卡尔曼滤波的通俗理解可以分为三步:
1、初始化卡尔曼滤波器
2、预测状态值和方差
3、更新+融合预测值和测量值
其中运用到的几个经典公式如下:
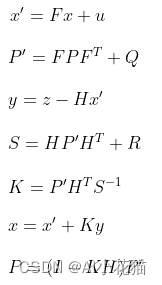
以卡尔曼滤波在目标跟踪中的运用为基准,详述卡尔曼滤波的整个过程如下:
1、定义状态空间:
通常目标检测中物体的检测框通常使用(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax)表示,依据sort中对于空间状态的定义,使用检测框的中心点坐标x,y长宽比a,高度h以及其对应图像坐标系中的速度进行定义,大致看可以表示为[x,y,a,h,vx,vy,va,vh]

目标跟踪过程中,主要需要不断更新获取的数据为均值和协方差:
其中:
均值mean就是状态空间变量[x,y,a,h,vx,vy,va,vh],包含位置和速度。位置为每次检测器检测得到的位置信息,速度一般初始化为0,实际使用的时候mean值通过观测矩阵H->[4,8]投射测量空间得到[x,y,a,h]。
协方差Covariance是状态估计的不确定性,sort中使用的是[8,8]的矩阵表示,对角线的数字越大表示不确定度越高。
2、初始化卡尔曼滤波器
主要是定义转移矩阵_motion_mat,以及观测矩阵_update_mat,以及表示运动不确定度的控制参数_std_weight_position以及_std_weight_velocity
def __init__(self):
ndim, dt = 4, 1.
# Create Kalman filter model matrices.
self._motion_mat = np.eye(2 * ndim, 2 * ndim)
for i in range(ndim):
self._motion_mat[i, ndim + i] = dt
self._update_mat = np.eye(ndim, 2 * ndim)
# Motion and observation uncertainty are chosen relative to the current
# state estimate. These weights control the amount of uncertainty in
# the model. This is a bit hacky.
self._std_weight_position = 1. / 20
self._std_weight_velocity = 1. / 160





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 6758
6758

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










