这段时间在研究Android DNS缓存机制,其中有个小点就是关于DNS缓存的时长,就在这里记录一下了
Android的DNS缓存机制是双重的:
- Java层的快速缓存
- Native C层的缓存
1,Java层
先来看Java层的快速缓存,应用层如果想要解析DNS,基本上都是调用InetAddress.getByName(String host)接口,最终调用的就是lookupHostByName:
private static InetAddress[] lookupHostByName(String host, int netId)
throws UnknownHostException {
BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onNetwork();
// Do we have a result cached?
Object cachedResult = addressCache.get(host, netId);
if (cachedResult != null) {
if (cachedResult instanceof InetAddress[]) {
// A cached positive result.
return (InetAddress[]) cachedResult;
} else {
// A cached negative result.
throw new UnknownHostException((String) cachedResult);
}
}
......
}
public Object get(String hostname, int netId) {
AddressCacheEntry entry = cache.get(new AddressCacheKey(hostname, netId));
// Do we have a valid cache entry?
if (entry != null && entry.expiryNanos >= System.nanoTime()) {
return entry.value;
}
// Either we didn't find anything, or it had expired.
// No need to remove expired entries: the caller will provide a replacement shortly.
return null;
}
这里的AddressCache就是Java层的快速缓存,那么AddressCache在添加时候就会对每个缓存设定一个有效时长
AddressCacheEntry(Object value) {
this.value = value;
this.expiryNanos = System.nanoTime() + TTL_NANOS;
}
this.expiryNanos = System.nanoTime() + TTL_NANOS就是这个DNS缓存的有效时间点,保存时的当前系统时间加上TTL_NANOS,所以在get的时候expiryNanos大于当前系统时间,则认为DNS缓存过期。
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 16;
// The TTL for the Java-level cache is short, just 2s.
private static final long TTL_NANOS = 2 * 1000000000L;
// The actual cache.
private final BasicLruCache<AddressCacheKey, AddressCacheEntry> cache
= new BasicLruCache<AddressCacheKey, AddressCacheEntry>(MAX_ENTRIES);
看上面的代码,我们就可以总结一下Java层的快速缓存了:
- 每个缓存的有效时长是一个定值TTL_NANOS也就是2s
- Java层最多缓存16个地址
- 管理方式采用的是LRU算法,也就是BasicLruCache类进行管理,有兴趣可以学习下源码
2,Native C层
InetAddress.getByName接口最终会通过JNI进入libc的getaddrinfo函数,getaddrinfo这个函数的过程比较复杂,还会跟netd进程进行socket通信,这里就不讲了,这里主要讲跟DNS缓存时长相关的地方,DNS请求由res_nsend函数发出:
int res_nsend(res_state statp,
const u_char *buf, int buflen, u_char *ans, int anssiz)
{
int gotsomewhere, terrno, try, v_circuit, resplen, ns, n;
char abuf[NI_MAXHOST];
ResolvCacheStatus cache_status = RESOLV_CACHE_UNSUPPORTED;
......
int anslen = 0;
cache_status = _resolv_cache_lookup(
statp->netid, buf, buflen,
ans, anssiz, &anslen);
if (cache_status == RESOLV_CACHE_FOUND) {
return anslen;
} else if (cache_status != RESOLV_CACHE_UNSUPPORTED) {
// had a cache miss for a known network, so populate the thread private
// data so the normal resolve path can do its thing
_resolv_populate_res_for_net(statp);
}
if (statp->nscount == 0) {
// We have no nameservers configured, so there's no point trying.
// Tell the cache the query failed, or any retries and anyone else asking the same
// question will block for PENDING_REQUEST_TIMEOUT seconds instead of failing fast.
_resolv_cache_query_failed(statp->netid, buf, buflen);
errno = ESRCH;
return (-1);
}
......
}
_resolv_cache_lookup函数就是取搜索DNS缓存的函数
ResolvCacheStatus _resolv_cache_lookup( unsigned netid,
const void* query,
int querylen,
void* answer,
int answersize,
int *answerlen )
{
......
lookup = _cache_lookup_p(cache, key);
e = *lookup;
if (e == NULL) {
XLOG( "NOT IN CACHE");
// calling thread will wait if an outstanding request is found
// that matching this query
if (!_cache_check_pending_request_locked(&cache, key, netid) || cache == NULL) {
goto Exit;
} else {
lookup = _cache_lookup_p(cache, key);
e = *lookup;
if (e == NULL) {
goto Exit;
}
}
}
now = _time_now();
/* remove stale entries here */
if (now >= e->expires) {
XLOG( " NOT IN CACHE (STALE ENTRY %p DISCARDED)", *lookup );
XLOG_QUERY(e->query, e->querylen);
_cache_remove_p(cache, lookup);
goto Exit;
}
......
}
与Java层一样,当now >= e->expires时,该缓存被认为过期,从缓存列表中清除,那么这个e->expires也是在添加缓存的时候设置的,接下来我们就找Add的地方_resolv_cache_add函数:
void _resolv_cache_add( unsigned netid,
const void* query,
int querylen,
const void* answer,
int answerlen )
{
......
if (cache->num_entries >= cache->max_entries) {
_cache_remove_expired(cache);
if (cache->num_entries >= cache->max_entries) {
_cache_remove_oldest(cache);
}
/* need to lookup again */
lookup = _cache_lookup_p(cache, key);
e = *lookup;
if (e != NULL) {
XLOG("%s: ALREADY IN CACHE (%p) ? IGNORING ADD",
__FUNCTION__, e);
goto Exit;
}
}
ttl = answer_getTTL(answer, answerlen);
if (ttl > 0) {
e = entry_alloc(key, answer, answerlen);
if (e != NULL) {
e->expires = ttl + _time_now();
_cache_add_p(cache, lookup, e);
}
}
......
}
可以看到e->expires是与ttl有关的,而ttl是什么?ttl是time to live,是DNS服务器回复时的报文中带回的一个属性值:
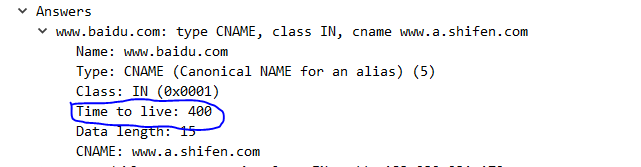
由上我们可以总结Native C层的DNS缓存:
- 每个缓存的有效时长就是ttl,也就是DNS服务器返回的一个属性值
- DNS缓存的最大个数为#define CONFIG_MAX_ENTRIES 64 * 2 * 5 640个
- DNS缓存的管理办法是,个数达到最大值,则一次性清除所有过期的缓存,如果没有过期缓存则删除最久的一个
以上就是对Android DNS缓存时长的总结,若有疑问,欢迎讨论!





 本文探讨了Android DNS缓存的双重机制,包括Java层的快速缓存(有效期2s,最多缓存16个地址,使用LRU算法)和Native C层的缓存(有效期为DNS服务器返回的TTL值,最多640个条目,按需清理)。详细分析了缓存的添加、过期判断及管理策略。
本文探讨了Android DNS缓存的双重机制,包括Java层的快速缓存(有效期2s,最多缓存16个地址,使用LRU算法)和Native C层的缓存(有效期为DNS服务器返回的TTL值,最多640个条目,按需清理)。详细分析了缓存的添加、过期判断及管理策略。
















 3303
3303










