- partition
- partitioner
- compute func
- dependency
- preferredLocation
trait Partition extends Serializable {
// Get the partition's index within its parent RDD
def index: Int
// A better default implementation of HashCode
override def hashCode(): Int = index
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = super.equals(other)
}private[spark] class ShuffledRDDPartition(val idx: Int) extends Partition {
override val index: Int = idx
} override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
Array.tabulate[Partition](part.numPartitions)(i => new ShuffledRDDPartition(i))
}JdbcRDD:
private[spark] class JdbcPartition(idx: Int, val lower: Long, val upper: Long) extends Partition
override def index: Int = idx
}
val jdbcDF = spark.read
.format("jdbc")
.option("url", "jdbc:postgresql:dbserver")
.option("dbtable", "schema.tablename")
.option("user", "username")
.option("password", "password")
.option("lowerBound", 1)
.option("upperBound", 100)
.option("numPartitions", 3)
.load()
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
// bounds are inclusive, hence the + 1 here and - 1 on end
val length = BigInt(1) + upperBound - lowerBound
(0 until numPartitions).map { i =>
val start = lowerBound + ((i * length) / numPartitions)
val end = lowerBound + (((i + 1) * length) / numPartitions) - 1
new JdbcPartition(i, start.toLong, end.toLong)
}.toArray
}HadoopRDD:
private[spark] class HadoopPartition(rddId: Int, override val index: Int, s: InputSplit)
extends Partition {
val inputSplit = new SerializableWritable[InputSplit](s)
override def hashCode(): Int = 31 * (31 + rddId) + index
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = super.equals(other)
/**
* Get any environment variables that should be added to the users environment when running pipes
* @return a Map with the environment variables and corresponding values, it could be empty
*/
def getPipeEnvVars(): Map[String, String] = {
val envVars: Map[String, String] = if (inputSplit.value.isInstanceOf[FileSplit]) {
val is: FileSplit = inputSplit.value.asInstanceOf[FileSplit]
// map_input_file is deprecated in favor of mapreduce_map_input_file but set both
// since it's not removed yet
Map("map_input_file" -> is.getPath().toString(),
"mapreduce_map_input_file" -> is.getPath().toString())
} else {
Map()
}
envVars
}
}override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
val jobConf = getJobConf()
// add the credentials here as this can be called before SparkContext initialized
SparkHadoopUtil.get.addCredentials(jobConf)
val allInputSplits = getInputFormat(jobConf).getSplits(jobConf, minPartitions)
val inputSplits = if (ignoreEmptySplits) {
allInputSplits.filter(_.getLength > 0)
} else {
allInputSplits
}
val array = new Array[Partition](inputSplits.size)
for (i <- 0 until inputSplits.size) {
array(i) = new HadoopPartition(id, i, inputSplits(i))
}
array
}Partition数量太少 ,太少的影响显而易见,就是资源不能充分利用,例如local模式下,有16core,但是Partition数量仅为8的话,有一半的core没利用到。
Partition数量太多,资源利用没什么问题,但是导致task过多,task的序列化和传输的时间开销增大
调整:reparation是coalesce(numPartitions, shuffle = true),repartition不仅会调整Partition数,也会将Partitioner修改为hashPartitioner,产生shuffle操作。coalesce函数可以控制是否shuffle,但当shuffle为false时,只能减小Partition数,无法增大
abstract class Partitioner extends Serializable {
//< 返回 partition 数量
def numPartitions: Int
//< 返回 key 应该属于哪个
partition def getPartition(key: Any): Int
}object Partitioner {
def defaultPartitioner(rdd: RDD[_], others: RDD[_]*): Partitioner = {
val rdds = (Seq(rdd) ++ others)
val hasPartitioner = rdds.filter(_.partitioner.exists(_.numPartitions > 0))
val hasMaxPartitioner: Option[RDD[_]] = if (hasPartitioner.nonEmpty) {
Some(hasPartitioner.maxBy(_.partitions.length))
} else {
None
}
val defaultNumPartitions = if (rdd.context.conf.contains("spark.default.parallelism")) {
rdd.context.defaultParallelism
} else {
rdds.map(_.partitions.length).max
}
// If the existing max partitioner is an eligible one, or its partitions number is larger
// than the default number of partitions, use the existing partitioner.
if (hasMaxPartitioner.nonEmpty && (isEligiblePartitioner(hasMaxPartitioner.get, rdds) ||
defaultNumPartitions < hasMaxPartitioner.get.getNumPartitions)) {
hasMaxPartitioner.get.partitioner.get
} else {
new HashPartitioner(defaultNumPartitions)
}
}
.......
}Partitioner 共有两种实现,分别是 HashPartitioner 和 RangePartitioner
HashPartitioner :
class HashPartitioner(partitions: Int) extends Partitioner {
require(partitions >= 0, s"Number of partitions ($partitions) cannot be negative.")
