欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
问题
给定3个不同共线的点p1,p2,p3, 和点p4。判断p4是与前3点外接圆关系,圆外,圆内,圆上。
求圆法
先利用三点求出圆,然后判断p4与圆的距离。
求圆可以使用解方程和尺规作图。
解方程
圆的方程
(
x
−
a
)
2
+
(
y
−
b
)
2
=
r
2
(x-a)^2+(y-b)^2=r^2
(x−a)2+(y−b)2=r2
推导解方程过程如下:
将点代入得到3条方程
( x 1 − a ) 2 + ( y 1 − b ) 2 = r 2 . . . . ( 1 ) (x_1-a)^2+(y_1-b)^2=r^2\ ....(1) (x1−a)2+(y1−b)2=r2 ....(1)
( x 2 − a ) 2 + ( y 2 − b ) 2 = r 2 . . . . ( 2 ) (x_2-a)^2+(y_2-b)^2=r^2\ ....(2) (x2−a)2+(y2−b)2=r2 ....(2)
( x 3 − a ) 2 + ( y 3 − b ) 2 = r 2 . . . . ( 3 ) (x_3-a)^2+(y_3-b)^2=r^2\ ....(3) (x3−a)2+(y3−b)2=r2 ....(3)
令(1)=(2),(2)=(3)并展开,得到
x 1 2 − 2 x 1 a + a 2 + y 1 2 − 2 y 1 b + b 2 = x 2 2 − 2 x 2 a + a 2 + y 2 2 − 2 y 2 b + b 2 x_1^2-2x_1a+a^2+y_1^2-2y_1b+b^2=x_2^2-2x_2a+a^2+y_2^2-2y_2b+b^2 x12−2x1a+a2+y12−2y1b+b2=x22−2x2a+a2+y22−2y2b+b2
x 2 2 − 2 x 2 a + a 2 + y 2 2 − 2 y 2 b + b 2 = x 3 2 − 2 x 3 a + a 2 + y 3 2 − 2 y 3 b + b 2 x_2^2-2x_2a+a^2+y_2^2-2y_2b+b^2=x_3^2-2x_3a+a^2+y_3^2-2y_3b+b^2 x22−2x2a+a2+y22−2y2b+b2=x32−2x3a+a2+y32−2y3b+b2
移项,抵消a2,b2 得到:
x 1 2 − x 2 2 − 2 ( x 1 − x 2 ) a + y 1 2 − y 2 2 − 2 ( y 1 − y 2 ) b = 0 . . . . . ( 3 ) x_1^2-x_2^2-2(x_1-x_2)a+y_1^2-y_2^2-2(y_1-y_2)b=0\ .....(3) x12−x22−2(x1−x2)a+y12−y22−2(y1−y2)b=0 .....(3)
x 1 2 − x 3 2 − 2 ( x 1 − x 3 ) a + y 1 2 − y 3 2 − 2 ( y 1 − y 3 ) b = 0 . . . . . ( 4 ) x_1^2-x_3^2-2(x_1-x_3)a+y_1^2-y_3^2-2(y_1-y_3)b=0 \ .....(4) x12−x32−2(x1−x3)a+y12−y32−2(y1−y3)b=0 .....(4)
利用(3)式利到
b
=
x
1
2
−
x
2
2
−
2
(
x
1
−
x
2
)
a
+
y
1
2
−
y
2
2
2
(
y
1
−
y
2
)
b=\frac {x_1^2-x_2^2-2(x_1-x_2)a+y_1^2-y_2^2}{2(y_1-y_2)}
b=2(y1−y2)x12−x22−2(x1−x2)a+y12−y22
将b代入到(4)式得到
x 1 2 − x 3 2 − 2 ( x 1 − x 3 ) a + y 1 2 − y 3 2 − 2 ( y 1 − y 3 ) x 1 2 − x 2 2 − 2 ( x 1 − x 2 ) a + y 1 2 − y 2 2 2 ( y 1 − y 2 ) = 0 x_1^2-x_3^2-2(x_1-x_3)a+y_1^2-y_3^2-2(y_1-y_3)\frac {x_1^2-x_2^2-2(x_1-x_2)a+y_1^2-y_2^2}{2(y_1-y_2)}=0 x12−x32−2(x1−x3)a+y12−y32−2(y1−y3)2(y1−y2)x12−x22−2(x1−x2)a+y12−y22=0
=>
x 1 2 − x 3 2 + y 1 2 − y 3 2 − ( y 1 − y 3 ) x 1 2 − x 2 2 + y 1 2 − y 2 2 ( y 1 − y 2 ) = [ 2 ( x 1 − x 3 ) − 2 ( y 1 − y 3 ) ( x 1 − x 2 ) ( y 1 − y 2 ) ] a x_1^2-x_3^2+y_1^2-y_3^2-(y_1-y_3)\frac {x_1^2-x_2^2+y_1^2-y_2^2}{(y_1-y_2)}=[2(x_1-x_3)-\frac {2(y_1-y_3)(x_1-x_2)}{(y_1-y_2)}]a x12−x32+y12−y32−(y1−y3)(y1−y2)x12−x22+y12−y22=[2(x1−x3)−(y1−y2)2(y1−y3)(x1−x2)]a
