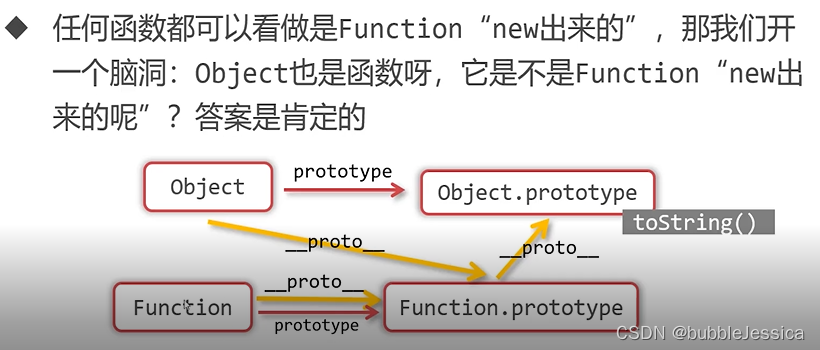
console.log(Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype); //true
console.log(Object.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype); //true
console.log(Function.__proto__ === Function.prototype); //true
console.log(Function instanceof Object); //true
console.log(Object instanceof Function); //true
console.log(Function instanceof Function); //true
console.log(Object instanceof Object); //true
借用构造函数(伪造对象/经典继承)
function People(name,age,sex){
this.name=name; //这里的this代表window对象
this.age=age;
this.sex=sex;
this.arr=[33,44,55];
}
function Student(name,age,sex,school,sid){
People(name,age,sex);
this.school=school;
this.sid=sid;
}
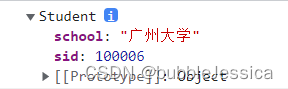
var xiaoming=new Student('小明',12,'男','广州大学',100006);
console.log(xiaoming);
function People(name,age,sex){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.sex=sex;
this.arr=[33,44,55];
}
function Student(name,age,sex,school,sid){
People.call(this,name,age,sex); //this代表Student的实例
this.school=school;
this.sid=sid;
}
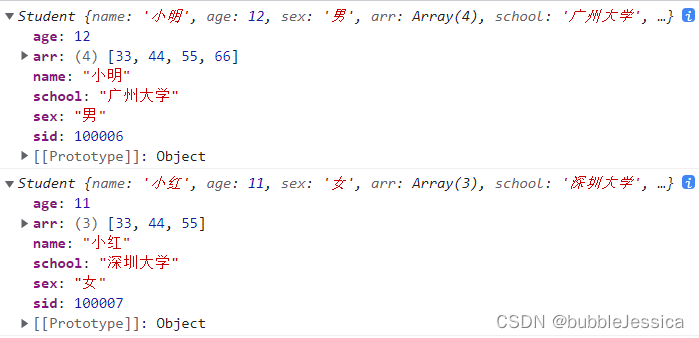
var xiaoming=new Student('小明',12,'男','广州大学',100006);
xiaoming.arr.push(66);
console.log(xiaoming);
var xiaohong=new Student('小红',11,'女','深圳大学',100007);
console.log(xiaohong);
组合继承(js最常用的继承模式)
将借用原型链和借用构造函数的技术组合到一起叫做组合继承,也叫作伪经典继承
// 父类
function People(name, age, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
People.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('你好,我是' + this.name + '今年' + this.age + '岁了');
}
People.prototype.sleep = function () {
console.log(this.name + '正在睡觉');
}
// 子类
function Student(name, age, sex, school, sid) {
// 借助构造函数
People.call(this, name, age, sex);
this.school = school;
this.sid = sid;
}
// 借助原型链
Student.prototype = new People();
Student.prototype.exam = function () {
console.log(this.name + '正在考试');
}
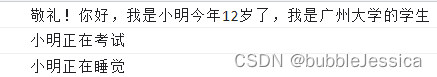
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('敬礼!你好,我是' + this.name + '今年' + this.age + '岁了,我是' + this.school + '的学生');
}
var xiaoming = new Student('小明', 12, '男', '广州大学', 100006);
xiaoming.sayHello();
xiaoming.exam();
xiaoming.sleep();
组合继承最大的缺点就是:无论什么情况,都会调用2次父类的构造函数:一次是在创建子类原型的时候,另一次是在子类构造函数的内部
原型式继承
Object.create()可以根据指定的对象为原型创建出新对象
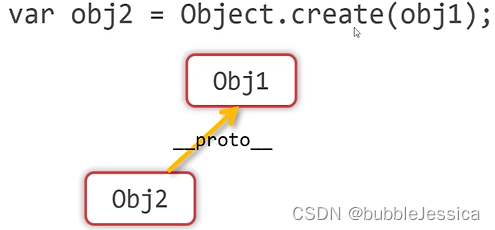
obj2的原型是obj1或者说以obj1为原型创建出obj2对象
var obj1 = {
a: 33,
b: 45,
c: 12
};
var obj2 = Object.create(obj1, {
d: {
value: 88
},
a: {
value: 2
}
});
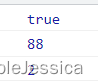
console.log(obj2.__proto__ === obj1);
console.log(obj2.d);
console.log(obj2.a);
面试:Object.create()的兼容性写法
// 函数的功能就是以o为原型,创建新对象
function object(o) {
// 创建一个临时构造函数
function F() {
}
// 让这个临时构造函数的prototype指向o,这样一来它new出来的对象,__proto__指向了o
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
var obj1 = {
a: 23,
b: 5
};
var obj2 = object(obj1);
console.log(obj2.__proto__ === obj1); //true
console.log(obj2.a); //23
console.log(obj2.b); //5
寄生式继承
编写一个函数,它接收一个参数o,返回以o为原型的新对象p,同时给p上添加预置的新方法
var o1 = {
name: '晓君',
age: 20,
sex: '女'
}
function f(o) {
// 以o为原型创建出新对象
var p = Object.create(o);
// 补充方法
p.sayHello = function () {
console.log('你好,我是' + this.name + '今年' + this.age + '岁了');
}
p.sleep = function () {
console.log(this.name + '正在睡觉');
}
return p;
}
var p1 = f(o1);
p1.sayHello();
![]()

