我们都对于“+”,“-”,“*”,“/”等等运算符(操作符)很熟悉,代码中天天敲这些东西。
但是我们知道这些操作符都只能对基本类型进行运算,比如int,double什么的。
现在我们学习了C++,每天都写了很多类,对象,但是有一件事情很苦恼,那就是我们想对类对象来实现以前运算符所能实现的功能时就必须写成员函数或者普通函数来调用函数,但是这样又很麻烦。
在学习了C++中字符串类String后,我们发现里面竟然可以使用以前的运算符,如“+”,“+=”,“>”,“>=”等这些运算符都可以使用,所以我们也想在自己写的类中也可以使用这些运算符。
这时候我们就要用到运算符重载操作:
运算符重载:
关键字:operator
书写形式:
返回值类型 operator 运算符(参数表)
{
函数体
}
作用:
运算符重载是对已有的运算符赋予多重含义,使同一个运算符作用于不同类型的数据时导致不同的行为。
下面举一个很简单的例子:
在一个复数类中重载“+”和“-”运算符,使其能够用于类对象的运算中。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex //复数类定义
{
public: //外部接口
Complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0) //构造函数
:real(r),imag(i)
{}
Complex operator+(const Complex& c2)const; //运算符+重载函数
Complex operator-(const Complex& c2)const; //运算符-重载函数
void display()const; //输出复数
private: //私有数据成员
double real; //复数实部
double imag; //复数虚部
};
Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& c2)const
{
return Complex(real + c2.real, imag + c2.imag); //创建一个临时无名对象作为返回值
}
Complex Complex::operator-(const Complex& c2)const
{
return Complex(real - c2.real, imag - c2.imag);
}
void Complex::display()const
{
if (imag > 0)
{
cout << real << "+" << imag << "i" << endl;
}
else if (imag == 0)
{
cout << real << endl;
}
else
{
cout << real << imag << "i" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Complex c1(5, 4), c2(2, 10), c3;
cout << "c1=";
c1.display();
cout << "c2=";
c2.display();
c3 = c1 - c2;
cout << "c3=c1-c2=";
c3.display();
c3 = c1 + c2;
cout << "c3=c1+c2=";
c3.display();
return 0;
}

