1、最终用户空间的系统调用会调用到sys_select函数
asmlinkage long sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp,
fd_set __user *exp, struct timeval __user *tvp)
{
s64 timeout = -1;
struct timeval tv;
int ret;
if (tvp) {
if (copy_from_user(&tv, tvp, sizeof(tv)))//从用户空间拷贝时间
return -EFAULT;
if (tv.tv_sec < 0 || tv.tv_usec < 0)
return -EINVAL;
/* Cast to u64 to make GCC stop complaining */
if ((u64)tv.tv_sec >= (u64)MAX_INT64_SECONDS)
timeout = -1; /* infinite */
else {
timeout = DIV_ROUND_UP(tv.tv_usec, USEC_PER_SEC/HZ);
timeout += tv.tv_sec * HZ;
}
}
ret = core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, &timeout);//selcet的调用入口
if (tvp) {
struct timeval rtv;
if (current->personality & STICKY_TIMEOUTS)
goto sticky;
rtv.tv_usec = jiffies_to_usecs(do_div((*(u64*)&timeout), HZ));
rtv.tv_sec = timeout;
if (timeval_compare(&rtv, &tv) >= 0)
rtv = tv;
if (copy_to_user(tvp, &rtv, sizeof(rtv))) {
sticky:
/*
* If an application puts its timeval in read-only
* memory, we don't want the Linux-specific update to
* the timeval to cause a fault after the select has
* completed successfully. However, because we're not
* updating the timeval, we can't restart the system
* call.
*/
if (ret == -ERESTARTNOHAND)
ret = -EINTR;
}
}
return ret;
}2、继续调用core_sys_select
static int core_sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp,
fd_set __user *exp, s64 *timeout)
{
fd_set_bits fds;
void *bits;
int ret, max_fds;
unsigned int size;
struct fdtable *fdt;
/* Allocate small arguments on the stack to save memory and be faster */
long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)];
ret = -EINVAL;
if (n < 0)
goto out_nofds;
/* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */
rcu_read_lock();
fdt = files_fdtable(current->files);
max_fds = fdt->max_fds;
rcu_read_unlock();
if (n > max_fds)
n = max_fds;
/*
* We need 6 bitmaps (in/out/ex for both incoming and outgoing),需要6个位图,分别为输出和输出
* since we used fdset we need to allocate memory in units of
* long-words.
*/
size = FDS_BYTES(n);//szie大小取决于n,n=1024时,size = 128字节,对应1024位
bits = stack_fds;//bits = 64;
if (size > sizeof(stack_fds) / 6) {