=>
a = x 1 2 − x 3 2 + y 1 2 − y 3 2 − ( y 1 − y 3 ) x 1 2 − x 2 2 + y 1 2 − y 2 2 ( y 1 − y 2 ) 2 ( x 1 − x 3 ) − 2 ( y 1 − y 3 ) ( x 1 − x 2 ) a ( y 1 − y 2 ) a=\frac {x_1^2-x_3^2+y_1^2-y_3^2-(y_1-y_3)\frac {x_1^2-x_2^2+y_1^2-y_2^2}{(y_1-y_2)}}{2(x_1-x_3)-\frac {2(y_1-y_3)(x_1-x_2)a}{(y_1-y_2)}} a=2(x1−x3)−(y1−y2)2(y1−y3)(x1−x2)ax12−x32+y12−y32−(y1−y3)(y1−y2)x12−x22+y12−y22
得到a,b; 代入任意一点得到r
r = ( x 1 − a ) 2 + ( y 1 − b ) 2 r=\sqrt{(x_1-a)^2+(y_1-b)^2} r=(x1−a)2+(y1−b)2
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.6f %.6f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() const {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && fabs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
;
class Point3D {
public:
double x, y, z;
Point3D() {}
Point3D(double a, double b, double c) :x(a), y(b), z(c) {}
Point3D(const Point3D& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y),z(p.z) {}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y+z*z);
}
Point3D operator -(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x - p.x, y - p.y, z-p.z);
}
Point3D operator +(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x + p.x, y + p.y, z+p.z);
}
Point3D operator *(double d)const {
return Point3D(x * d, y * d, z*d);
}
Point3D operator /(double d)const {
return Point3D(x / d, y / d, z/d);
}
void operator -=(Point3D& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
z -= p.z;
}
void operator +=(Point3D& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
z += p.z;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
z *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
};
// 向量操作
Point3D cross(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return Point3D(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, -a.x * b.z + a.z * b.x,
a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x);
}
double dot(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y+a.z*b.z;
}
pair<Point, double> getCircle(const vector<Point> &ps) {
Point center;
double l = ps[0].dis2()-ps[2].dis2() - (ps[0].y-ps[2].y)*(ps[0].dis2() - ps[1].dis2())/(ps[0].y-ps[1].y);
double r = -2 * (ps[0].x - ps[1].x) * (ps[0].y - ps[2].y) / (ps[0].y - ps[1].y) + 2 * (ps[0].x - ps[2].x);