运算符重载的规则:
(1)只能重载已有的运算符,不能创造新的运算符;
(2)“.” , “.*” , “::” , “?::” 这四个运算符不允许重载;
(3)重载运算符时,如果其所有操作数都是内置类型(即所有操作数都是int,double这一类),则不能重载;
(4)“=” , “[]” , “()” , “->” 只能以成员形式重载;
(5)重载运算符不会改变运算符三大特性(优先级,结合方向,操作数);
(6)单目运算符:
a.成员函数形式(无参),唯一操作数传给this;
b.普通函数形式(单参),唯一操作数传给参数;
双目运算符:
a.成员函数形式(单参),左操作数传给this,右操作数传给参数;
b.普通函数形式(双参),左操作数传给第一个参数,右操作数传给第二个参数;
*(7)重载运算符应该尽可能保证所作操作与原运算符功能一致或相近。
注:
创建一个类什么都不写时类中会有六个默认函数
(1)构造函数
(2)拷贝构造函数
(3)析构函数
(4)“=”赋值函数
(5)“&”取地址函数
(6)“const 类名 * p=&对象名” 取常地址函数
其中后三个都属于运算符重载。
下面的例子是我自己写的String类,其中可以实现“=” , “+=” , “+”等运算符重载
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char* ps;
public:
String(char* p = "")
:ps(new char[strlen(p) + 1])
{
strcpy(ps, p);
//cout << "String(char*)" << endl;
}
~String()
{
//cout << "~String()" << endl;
delete[] ps;
ps = NULL;
//delete free close destory ...
}
String(const String& ref)
:ps(new char[strlen(ref.ps) + 1])
{
strcpy(ps, ref.ps);
//cout << "String(const String&)" << endl;
}
String& operator=(const String& ref)
{
if (this->ps != NULL)
{
delete[] this->ps;
this->ps = NULL;
}
this->ps = new char[strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(this->ps, ref.ps);
return *this;
}
String operator+(const String& ref)const
{
String a;
a.ps = new char[strlen(this->ps) + strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(a.ps, this->ps);
strcat(a.ps, ref.ps);
return a;
}
String& operator+=(const String& ref)
{
String a;
a.ps = new char[strlen(this->ps) + strlen(ref.ps) + 1];
strcpy(a.ps, this->ps);
strcat(a.ps, ref.ps);
this->ps = new char[strlen(a.ps) + 1];
strcpy(this->ps, a.ps);
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) == 0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
bool operator<(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps)< 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator<=(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) < 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator>(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps)> 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const String& ref)const
{
if (strcmp(this->ps, ref.ps) >=0 )
return true;
else
return false;
}
char operator[](const int i)const
{
return this->ps[i];
}
public:
void Show()const
{
cout << ps << endl;
}
};
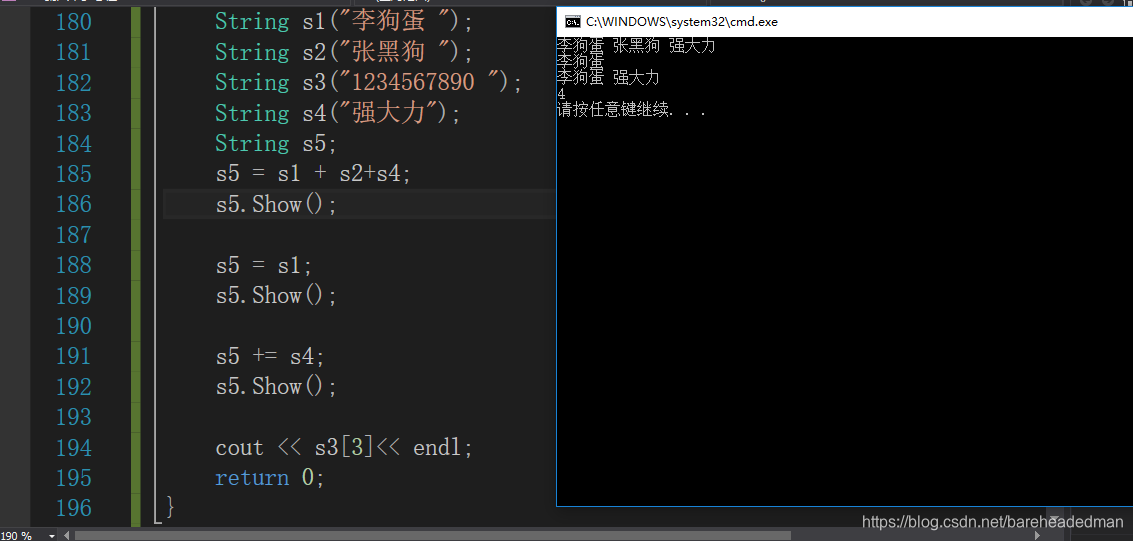
int main()
{
String s1("李狗蛋 ");
String s2("张黑狗 ");
String s3("1234567890 ");
String s4("强大力");
String s5;
s5 = s1 + s2+s4;
s5.Show();
s5 = s1;
s5.Show();
s5 += s4;
s5.Show();
cout << s3[3]<< endl;
return 0;
}
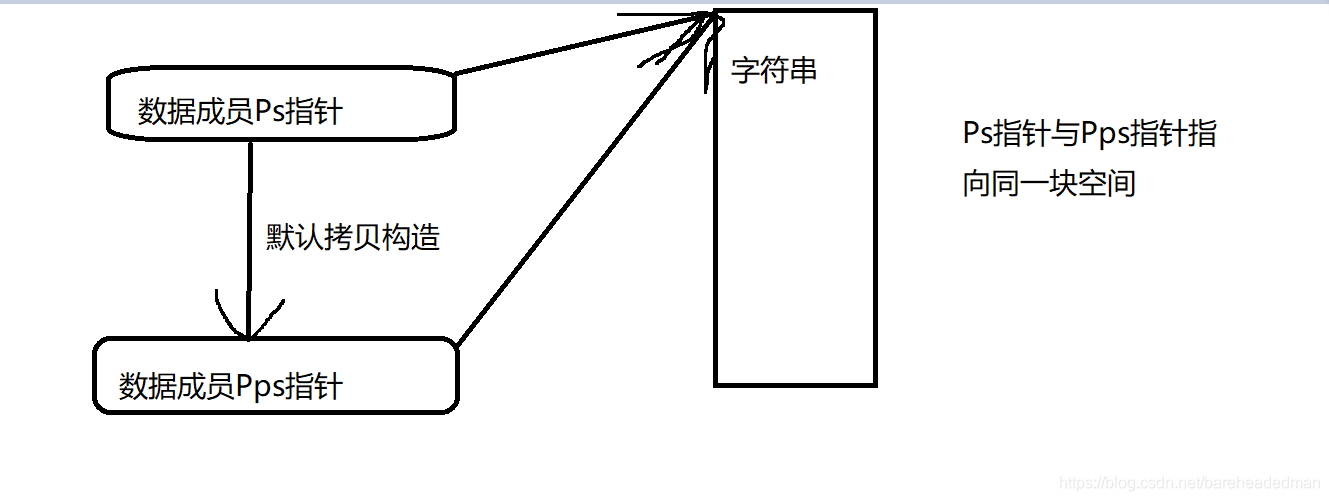
里面还涉及了一些深拷贝和浅拷贝的问题:
简单来说:平常默认的拷贝构造函数就属于浅拷贝,浅拷贝可以解决大部分问题,但是有的时候我们的类中数据成员并不是类所表示的全部属性,比如字符串类中,只有一个数据成员是一个指针,它指向的空间才是存放字符串的地方,而浅拷贝只是将类中的指针成员复制了一份,这样两个类对象指向的就是同一块空间,其中一个变了另一个也就会变化,当一个执行析构函数释放空间时,另一个再调用析构函数的话就会出问题。
如图:
而深拷贝构造就是在对类中数据成员进行复制时将其所指向的空间也一起复制
如图:





 本文详细介绍了C++中的运算符重载概念,包括如何在自定义类中使用运算符,如“+”,“-”,“*”,“/”等,并通过复数类和字符串类的实例展示了重载过程及规则。
本文详细介绍了C++中的运算符重载概念,包括如何在自定义类中使用运算符,如“+”,“-”,“*”,“/”等,并通过复数类和字符串类的实例展示了重载过程及规则。
















 3048
3048