/* Not enough space in on-stack array; must use kmalloc */
ret = -ENOMEM;
bits = kmalloc(6 * size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bits)
goto out_nofds;
}
fds.in = bits;
fds.out = bits + size;
fds.ex = bits + 2*size;
fds.res_in = bits + 3*size;
fds.res_out = bits + 4*size;
fds.res_ex = bits + 5*size;
/*-------------------------
| 128 | 128 | ...| 128 |
-------------------------
总共6个size。每个size是32个long类型存贮,因此是1024位,最大监听1024个文件描述符,每一位都代表一个fd
*/
if ((ret = get_fd_set(n, inp, fds.in)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, outp, fds.out)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, exp, fds.ex)))//拷贝用户空间要监听的fd,分别在可写、可读、异常中复制一份
goto out;
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_in);//将输出清零
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_out);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_ex);
ret = do_select(n, &fds, timeout);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
if (!ret) {
ret = -ERESTARTNOHAND;
if (signal_pending(current))
goto out;
ret = 0;
}
if (set_fd_set(n, inp, fds.res_in) ||//如果都没有设置则返回错误,或者等待时间超时
set_fd_set(n, outp, fds.res_out) ||
set_fd_set(n, exp, fds.res_ex))
ret = -EFAULT;
out:
if (bits != stack_fds)
kfree(bits);
out_nofds:
return ret;
}3、继续调用do_select
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, s64 *timeout)
{
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i;
rcu_read_lock();
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);//fd监听的最大值
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
if (!*timeout)
wait = NULL;
retval = 0;
for (;;) {//死循环
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
long __timeout;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);//此任务可以被中断
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) {
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;//当前的位置没有置位,则继续下一个位循环,一个位一个位的循环遍历
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS;
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) {//按照8*long大小轮询
int fput_needed;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);//根据i查找有没有对应的虚拟文件,也就是文件描述符
if (file) {
