概念
利用C++的构造和析构函数实现自动维护对象的引用计数。
智能指针是一个对象,构造时增加引用对象的引用计数,析构时减少应用计数。最终目的是辅助释放 new 出来的内存
Android 中共有 3 中智能指针: 轻量级,强指针 sp,弱指针 wp,
对象释放时机的三种模式
1.默认(flag = 0):强引用计数控制生命周期,强引用为 0 时回收
2 OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK(flag = 0x0001): 弱引用计数控制生命周期,弱引用计数为 0 时回收
3 OBJECT_LIFETIME_FOREVER(flag = 0x0003):生命周期不由引用计数控制,需要手动 delete
追源码的时候没有这个了 OBJECT_LIFETIME_FOREVER,应该是移除了
enum { OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG = 0x0000, OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK = 0x0001, OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK = 0x0001 };
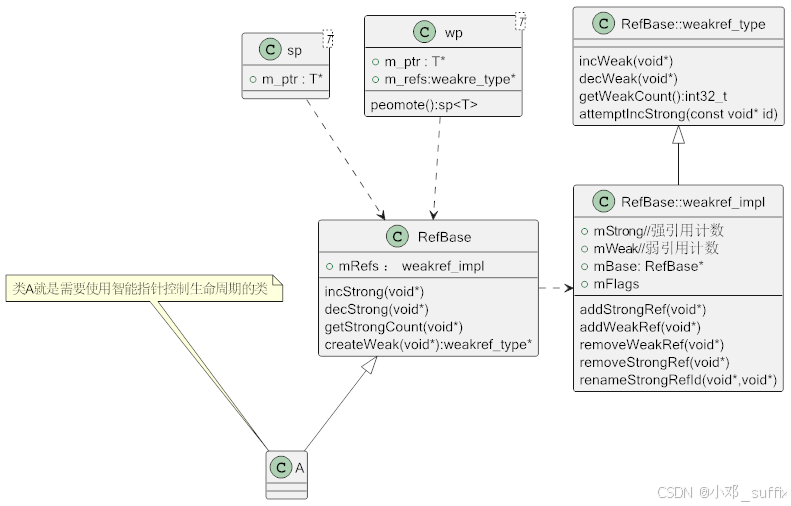
类图
先上类图

省略部分方法:
@startuml
class "RefBase::weakref_impl" as weakref_impl
class "RefBase::weakref_type" as weakref_type
class A extends RefBase{
}
class RefBase {
+ mRefs : weakref_impl
incStrong(void*)
decStrong(void*)
getStrongCount(void*)
createWeak(void*):weakref_type*
}
class weakref_type {
incWeak(void*)
decWeak(void*)
getWeakCount():int32_t
attemptIncStrong(const void* id)
}
class weakref_impl extends weakref_type {
+ mStrong//强引用计数
+ mWeak//弱引用计数
+mBase: RefBase*
+mFlags
addStrongRef(void*)
addWeakRef(void*)
removeWeakRef(void*)
removeStrongRef(void*)
renameStrongRefId(void*,void*)
}
class sp<T> {
+ m_ptr : T*
}
class wp<T> {
+ m_ptr : T*
+ m_refs:weakre_type*
peomote():sp<T>
}
note "类A就是需要使用智能指针控制生命周期的类" as n1
n1..A
RefBase .> weakref_impl
sp..>RefBase
wp..>RefBase
@enduml
源码分析
需要通过引用计数控制生命周期的类 A 继承 RefBase,在创建 A 的对象时调用父类构造方法,同步创建一个 Weakref_impl。
//system/core/libutils/binder/RefBase.cpp
RefBase::RefBase()
: mRefs(new weakref_impl(this))
{
}
//new A 的时候调用父类构造方法 new一个weakref_impl对象保存在mRefs中。
//weakref_impl 的构造方法
class RefBase::weakref_impl : public RefBase::weakref_type
weakref_impl(RefBase* base)
: mStrong(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE)//强引用计数
, mWeak(0)//弱引用计数
, mBase(base)
, mFlags(OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG)
, mStrongRefs(NULL)
, mWeakRefs(NULL)
, mTrackEnabled(!!DEBUG_REFS_ENABLED_BY_DEFAULT)
, mRetain(false)
{
}
强引用和弱引用的使用方法:
演示一下通过强弱应用控制对象的生命周期
A * PA=new A();//new 一个A
sp<A> spA(PA);//强引用
wp<A> wpA(PA)
//sp的构造函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other)
{
if (other) other->incStrong(this);
}
//wp的构造函数
template<typename T>
wp<T>::wp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other)
{
if (other) m_refs = other->createWeak(this);
}
强应用计数加 1 的过程:
void RefBase::incStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->incWeak(id);//从名字看这里是增加弱应用计数
refs->addStrongRef(id);
//原子加1 C是加1之前的值
const int32_t c = refs->mStrong.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
ALOG_ASSERT(c > 0, "incStrong() called on %p after last strong ref", refs);
#if PRINT_REFS
