「链表 Linked List」是一种线性数据结构,其每个元素都是一个节点对象,各个节点之间通过指针连接,从当前节点通过指针可以访问到下一个节点。由于指针记录了下个节点的内存地址,因此无需保证内存地址的连续性,从而可以将各个节点分散存储在内存各处。
链表「节点 Node」包含两项数据,一是节点「值 Value」,二是指向下一节点的「指针 Pointer」,或称「引用 Reference」。 – 来源 hello 算法
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
}
如何操作链表?
不管是什么结构,最开始一定要搞明白 增删改查 + 创建
- 如何创建(初始化) 链表 ?
/**
* 初始化数组
*
* @param array 数组
* @return 链表
*/
public static Node initLinkList(int[] array) {
Node head = null, cur = null;
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 创建 Node 对象
Node newNode = new Node(array[i]);
newNode.next = null;
// 如果是第一个,那么创建的 Node 需要充当头节点
if (i == 0) {
head = newNode;
cur = newNode;
} else {
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode;
}
}
return head;
}
- 链表的插入
/**
* 链表插入
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @param nodeInsert 待插入节点
* @param position 待插入位置。 是从 1 开始计算的
* @return 插入后得到的链表头节点
*/
public static Node insertNode(Node head, Node nodeInsert, int position) {
// 先判断头节点是否为 null
if (head == null) {
return nodeInsert;
}
// 判断插入的位置
int size = getLength(head);
// 这里的边界条件有点意识,需要注意这里是 size + 1 意识就是 size + 1 也能够插入到链表之中
// 原因就是可以充当 最后一个节点的下一个位置
if (position > size + 1 || position < 1) {
System.out.println("插入的数组越界!");
return head;
}
// 如如果插入头节点
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = head;
head = nodeInsert;
return head;
}
int index = 1;
Node current = head;
while (index < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
nodeInsert.next = current.next;
current.next = nodeInsert;
return head;
}
示意图
- 当插入的是头节点时

- 当插入的最后的节点

- 当插入的时中间位置时
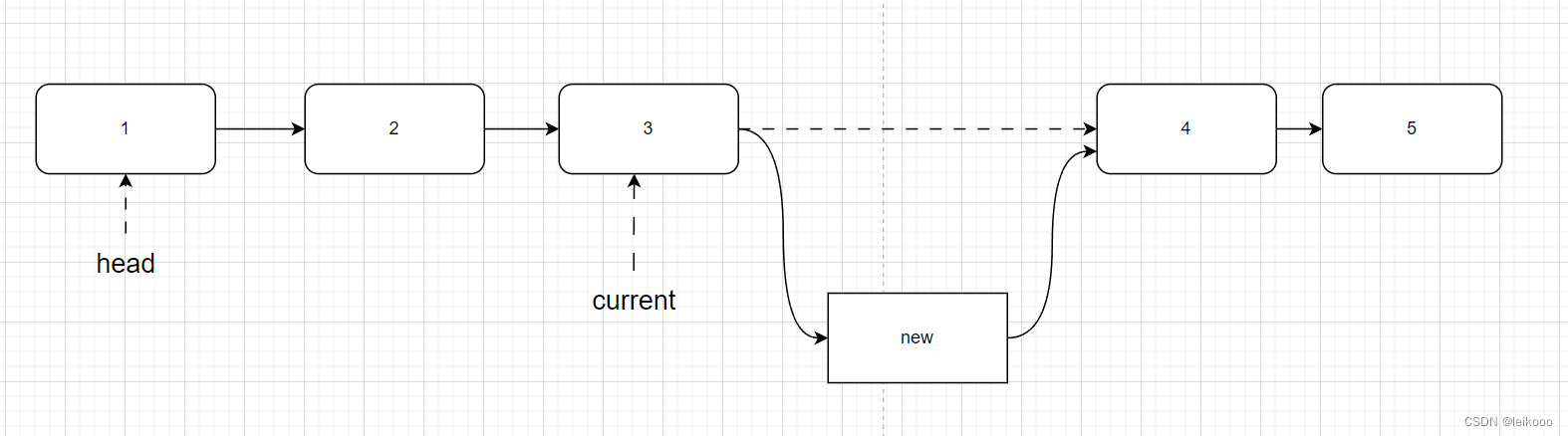 这里就是把 current.next = new.next; 然后把 current.next = new 。
这里就是把 current.next = new.next; 然后把 current.next = new 。
这里不能交换顺序! 如果先把 current.next = new 那么我们及会失去 4 号位置的地址值
- 删除节点
/**
* 删除节点
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @param position 删除节点位置,取值从1开始
* @return 删除后的链表头节点
*/
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (position > getLength(head) || position < 1) {
return head;
}
Node current = head;
// 如果索引是 1 的话
if (position == 1) {
head = current.next;
return head;
}
int index = 1;
while (index < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
current.next = current.next.next;
return head;
}
示意图

直接把赋值就 ok 了。
要删除的 4 号节点的下一个仍然指向 5 号位置 , 需要手动设置为 null 吗 ?
不需要! JVM 会帮助我们回收的。而且我们也无法访问到被删除的节点
- 其他方法
获取链表长度
/**
* 获取链表长度
*
* @param head 链表头节点
* @return 链表长度
*/
public static int getLength(Node head) {
int length = 0;
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
输出 node 的值
/**
* 输出 node 的值
*
* @param head 头节点
* @return 数据
*/
public static String toString(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
if (cur == null) {
return "";
}
// 线程安全的 StringBuilder
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (cur.next != null) {
sb.append(cur.data).append("\t\t");
// 指针向后
cur = cur.next;
}
return sb.toString();
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