f_op = file->f_op;//获取处理函数
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll)//poll函数指针不为空
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, retval ? NULL : wait);//wait是回调,是否存在事件触发
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
}//根据每一位是否存在可读、可写、异常的设置,分别将对应的事件信息放在结果的数组中
}
cond_resched();
}
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
}
wait = NULL;
if (retval || !*timeout || signal_pending(current))
break;
if(table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
if (*timeout < 0) {
/* Wait indefinitely */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
} else if (unlikely(*timeout >= (s64)MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1)) {
/* Wait for longer than MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT. Do it in a loop */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1;
*timeout -= __timeout;
} else {
__timeout = *timeout;
*timeout = 0;
}
__timeout = schedule_timeout(__timeout);
if (*timeout >= 0)
*timeout += __timeout;
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}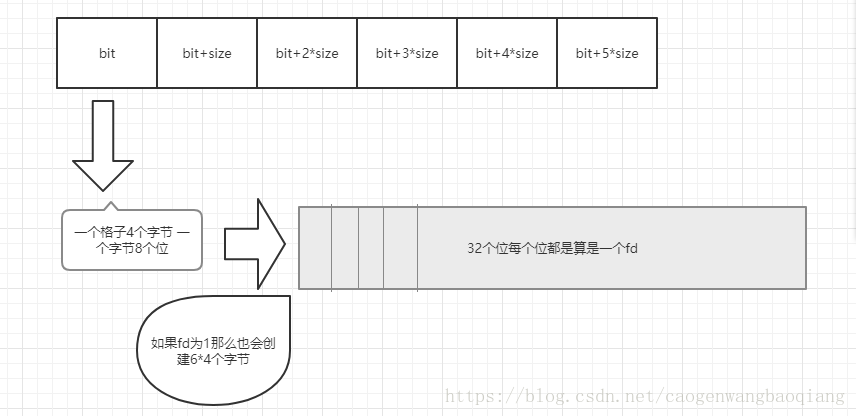
上面的图是说明select在进行监听前是怎样组织数据的,但是每个size不是4个字节,是按照需要监听的最大文件描述符按照有多少个long形式可以满足监听的需求,每一位代表一个文件描述符。加入监听1024个,则需要128字节,需要32个long类型的数据。如果fd为1,则只需要一个long类型的数据,同样要申请6个size的空间。
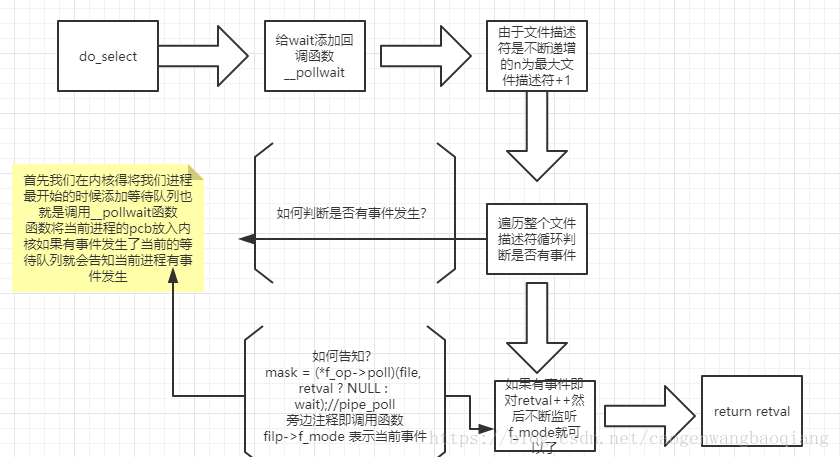
这是select怎样判断是否存在可读、可写、以及异常的事件。都是通过调用回调函数。
尤其注意的是select方式在循环检测的方法,这是select主要的模型方法。空间消耗和时间消耗比较大。
图片的来源:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/leaf_cold/article/details/79452371
再综合看另外一张图:
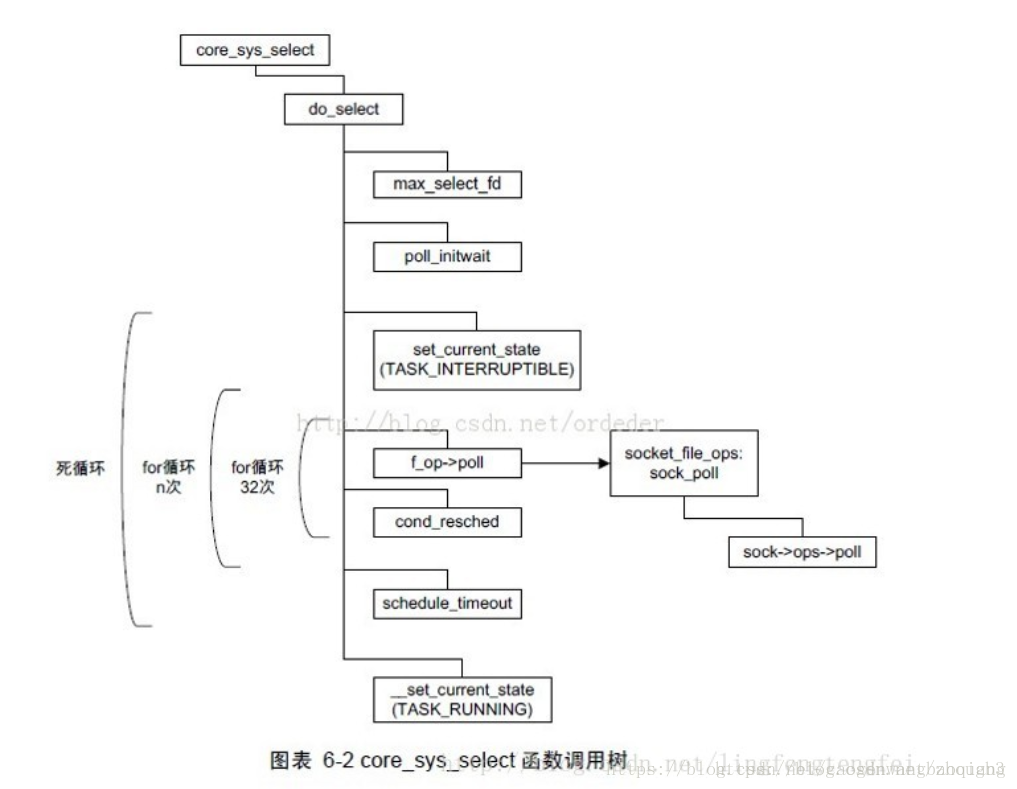
比较清晰的画出了select的调用过程
图片来源:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhougb3/article/details/79792089
参考文章:1、select用法&原理详解(源码剖析):https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhougb3/article/details/79792089
2、select 源码剖析:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/leaf_cold/article/details/79452371




 本文详细解析了Linux系统中select系统调用的工作原理,包括其内部实现机制、数据组织方式及事件判断流程,并附有清晰的调用过程图示。
本文详细解析了Linux系统中select系统调用的工作原理,包括其内部实现机制、数据组织方式及事件判断流程,并附有清晰的调用过程图示。
















 5280
5280

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