ALOGD("incStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d\n", this, id, c);
#endif
//INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE是初始值 #define INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE (1<<28)
//这里判断是不是首次强引用,是就直接返回
if (c != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
return;
}
check_not_on_stack(this);
//不是首次引用 减去INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE
int32_t old __unused = refs->mStrong.fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, std::memory_order_relaxed);
// A decStrong() must still happen after us.
ALOG_ASSERT(old > INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, "0x%x too small", old);
refs->mBase->onFirstRef();
}
弱引用计数+1:
void RefBase::weakref_type::incWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->addWeakRef(id);
//弱应用计数加1
const int32_t c __unused = impl->mWeak.fetch_add(1,
std::memory_order_relaxed);
ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 0, "incWeak called on %p after last weak ref", this);
}
总结: 创建 sp 强引用计数+1 弱引用计数+1 ,其中对强引用计数的+1 操作涉及到一个是否是初次强引用判断
接下来是 wp 创建时 createWeak:
RefBase::weakref_type* RefBase::createWeak(const void* id) const
{
//弱引用计数+1
mRefs->incWeak(id);
//mRefs赋值给wp的m_refs
return mRefs;
}
然后是析构函数:
sp<T>::~sp()
{
//从强引用计数-1
if (m_ptr) m_ptr->decStrong(this);
}
看看 decStrong 具体逻辑
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->removeStrongRef(id);
//强引用-1,c是减1之前的值
const int32_t c = refs->mStrong.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_release);
#if PRINT_REFS
ALOGD("decStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d\n", this, id, c);
#endif
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(BAD_STRONG(c), "decStrong() called on %p too many times",
refs);
//c==1 ,减1之前为1 表示是最后一个强引用
if (c == 1) {
std::atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire);
refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
int32_t flags = refs->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
/*
enum {
OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG = 0x0000,
OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK = 0x0001,
OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK = 0x0001
};
*/
//这个判断是在判断生命周期是不是受强引用控制 flags=0时 条件满足 delete A
if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
delete this;
// The destructor does not delete refs in this case.
}
}
// Note that even with only strong reference operations, the thread
// deallocating this may not be the same as the thread deallocating refs.
// That's OK: all accesses to this happen before its deletion here,
// and all accesses to refs happen before its deletion in the final decWeak.
// The destructor can safely access mRefs because either it's deleting
// mRefs itself, or it's running entirely before the final mWeak decrement.
