/Thesis/build/B.mtx");
// Initialize the clock which will measure the solvers
std::clock_t start;
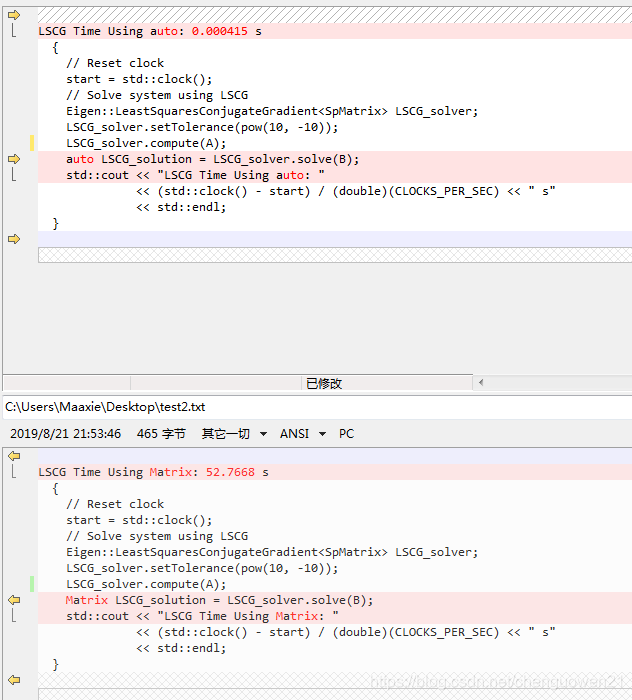
LSCG Time Using auto: 0.000415 s
{
// Reset clock
start = std::clock();
// Solve system using LSCG
Eigen::LeastSquaresConjugateGradient<SpMatrix> LSCG_solver;
LSCG_solver.setTolerance(pow(10, -10));
LSCG_solver.compute(A);
// Use auto specifier to hold the return value of solve. Eigen::Solve object
// is being returned
auto LSCG_solution = LSCG_solver.solve(B);
std::cout << "LSCG Time Using auto: "
<< (std::clock() - start) / (double)(CLOCKS_PER_SEC) << " s"
<< std::endl;
}
LSCG Time Using Matrix: 52.7668 s
{
// Reset clock
start = std::clock();
// Solve system using LSCG
Eigen::LeastSquaresConjugateGradient<SpMatrix> LSCG_solver;
LSCG_solver.setTolerance(pow(10, -10));
LSCG_solver.compute(A);
// Use Matrix specifier instead of auto. Implicit conversion taking place(?)
Matrix LSCG_solution = LSCG_solver.solve(B);
std::cout << "LSCG Time Using Matrix: "
<< (std::clock() - start) / (double)(CLOCKS_PER_SEC) << " s"
<< std::endl;
}
SimplicialLDLT Time Using auto: 0.216593 s
{
// Reset clock
start = std::clock();
// Solve system using SimplicialLDLT
Eigen::SimplicialLDLT<SpMatrix> SLDLT_solver;
SLDLT_solver.compute(A.transpose() * A);
auto SLDLT_solution = SLDLT_solver.solve(A.transpose() * B);
std::cout << "SimplicialLDLT Time Using auto: "
<< (std::clock() - start) / (double)(CLOCKS_PER_SEC) << " s"
<< std::endl;
}
SimplicialLDLT Time Using Matrix: 0.239976 s
{
// Reset clock
start = std::clock();
// Solve system using SimplicialLDLT
Eigen::SimplicialLDLT<SpMatrix> SLDLT_solver;
SLDLT_solver.compute(A.transpose() * A);
// Use Matrix specifier instead of auto. Implicit conversion taking place(?)
Matrix SLDLT_solution = SLDLT_solver.solve(A.transpose() * B);
std::cout << "SimplicialLDLT Time Using Matrix: "
<< (std::clock() - start) / (double)(CLOCKS_PER_SEC) << " s"
<< std::endl;
}
return 0;上述代码的运行时间分别为:
LSCG Time Using auto : 0.000415 s
LSCG Time Using Matrix: 52.7668 s
SimplicialLDLT Time Using auto: 0.216593 s
SimplicialLDLT Time Using Matrix: 0.239976 s
As the results proove when I use Eigen::MatrixXd instead of auto I get the situation ggael described in one of his comments, namely LSCG not achieving a solution without setting a higher tolerance and SimplicialLDLT being much faster.
- Are the solvers actually solving the system when I use auto?
- Is the Solver object being implicitly converted to a Matrix Object when I use the Matrix specifier? Since When using LSCG the only change in the first two cases is the use of auto and Matrix respectively,does this implicit conversion to Matrix take 52.7668-0.000415 seconds?
- Is there a faster way to extract the solution Matrix from the Solve object?
由于A'*A是对称正定,用LDLT的求解方法可以更快
Given the sparsity pattern of your matrix A, forming the normal equation explicitly and using a direct solver such as SimplicialLDLT will be much faster. Also better use a dense type for B since it is dense anyway and that internally, all solvers will convert the sparse right-hand-side to dense columns:
Eigen::MatrixXd dB = B; // or directly fill dB
Eigen::SimplicialLDLT<SpMatrix> solver;
solver.compute(A.transpose()*A);
MatrixXd x = solver.solve(A.transpose()*dB);This takes 0.15s, in contrast to 6s for LSCG after the setting the tolerance of LSCG to 1E-14.








 本文探讨了使用Eigen库求解线性方程组Ax=b的方法,特别是针对稀疏矩阵的情况。通过对比不同求解器如LSCG和SimplicialLDLT的性能,发现对于对称正定矩阵,SimplicialLDLT求解器更为高效。文章还提供了代码示例和运行时间对比。
本文探讨了使用Eigen库求解线性方程组Ax=b的方法,特别是针对稀疏矩阵的情况。通过对比不同求解器如LSCG和SimplicialLDLT的性能,发现对于对称正定矩阵,SimplicialLDLT求解器更为高效。文章还提供了代码示例和运行时间对比。
















 1407
1407

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








