
转换流可以规定码型:
package properties;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class I {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String directoryPath = "E:\\mytemp";
File file = new File(directoryPath);//在此路径上创建对象来实现一系列操作
if (!file.exists()){
if (file.mkdir()){//创建文件夹,一定要会
System.out.println("文件夹创建成功");
}else{
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
String filePath = directoryPath + "\\hello.txt";//这种表示方式要会,特别是前面的\\
file = new File(filePath);//创建新的引用
if (!file.exists()){
if (file.createNewFile()){
System.out.println("hello创建成功");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
bufferedWriter.write("hello,");
bufferedWriter.close();
}else{
System.out.println("文件创建失败");
}
}else{
System.out.println("文件已经存在,不重复创建了");
}
}
}
小tips :字节流和字符流,字节流是最底层的流,字符流呢高级一点,但是我们使用的过程中,字符流的效率高一点,所以我们会用到转换流,将字节流转换成字符流,这只是其中的一方面,另外一个方面是,字节流能人为规定编码类型,比如读取的时候能够将其提前规定好编码类型,因此,九江前面的学习内容串联在一起了。像下面一样改进。

package properties;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class P {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "E:\\hello.txt";
BufferedReader br = null;
String line = "";
int i = 1;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));//考虑到作用域问题,将其分为两部来看。
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
//按照行来读取
System.out.println(i++ + line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (br != null){
br.close();
}
}
}
}
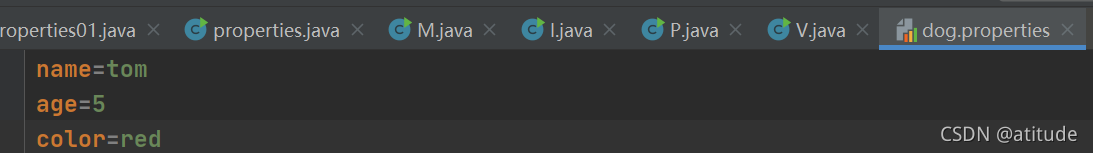
package properties;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class V {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "src\\properties\\dog.properties";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileReader(filePath));
// properties.list(System.out);//打印输出
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
// System.out.println(name);
//或者这一样
String age1 = properties.getProperty("age");
int age = Integer.parseInt(age1);
String color = properties.getProperty("color");
// String o = properties.get(name) + "";Object -->Sting
// System.out.println(o);
Dog dog = new Dog(name, age, color);
System.out.println("=======");
System.out.println(dog);
//将其序列化到dog.dat文件
String serFilePath = "e:\\dog.dat";
//对象流
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serFilePath));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(dog);//将狗写进去
objectOutputStream.close();//序列化结束
}
//编写一个方法实现反序列化
@Test
public void m() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String serFilePath = "e:\\dog.dat";
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serFilePath));
Dog dog = (Dog)objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println("反序列化后的结果");
System.out.println(dog);
objectInputStream.close();
}
}
class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Dog(String name, int age, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Java中流的转换流概念,重点展示了如何通过BufferedReader和FileReader进行字节流到字符流的转换,并探讨了如何在创建流时指定编码。同时涵盖了编码设置对字符流效率的影响以及实际编程中的应用场景。
本文详细介绍了Java中流的转换流概念,重点展示了如何通过BufferedReader和FileReader进行字节流到字符流的转换,并探讨了如何在创建流时指定编码。同时涵盖了编码设置对字符流效率的影响以及实际编程中的应用场景。
















 2219
2219

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








