任务说明
- 任务主题:论文代码统计,统计所有论文出现代码的相关统计;
- 任务内容:使用正则表达式统计代码连接、页数和图表数据;
- 任务成果:学习正则表达式统计;
数据处理步骤
在原始arxiv数据集中作者经常会在论文的comments或abstract字段中给出具体的代码链接,所以我们需要从这些字段里面找出代码的链接。
- 确定数据出现的位置;
- 使用正则表达式完成匹配;
- 完成相关的统计;
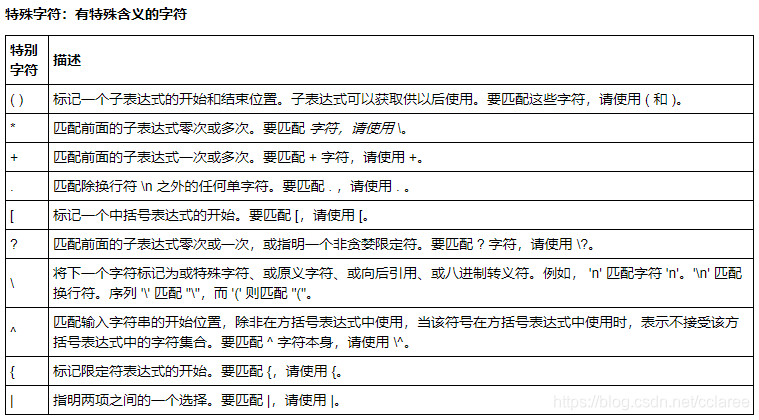
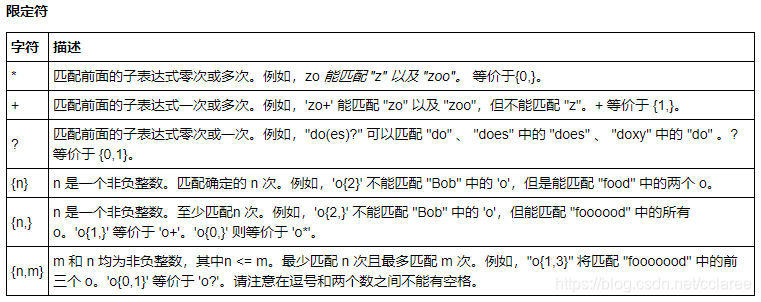
正则表达式
正则表达式(regular expression)描述了一种字符串匹配的模式(pattern),可以用来检查一个串是否含有某种子串、将匹配的子串替换或者从某个串中取出符合某个条件的子串等。