//
// Since we're doing atomic loads of `flags`, the static analyzer assumes
// they can change between `delete this;` and `refs->decWeak(id);`. This is
// not the case. The analyzer may become more okay with this patten when
// https://bugs.llvm.org/show_bug.cgi?id=34365 gets resolved. NOLINTNEXTLINE
//强引用计数-1 伴随着弱应用计数-1
refs->decWeak(id);
}
总结 sp 析构的时候强引用计数-1 弱引用计数-1 当减 1 后强应用计数为 0 时在判断 生命周期受强引用计数后 delete this。
接下来看 wp 析构时:
template<typename T>
wp<T>::~wp()
{
if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this);
}
void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->removeWeakRef(id);
//弱引用计数 -1
const int32_t c = impl->mWeak.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_release);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(BAD_WEAK(c), "decWeak called on %p too many times",
this);
//不是最后一个弱引用,-1后直接返回
if (c != 1) return;
atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire);
int32_t flags = impl->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
//这里的两个判断是判断生命周期受强引用计数影响 ,且强引用为初始值,也就是说没有被强引用过。此时弱引用为0了,什么也不做不需要释放
//也就是说弱引用计数指向的对象是可以未初始化的
if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
// This is the regular lifetime case. The object is destroyed
// when the last strong reference goes away. Since weakref_impl
// outlives the object, it is not destroyed in the dtor, and
// we'll have to do it here.
if (impl->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed)
== INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
// Decrementing a weak count to zero when object never had a strong
// reference. We assume it acquired a weak reference early, e.g.
// in the constructor, and will eventually be properly destroyed,
// usually via incrementing and decrementing the strong count.
// Thus we no longer do anything here. We log this case, since it
// seems to be extremely rare, and should not normally occur. We
// used to deallocate mBase here, so this may now indicate a leak.
ALOGW("RefBase: Object at %p lost last weak reference "
"before it had a strong reference", impl->mBase);
//以前会在这里delete impl->mBase的,现在改了。似乎逻辑就是当一个对象从来没有被强引用过时不该有弱引用。如果有表示代码存在内存泄漏
} else {
//有过强引用但是弱引用计数归零了。delete weakref_impl
// ALOGV("Freeing refs %p of old RefBase %p\n", this, impl->mBase);
//delete weakref_impl