center.x = l / r;
center.y = (ps[0].dis2() - ps[1].dis2() -2 * (ps[0].x - ps[1].x) * center.x) / (2 * (ps[0].y - ps[1].y));
double raduis = (ps[0] - center).dis();
return { center, raduis };
}
int main() {
vector<Point> ps(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
ps[i].in();
//ps[i].out();
}
auto res = getCircle(ps);
res.first.out();
printf("%.6f\n", res.second);
for (auto p : ps) {
printf("%.6f\n",(p - res.first).dis());
}
return 0;
}
/*
0.234234 0.33424
-234.33324 2342.8883
3938.2343 -98723.333
0 1
1 0
-1 0
*/
测试结果
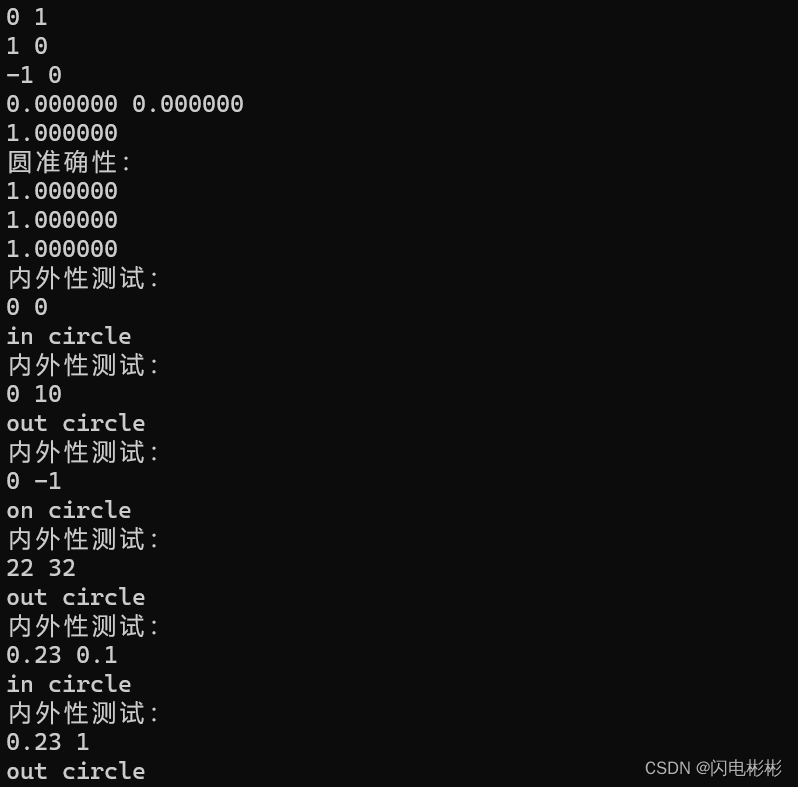
尺规作图找圆心
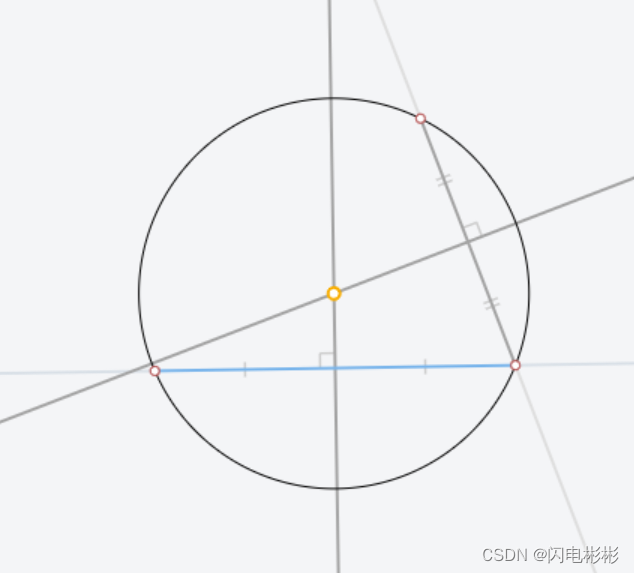
根据圆定义只要找到1点O到所有点距离相同即可。
可以使用中垂线交点得到圆心。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.6f %.6f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() const {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && fabs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
/*
点p 到 p+r 表示线段1
点q 到 q+s 表示线段2
线段1 上1点用 p' = p+t*r (0<=t<=1)
线段2 上1点用 q' = q+u*s (0<=u<=1)
让两式相等求交点 p+t*r = q+u*s
两边都叉乘s
(p+t*r)Xs = (q+u*s)Xs
pXs + t*rXs = qXs
t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
同理,
u = (p-q)Xr/(sXr) -> u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
以下分4种情况:
1. 共线,sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr==0, 计算 (q-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t0,
计算(q+s-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t1,查看[t0, t1]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
如果t0>t1, 则比较[t1, t0]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
t0 = (q-p)*r/(r*r)
t1 = (q+s-p)*r/(r*r) = t0 + s · r / (r · r)
2. 平行sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr!=0
3. 0<=u<=1 && 0<=t<=1 有交点
4. 其他u, t不在0到范围内,没有交点。
*/
Point intersection(Point &q, Point &s, Point &p, Point &r) {
// 计算 (q-p)Xr
auto qpr = cross(q - p, r);
auto qps = cross(q - p, s);
auto rXs = cross(r, s);
// 求解t, u
// t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
auto t = qps / rXs;
// u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
auto u = qpr / rXs;
Point p0 = p + r * t;
return p0;
}
// 点法式求交得到圆心和半径
pair<Point, double> getCircle(const vector<Point> &ps) {
Point center;
Point l1 = (ps[0] + ps[1]) / 2;
Point l2 = (ps[0] + ps[2]) / 2;
