单链表主类
检测思路
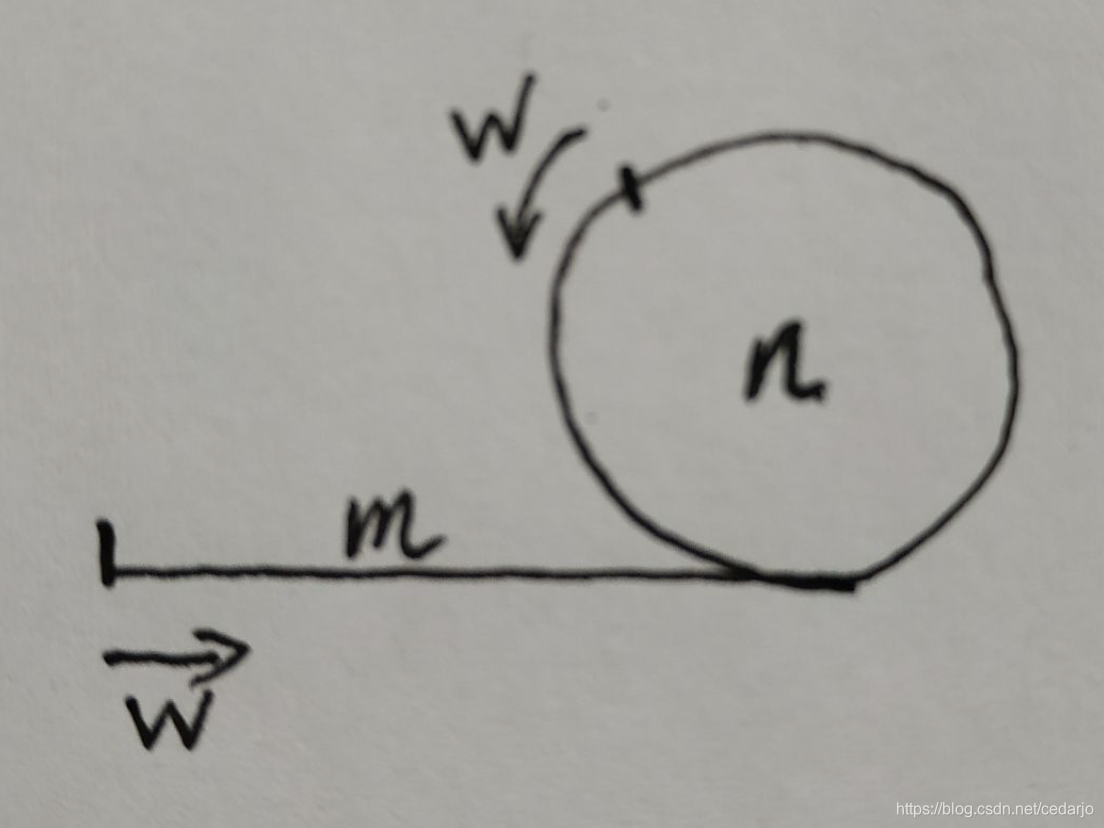
假设一个单链表是环形链表,那么该链表的元素总数可分为两部分
size = m + n
其中m是直线部分,n是环形部分
假想这是一个跑道,从直线跑道为起点,之后进入环形跑道,然后一直绕着环形跑道跑
现在有两个人一起从起点出发,速度不一致,快的速度为v,慢的速度为w,有v>w>0
假设两人足够有力量跑下去,那么这两人会不会在环形跑道的某点相遇呢?