delete impl;
}
} else {
// This is the OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK case. The last weak-reference
// is gone, we can destroy the object.
impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id);
//这里delete A
delete impl->mBase;
}
}
到这里 强/弱引用计数+1 -1 会发生什么都分析完了。
最后还有一个由弱生强
sp 通过 运算符重写 使得可以访问引用对象。而 wp 是没有对应运算符重载的所以想要由弱引用使用被引用对象需要先由弱生强
inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; }
inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; }
inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; }
template<typename T>
sp<T> wp<T>::promote() const
{
sp<T> result;
if (m_ptr && m_refs->attemptIncStrong(&result)) {
result.set_pointer(m_ptr);
}
return result;
}
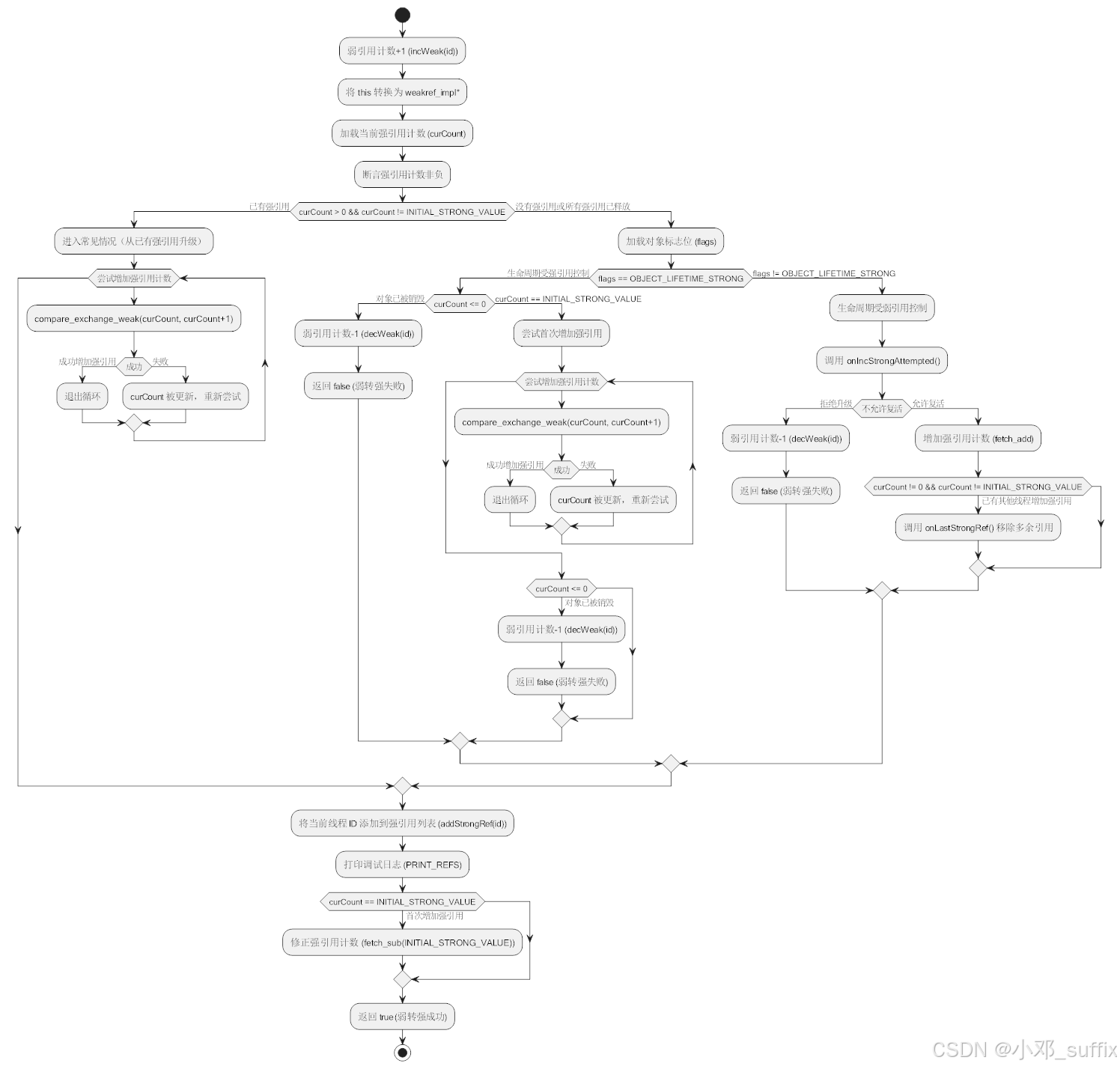
attemptIncStrong:
这个函数主要是在不使用锁的情况下去考虑多线程情况,所以比较麻烦
bool RefBase::weakref_type::attemptIncStrong(const void* id)
{
//弱引用计数+1
incWeak(id);
//强制类型转换
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
int32_t curCount = impl->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
//断言强引用计数非负
ALOG_ASSERT(curCount >= 0,
"attemptIncStrong called on %p after underflow", this);
//正常情况下(已经有强引用存在),比较交换,while循环是为了保证多线程下也确保+1被执行,+1后curcount为+1前的值
while (curCount > 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
// we're in the easy/common case of promoting a weak-reference
// from an existing strong reference.
if (impl->mStrong.compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1,
std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
break;
}
// the strong count has changed on us, we need to re-assert our
// situation. curCount was updated by compare_exchange_weak.
}
//没有强引用或者所有强应用已被释放
if (curCount <= 0 || curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
// we're now in the harder case of either:
// - there never was a strong reference on us
// - or, all strong references have been released
int32_t flags = impl->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
//生命周期受强引用计数影响
if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
// this object has a "normal" life-time, i.e.: it gets destroyed
// when the last strong reference goes away
//此时对象已经被delete,弱引用计数-1 抵消前面的+1 弱转强失败
if (curCount <= 0) {
// the last strong-reference got released, the object cannot
// be revived.