//直接返回主构造函数中传入的 partitions 参数
def numPartitions: Int = partitions
//为参数 key 计算一个 hash 值,该哈希值对 partition 个数取余结果为正,则该结果即该 key 归属的 partition index;否则,以该结果加上 partition 个数为 partition index
def getPartition(key: Any): Int = key match {
case null => 0
case _ => Utils.nonNegativeMod(key.hashCode, numPartitions)
}
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {
case h: HashPartitioner =>
h.numPartitions == numPartitions
case _ =>
false
}
override def hashCode: Int = numPartitions
}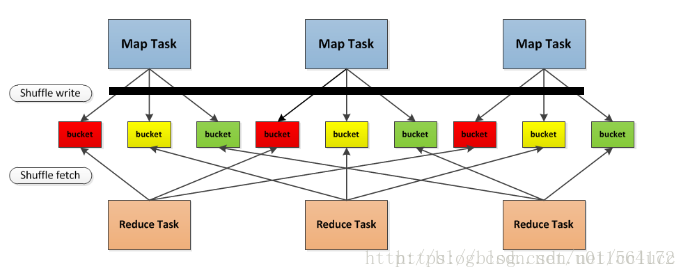
try {
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
.....
}override def getWriter[K, V](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V] = {
numMapsForShuffle.putIfAbsent(
handle.shuffleId, handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[_, _, _]].numMaps)
val env = SparkEnv.get
handle match {
case unsafeShuffleHandle: SerializedShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new UnsafeShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
context.taskMemoryManager(),
unsafeShuffleHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case bypassMergeSortHandle: BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
shuffleBlockResolver.asInstanceOf[IndexShuffleBlockResolver],
bypassMergeSortHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf)
case other: BaseShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked, _] =>
new SortShuffleWriter(shuffleBlockResolver, other, mapId, context)
}
}while (records.hasNext()) {
final Product2<K, V> record = records.next();
final K key = record._1();
partitionWriters[partitioner.getPartition(key)].write(key, record._2());
}override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
sorter.insertAll(records)
....
}def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
.....
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
kv = records.next()
map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
}
.....
}private def getPartition(key: K): Int = {
if (shouldPartition) partitioner.get.getPartition(key) else 0
}override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[U] =
f(context, split.index, firstParent[T].iterator(split, context)) def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] 方法用来获取 split 指定的 Partition 对应的数据的迭代器,有了这个迭代器就能一条一条取出数据来按 compute chain 来执行一个个transform 操作。iterator 的实现如下:
final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) {
SparkEnv.get.cacheManager.getOrCompute(this, split, context, storageLevel)
} else {
computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context)
}
}
private[spark] def computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] =
{
if (isCheckpointedAndMaterialized) {
firstParent[T].iterator(split, context)
} else {
compute(split, context)
}
}private[spark] def getOrCompute(partition: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
val blockId = RDDBlockId(id, partition.index)
var readCachedBlock = true
// This method is called on executors, so we need call SparkEnv.get instead of sc.env.
SparkEnv.get.blockManager.getOrElseUpdate(blockId, storageLevel, elementClassTag, () => {
readCachedBlock = false
computeOrReadCheckpoint(partition, context)
}) match {
case Left(blockResult) =>
if (readCachedBlock) {
val existingMetrics = context.taskMetrics().inputMetrics
existingMetrics.incBytesRead(blockResult.bytes)
new InterruptibleIterator[T](context, blockResult.data.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]]) {
override def next(): T = {
existingMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
delegate.next()
}
}
} else {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, blockResult.data.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]])
}
case Right(iter) =>
new InterruptibleIterator(context, iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]])
}
}override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = {
val dep = dependencies.head.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]]
SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(dep.shuffleHandle, split.index, split.index + 1, context)
.read()
.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
} override def compute(thePart: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = new NextIterator[T]
{
context.addTaskCompletionListener{ context => closeIfNeeded() }
val part = thePart.asInstanceOf[JdbcPartition]
val conn = getConnection()
val stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql, ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY)
val url = conn.getMetaData.getURL
if (url.startsWith("jdbc:mysql:")) {
// setFetchSize(Integer.MIN_VALUE) is a mysql driver specific way to force
// streaming results, rather than pulling entire resultset into memory.