Point d1 = (ps[1] - ps[0]);
d1 /= d1.dis();
d1 = Point(d1.y, -d1.x); // 旋转90度
Point d2 = (ps[2] - ps[0]);
d2 /= d2.dis();
d2 = Point(d2.y, -d2.x);
center = intersection(l1, d1, l2, d2);
double r = (ps[0] - center).dis();
return { center, r };
}
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d < 0)return -1;
return 1;
}
int main() {
vector<Point> ps(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
ps[i].in();
//ps[i].out();
}
auto res = getCircle(ps);
res.first.out();
printf("%.6f\n", res.second);
printf("圆准确性:\n");
for (auto p : ps) {
printf("%.6f\n",(p - res.first).dis());
}
int n = 10;
while (n--) {
printf("内外性测试:\n");
Point p;
p.in();
auto d = cmp((p - res.first).dis() - res.second);
if (d == 0)puts("on circle");
else if (d < 0)puts("in circle");
else puts("out circle");
}
return 0;
}
/*
0.234234 0.33424
-234.33324 2342.8883
3938.2343 -98723.333
0 1
1 0
-1 0
*/
测试结果
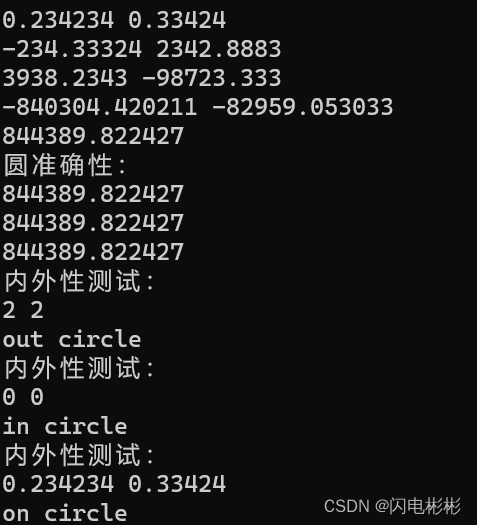
利用三维抛物面判断
性质
设有圆O,将圆上所有点映射到f(x, y) = x2+y2 抛物面上。
则有如下性质。
性质1所有映射点在同一个平面上。
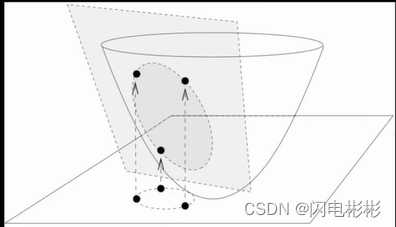
证明:
x, y, z关系如下:
根据映射公式,z=x2+y2。
同时,满足平面圆
(
x
−
x
c
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
c
)
2
=
r
2
(x-x_c)^2+(y-y_c)^2=r^2
(x−xc)2+(y−yc)2=r2
展开后得
x
2
−
2
x
⋅
x
c
+
x
c
2
+
y
2
−
2
y
⋅
y
c
+
y
c
2
=
r
2
x^2-2x\cdot x_c+x_c^2+y^2-2y\cdot y_c+y_c^2=r^2
x2−2x⋅xc+xc2+y2−2y⋅yc+yc2=r2
替换 x2+y2
−
2
x
c
⋅
x
−
2
y
c
⋅
y
+
z
+
x
c
2
+
y
c
2
−
r
2
=
0
-2x_c\cdot x-2y_c\cdot y + z+ x_c^2 + y_c^2 -r^2=0
−2xc⋅x−2yc⋅y+z+xc2+yc2−r2=0
x,y,z满足平面表达关系,所以所有映射点在同一个平面上。
性质2可以根据抛物面映射判断点是与圆的关系。
从上述性质可以看出,圆在抛物面上的映射所形成的曲线是一个平面与抛物面的交线。
通过平面可以把抛物面分成两个部分,一个是像一个碗状,另外是其他部分。
假设平面的法向是朝上,则可以通过映射点与平面的关系判断与圆的关系。
距离d
d=0, 在圆上。
d<0, 在圆内。
d>0, 在圆外。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.6f %.6f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() const {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return fabs(x - a.x) < EPS && fabs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Point3D {
public:
double x, y, z;
Point3D() {}
Point3D(double a, double b, double c) :x(a), y(b), z(c) {}
Point3D(const Point3D& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), z(p.z) {}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
}