经过时间t之后,如果满足如下公式,则两人可再次相遇
vt - wt = kn
其中k为整数
另一种说法就是:足够时间后,跑快的人是否一定可以超跑慢的人正好整数圈呢?
答案是肯定的,n就算再大,也经不起足够长的时间t,v-w就算再小,只要是个正数,就一定能在某个时间t后正好甩另一个人正好整数圈
单链表中环的检测就是利用了这个思想
代码
public boolean isCircle() {
// 边界
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
// 相同的起跑线
SinglyLinkedNode<T> faster = header, lower = header;
// 如果跑快的人到达了终点,说明这条跑道没有环形部分
while (faster != null && faster.getNext() != null) {
// 跑慢的人一次跑一步
lower = lower.getNext();
// 跑快的人一次跑两步
faster = faster.getNext().getNext();
// 如果两人相遇,表示有环形部分
if (lower == faster) {
return true;
}
// 两人未相遇则继续跑(根据前边的简单说明,有环形部分则一定会在某时某刻相遇,没有环形部分,则跑快的人肯定会先跑完,所以不会死循环)
}
return false;
}
环形入口定位思路
假定单链表确实存在环,接下来看怎么定位环的入口位置
在实现代码中可以看到,假定跑快的人速度为2,跑慢的人速度为1。
即v=2, w=1
带入上述公式vt - wt = kn得
t = kn
现在来看下跑快的人和跑慢的人各跑了多远
跑快的人:2kn
跑慢的人:kn
因为是在环上相遇,可计算出两人刚才各在环上跑了多远
跑快的人:2kn - m
跑慢的人:kn - m
现在暂时只考虑环上部分,他二人进入环形跑道的入口就是要定位的点,只要跑了整数圈就肯定还会回到改点。从二人已经在环上跑的路程来看,他们现在距离入口的距离相同,都是m,正好是直线跑道的距离。
而如果现在让刚才跑快的人休息,跑慢的人继续按原速度w=1跑,另外有一个人从直线的起点也按w=1开始跑,那么他二人一定会在环的入口相遇
代码
public SinglyLinkedNode<T> circleStartNode() {
// 这里修改了isCircle方法的返回值为第一次相遇的节点位置
SinglyLinkedNode<T> one = isCircle();
if (one == null) {
return null;
}
SinglyLinkedNode<T> another = header;
while (one != another) {
one = one.getNext();
another = another.getNext();
}
return one;
}
环的长度思路
回到刚才快慢二人在环上相遇,因为二人的速度差是1,所以同一起点出发,不会出现某时刻快的人超过慢的人的问题
v=2, w=1
这是个追及问题,经过时间t后,快的人会正好超过慢的人一圈,即n
vt - wt = n带入求解t = n
所以t就等于环的长度值
代码
public int circleLength() {
SinglyLinkedNode<T> start = isCircle();
if (start == null) {
return 0;
}
SinglyLinkedNode<T> faster = start, lower = start;
int length = 0;
while (length == 0 || faster != lower) {
lower = lower.getNext();
faster = faster.getNext().getNext();
length++;
}
return length;
}
测试结果
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G;
isCircle ? false
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> a
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : A; index[8] : B; index[9] : C;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : A
circle length : 7
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> b
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : B; index[8] : C; index[9] : D;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : B
circle length : 6
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> c
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : C; index[8] : D; index[9] : E;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : C
circle length : 5
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g - > d
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : D; index[8] : E; index[9] : F;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : D
circle length : 4
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> e
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : E; index[8] : F; index[9] : G;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : E
circle length : 3
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> f
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : F; index[8] : G; index[9] : F;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : F
circle length : 2
a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g -> g
index[0] : A; index[1] : B; index[2] : C; index[3] : D; index[4] : E; index[5] : F; index[6] : G; index[7] : G; index[8] : G; index[9] : G;
isCircle ? true
circle start node : G
circle length : 1





 本文介绍了如何使用快慢指针检测单链表中的环,详细阐述了检测思路,包括当快慢指针在环内相遇时如何定位环的入口,以及如何计算环的长度。通过具体的Java代码实现,配合测试结果,充分解释了算法的逻辑和有效性。
本文介绍了如何使用快慢指针检测单链表中的环,详细阐述了检测思路,包括当快慢指针在环内相遇时如何定位环的入口,以及如何计算环的长度。通过具体的Java代码实现,配合测试结果,充分解释了算法的逻辑和有效性。
















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