// See the below URL
// dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/5.1/en/connector-j-reference-implementation-notes.html
stmt.setFetchSize(Integer.MIN_VALUE)
} else {
stmt.setFetchSize(100)
}
logInfo(s"statement fetch size set to: ${stmt.getFetchSize}")
stmt.setLong(1, part.lower)
stmt.setLong(2, part.upper)
val rs = stmt.executeQuery()
override def getNext(): T = {
if (rs.next()) {
mapRow(rs)
} else {
finished = true
null.asInstanceOf[T]
}
}
}abstract class Dependency[T] extends Serializable {
def rdd: RDD[T]
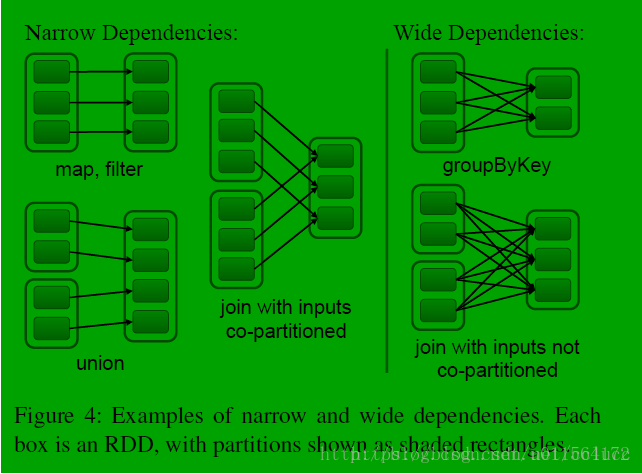
}RDD 依赖是一个 Seq 类型:dependencies_ : Seq[Dependency[_]],因为一个 RDD 可以有多个父 RDD。共有两种依赖:
- 窄依赖:父 RDD 的 partition 至多被一个子 RDD partition 依赖
- 宽依赖:父 RDD 的 partition 被多个子 RDD partitions 依赖
abstract class NarrowDependency[T](_rdd: RDD[T]) extends Dependency[T] {
/**
* Get the parent partitions for a child partition.
* @param partitionId a partition of the child RDD
* @return the partitions of the parent RDD that the child partition depends upon
*/
def getParents(partitionId: Int): Seq[Int]
override def rdd: RDD[T] = _rdd
}class OneToOneDependency[T](rdd: RDD[T]) extends NarrowDependency[T](rdd) {
override def getParents(partitionId: Int): List[Int] = List(partitionId)
}class RangeDependency[T](rdd: RDD[T], inStart: Int, outStart: Int, length: Int)
extends NarrowDependency[T](rdd) {
override def getParents(partitionId: Int): List[Int] = {
if (partitionId >= outStart && partitionId < outStart + length) {
List(partitionId - outStart + inStart)
} else {
Nil
}
}
}class ShuffleDependency[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, C: ClassTag](
@transient private val _rdd: RDD[_ <: Product2[K, V]],
val partitioner: Partitioner,
val serializer: Serializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer,
val keyOrdering: Option[Ordering[K]] = None,
val aggregator: Option[Aggregator[K, V, C]] = None,
val mapSideCombine: Boolean = false)
extends Dependency[Product2[K, V]] {
override def rdd: RDD[Product2[K, V]] = _rdd.asInstanceOf[RDD[Product2[K, V]]]
private[spark] val keyClassName: String = reflect.classTag[K].runtimeClass.getName
private[spark] val valueClassName: String = reflect.classTag[V].runtimeClass.getName
// Note: It's possible that the combiner class tag is null, if the combineByKey
// methods in PairRDDFunctions are used instead of combineByKeyWithClassTag.
private[spark] val combinerClassName: Option[String] =
Option(reflect.classTag[C]).map(_.runtimeClass.getName)
val shuffleId: Int = _rdd.context.newShuffleId()
val shuffleHandle: ShuffleHandle = _rdd.context.env.shuffleManager.registerShuffle(
shuffleId, _rdd.partitions.length, this)
_rdd.sparkContext.cleaner.foreach(_.registerShuffleForCleanup(this))
}
到处都在调用
- PROCESS_LOCAL 数据位于与运行代码相同的JVM中。这是最好的地方。
- NODE_LOCAL 数据位于同一节点上。示例:可能在同一个节点上的HDFS中,或者在同一个节点上的另一个executor中。这比PROCESS_LOCAL稍微慢一些,因为数据必须在进程之间来回移动。
- NO_PREF 数据在任何地方都可以同样快速地访问,并且没有本地偏好。
- RACK_LOCAL 数据位于同一台服务器上。数据在同一机架上的不同服务器上,所以需要通过网络发送,通常是通过一个交换机。
- ANAY 数据在网络上的其他地方,而不是在同一个机架上。
final def preferredLocations(split: Partition): Seq[String] = {
checkpointRDD.map(_.getPreferredLocations(split)).getOrElse {
getPreferredLocations(split)
}
}ShuffledRDD:
override protected def getPreferredLocations(partition: Partition): Seq[String] = {
val tracker = SparkEnv.get.mapOutputTracker.asInstanceOf[MapOutputTrackerMaster]
val dep = dependencies.head.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]]
tracker.getPreferredLocationsForShuffle(dep, partition.index)
}






 本文详细介绍了Spark中RDD的五大核心要素:partition、partitioner、compute、dependency和preferredLocation,深入探讨了各要素的功能、实现原理及其应用场景。
本文详细介绍了Spark中RDD的五大核心要素:partition、partitioner、compute、dependency和preferredLocation,深入探讨了各要素的功能、实现原理及其应用场景。
















 778
778

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