Point3D operator -(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x - p.x, y - p.y, z - p.z);
}
Point3D operator +(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x + p.x, y + p.y, z + p.z);
}
Point3D operator *(double d)const {
return Point3D(x * d, y * d, z * d);
}
Point3D operator /(double d)const {
return Point3D(x / d, y / d, z / d);
}
void operator -=(Point3D& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
z -= p.z;
}
void operator +=(Point3D& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
z += p.z;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
z *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
};
// 向量操作
Point3D cross(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return Point3D(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, -a.x * b.z + a.z * b.x,
a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x);
}
double dot(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
}
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d < 0)return -1;
return 1;
}
int inCircle(Point p0, Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
Point d1 = p1 - p0;
Point d2 = p2 - p0;
if (cross(d1, d2) < 0)return inCircle(p0, p2, p1, p3); // 保证平面法向向上
// 构建映射点
Point3D lift0(p0.x, p0.y, p0.dis2());
Point3D lift1(p1.x, p1.y, p1.dis2());
Point3D lift2(p2.x, p2.y, p2.dis2());
Point3D lift3(p3.x, p3.y, p3.dis2());
Point3D z1(lift1-lift0), z2(lift2-lift0);
Point3D normal = cross(z1, z2); // 计算平面法向
double project = dot(normal, lift3-lift0); // 计算点到平面距离
return cmp(project);
}
int main() {
vector<Point> ps(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
ps[i].in();
//ps[i].out();
}
int n = 10;
while (n--) {
printf("内外性测试:\n");
Point p;
p.in();
auto d = inCircle(ps[0], ps[1], ps[2], p);
if (d == 0)puts("on circle");
else if (d < 0)puts("in circle");
else puts("out circle");
}
return 0;
}
/*
0.234234 0.33424
-234.33324 2342.8883
3938.2343 -98723.333
0 1
1 0
-1 0
*/
测试

本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。








 博客围绕给定3个不共线点p1、p2、p3和点p4,探讨判断p4与前三点外接圆关系的方法。介绍了求圆法,包括解方程和尺规作图找圆心;还阐述利用三维抛物面判断,通过将圆上点映射到抛物面,根据映射点与平面关系判断点与圆的位置。
博客围绕给定3个不共线点p1、p2、p3和点p4,探讨判断p4与前三点外接圆关系的方法。介绍了求圆法,包括解方程和尺规作图找圆心;还阐述利用三维抛物面判断,通过将圆上点映射到抛物面,根据映射点与平面关系判断点与圆的位置。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