缺点:使用寄生式继承来为对象添加函数,会由于不能做到函数复用而降低效率,即方法没有写到prototype对象上
寄生组合式继承
通过借用构造函数来继承属性,通过原型链的混成形式来继承方法(节约了一次调用构造函数)
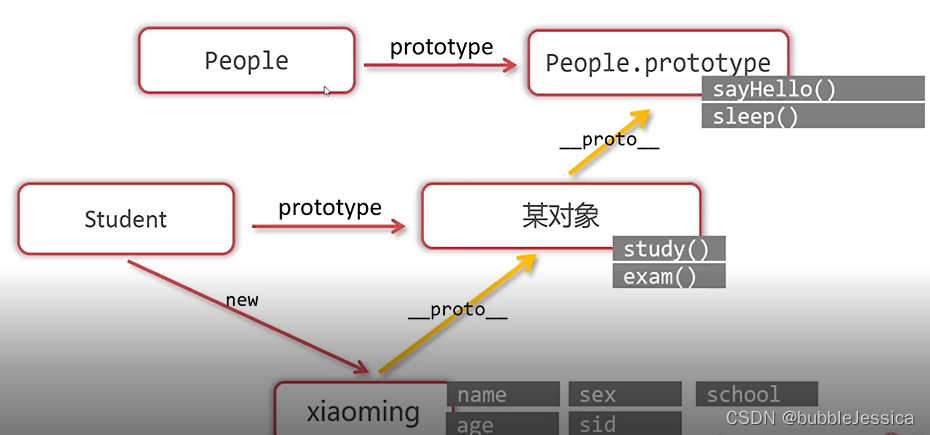
通过inheritPrototype函数,以父类.prototype对象(People.prototype)为原型创建某对象,然后子类.prototype对象指向刚才创建的某对象
// 这个函数接收两个参数,subType是子类的构造函数,superType是父类的构造函数
function inheritPrototype(subType, superType) {
var prototype = Object.create(superType.prototype);
subType.prototype = prototype;
}
// 父类
function People(name, sex, age) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
People.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('你好,我是' + this.name + '今年' + this.age + '岁了');
}
People.prototype.sleep = function () {
console.log(this.name + '正在睡觉');
}
// 子类
function Student(name, sex, age, school, sid) {
// 借助构造函数
People.call(this, name, sex, age);
this.school = school;
this.sid = sid;
}
// 调用我们自己编写的inheritPrototype函数,这个函数可以让Student类的prototype指向“以People.prototype为原型的一个新对象”
inheritPrototype(Student, People);
Student.prototype.exam = function() {
console.log(this.name + '正在考试');
};
Student.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log('敬礼!你好,我是' + this.name + '今年' + this.age + '岁了,我是' + this.school + '学校的学生');
};
var xiaoming = new Student('小明', '男', 12, '小慕学校', 100666);
xiaoming.sleep();
xiaoming.exam();
xiaoming.sayHello();
instanceof运算符





 文章详细介绍了JavaScript中的几种继承方式,包括构造函数继承、原型链继承、组合继承、Object.create()的原型式继承、寄生式继承以及优化后的寄生组合式继承,分析了各种继承方式的优缺点及实现原理。
文章详细介绍了JavaScript中的几种继承方式,包括构造函数继承、原型链继承、组合继承、Object.create()的原型式继承、寄生式继承以及优化后的寄生组合式继承,分析了各种继承方式的优缺点及实现原理。

















 1729
1729

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