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
// here, curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, which means
// there never was a strong-reference, so we can try to
// promote this object; we need to do that atomically.
//逻辑走到这里表示之前没有强引用,while循环同样是为了多线程情况,确保+1
while (curCount > 0) {
if (impl->mStrong.compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1,
std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
break;
}
}
//再次判断对象是否被销毁
if (curCount <= 0) {
// promote() failed, some other thread destroyed us in the
// meantime (i.e.: strong count reached zero).
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
} else {
// this object has an "extended" life-time, i.e.: it can be
// revived from a weak-reference only.
// Ask the object's implementation if it agrees to be revived
//这里表示生命周期是受弱引用计数控制,询问是否能“复活“,onIncStrongAttempted这里的实现只是再次判断了生命周期不是受强引用计数控制,受
//强引用计数控制返回false,decweak 强转弱失败。应该是可以重写实现自己的判断逻辑
if (!impl->mBase->onIncStrongAttempted(FIRST_INC_STRONG, id)) {
// it didn't so give-up.
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
// grab a strong-reference, which is always safe due to the
// extended life-time.
curCount = impl->mStrong.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
// If the strong reference count has already been incremented by
// someone else, the implementor of onIncStrongAttempted() is holding
// an unneeded reference. So call onLastStrongRef() here to remove it.
// (No, this is not pretty.) Note that we MUST NOT do this if we
// are in fact acquiring the first reference.
if (curCount != 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
impl->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
}
}
}
impl->addStrongRef(id);
#if PRINT_REFS
ALOGD("attemptIncStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d\n", this, id, curCount);
#endif
// curCount is the value of mStrong before we incremented it.
// Now we need to fix-up the count if it was INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE.
// This must be done safely, i.e.: handle the case where several threads
// were here in attemptIncStrong().
// curCount > INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE is OK, and can happen if we're doing
// this in the middle of another incStrong. The subtraction is handled
// by the thread that started with INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE.
//从curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE执行+1的线程,最终需要减去 INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE
if (curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
impl->mStrong.fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE,
std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
return true;
}
@startuml
start
:弱引用计数+1 (incWeak(id));
:将 this 转换为 weakref_impl*;
:加载当前强引用计数 (curCount);
:断言强引用计数非负;
if (curCount > 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) then (已有强引用)
:进入常见情况(从已有强引用升级);
while (尝试增加强引用计数)
:compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1);
if (成功) then (成功增加强引用)
:退出循环;
else (失败)
:curCount 被更新,重新尝试;
endif
endwhile
else (没有强引用或所有强引用已释放)
:加载对象标志位 (flags);
if (flags == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) then (生命周期受强引用控制)
if (curCount <= 0) then (对象已被销毁)
:弱引用计数-1 (decWeak(id));
:返回 false (弱转强失败);
else (curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE)
:尝试首次增加强引用;
while (尝试增加强引用计数)
:compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1);
if (成功) then (成功增加强引用)
:退出循环;
else (失败)
:curCount 被更新,重新尝试;
endif
endwhile
if (curCount <= 0) then (对象已被销毁)
:弱引用计数-1 (decWeak(id));
:返回 false (弱转强失败);
endif
endif
else (flags != OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG)
:生命周期受弱引用控制;
:调用 onIncStrongAttempted();
if (不允许复活) then (拒绝升级)
:弱引用计数-1 (decWeak(id));
:返回 false (弱转强失败);
else (允许复活)
:增加强引用计数 (fetch_add);
if (curCount != 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) then (已有其他线程增加强引用)
:调用 onLastStrongRef() 移除多余引用;
endif
endif
endif
endif
:将当前线程 ID 添加到强引用列表 (addStrongRef(id));
:打印调试日志 (PRINT_REFS);
if (curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) then (首次增加强引用)
:修正强引用计数 (fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE));
endif
:返回 true (弱转强成功);
stop
@enduml




















 767
767

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