 具体代码实现以及讲解
具体代码实现以及讲解
首先我们来统计论文页数,也就是在comments字段中抽取pages和figures和个数,首先完成字段读取。
# 导入所需的package
import seaborn as sns #用于画图
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #用于爬取arxiv的数据
import re #用于正则表达式,匹配字符串的模式
import requests #用于网络连接,发送网络请求,使用域名获取对应信息
import json #读取数据,我们的数据为json格式的
import pandas as pd #数据处理,数据分析
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #画图工具
def readArxivFile(path, columns=['id', 'submitter', 'authors', 'title', 'comments', 'journal-ref', 'doi',
'report-no', 'categories', 'license', 'abstract', 'versions',
'update_date', 'authors_parsed'], count=None):
'''
定义读取文件的函数
path: 文件路径
columns: 需要选择的列
count: 读取行数
'''
data = []
with open(path, 'r') as f:
for idx, line in enumerate(f):
if idx == count:
break
d = json.loads(line)
d = {col : d[col] for col in columns}
data.append(d)
data = pd.DataFrame(data)
return data
data = readArxivFile('arxiv-metadata-oai-snapshot.json', ['id', 'abstract', 'categories', 'comments'])
对pages进行抽取:
# 使用正则表达式匹配,XX pages
data['pages'] = data['comments'].apply(lambda x: re.findall('[1-9][0-9]* pages', str(x)))
# 筛选出有pages的论文
data = data[data['pages'].apply(len) > 0]
# 由于匹配得到的是一个list,如['19 pages'],需要进行转换
data['pages'] = data['pages'].apply(lambda x: float(x[0].replace(' pages', '')))
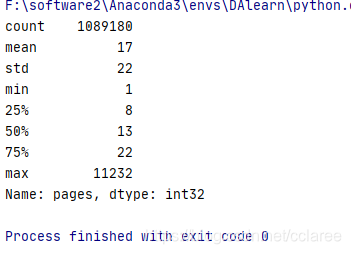
对pages进行统计,统计结果如下:论文平均的页数为17页,75%的论文在22页以内,最长的论文有11232页。
print(data['pages'].describe().astype(int))
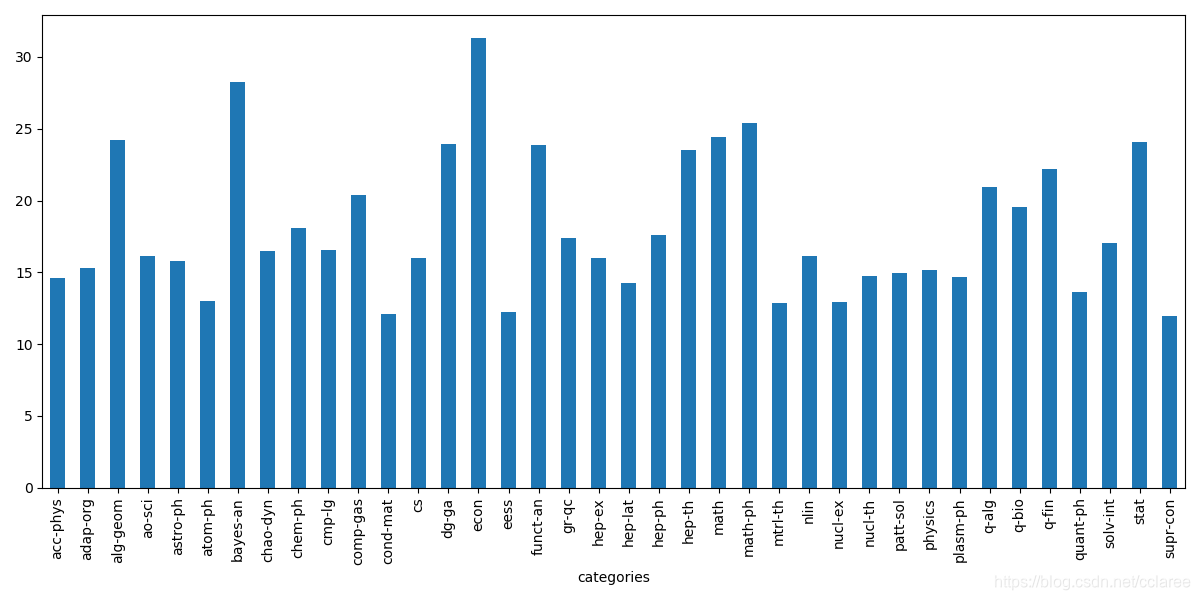
接下来按照分类统计论文页数,选取了论文的第一个类别的主要类别:
# 选择主要类别
data['categories'] = data['categories'].apply(lambda x: x.split(' ')[0])
data['categories'] = data['categories'].apply(lambda x: x.split('.')[0])
# 每类论文的平均页数
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
data.groupby(['categories'])['pages'].mean().plot(kind='bar')
plt.show()
接下来对论文图表个数进行抽取:
data['figures'] = data['comments'].apply(lambda x: re.findall('[1-9][0-9]* figures', str(x)))
data = data[data['figures'].apply(len) > 0]
data['figures'] = data['figures'].apply(lambda x: float(x[0].replace(' figures', '')))
最后我们对论文的代码链接进行提取,为了简化任务我们只抽取github链接:
# 筛选包含github的论文
data_with_code = data[
(data.comments.str.contains('github')==True)|
(data.abstract.str.contains('github')==True)
]
data_with_code['text'] = data_with_code['abstract'].fillna('') + data_with_code['comments'].fillna('')
# 使用正则表达式匹配论文
pattern = '[a-zA-z]+://github[^\s]*'
data_with_code['code_flag'] = data_with_code['text'].str.findall(pattern).apply(len)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:6: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:10: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
# Remove the CWD from sys.path while we load stuff.
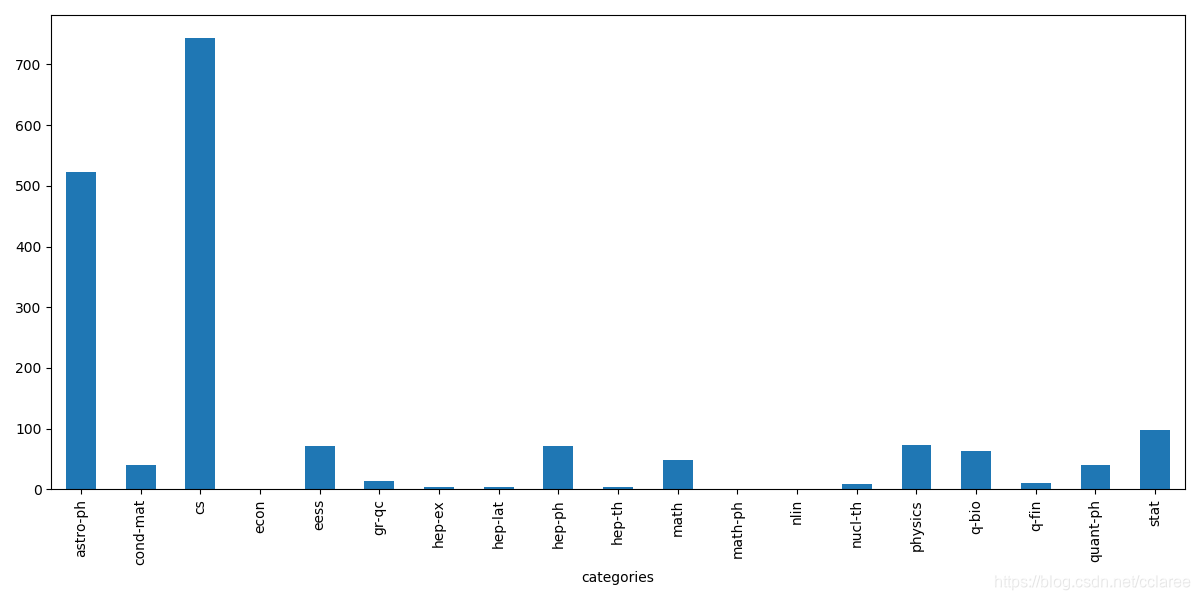
并对论文按照类别进行绘图:
data_with_code = data_with_code[data_with_code['code_flag'] == 1]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
data_with_code.groupby(['categories'])['code_flag'].count().plot(kind='bar')
plt.show()




















 532
532

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








