随着企业上云进程加速,云环境安全威胁日益复杂。Amazon GuardDuty作为AWS原生的智能威胁检测服务,能够帮助企业实现持续的安全监控。本文将详细介绍GuardDuty的配置、使用和最佳实践。
工作原理
Amazon GuardDuty 是一项威胁检测服务,它持续监控您的 AWS 账户和工作负载的恶意活动,并提供详细的安全检测结果以实现可见性和修复。
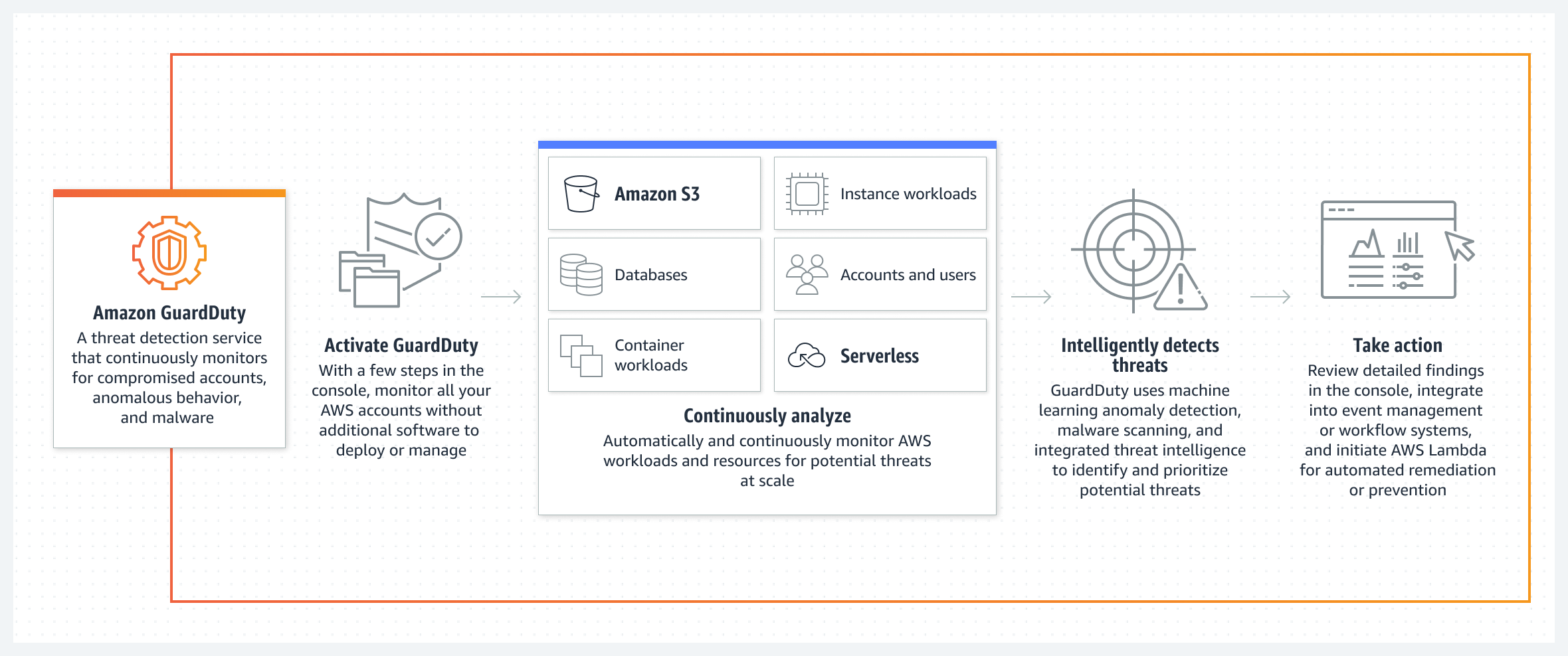
1. Amazon GuardDuty概述
Amazon GuardDuty是一种托管的威胁检测服务,它通过机器学习、异常检测和集成威胁情报,持续监控您的AWS环境中的恶意活动和未经授权的行为。
1.1 GuardDuty核心优势
-
智能威胁检测:使用机器学习模型识别异常和威胁
-
无需管理基础设施:完全托管服务,自动扩展
-
多数据源分析:分析CloudTrail、VPC Flow Logs和DNS日志
-
成本效益:按事件分析量计费,无前期成本
2. GuardDuty主要检测类型
GuardDuty能够检测多种安全威胁:
2.1 凭证泄露相关威胁
-
API调用异常:从不常见的位置或IP调用API
-
权限提升:用户突然尝试访问通常不访问的资源
-
凭证访问:从EC2实例元数据服务获取IAM角色凭证
2.2 实例威胁
-
比特币挖矿活动:检测与加密货币挖矿相关的网络活动
-
后门连接:实例与已知恶意IP通信
-
数据渗漏:大量数据被传输到外部地址
2.3 账户威胁
-
密码暴力破解:针对AWS服务的登录尝试
-
资源滥用:创建用于恶意目的的EC2实例
3. 启用和配置GuardDuty
3.1 启用GuardDuty
# 使用AWS CLI启用GuardDuty
import boto3
def enable_guardduty():
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
# 获取Detector ID(每个区域一个)
detectors = client.list_detectors()
if not detectors['DetectorIds']:
# 如果没有detector,则创建一个
response = client.create_detector(
Enable=True,
FindingPublishingFrequency='SIX_HOURS' # 可选择ONE_HOUR或SIX_HOURS
)
detector_id = response['DetectorId']
print(f"已创建Detector: {detector_id}")
else:
detector_id = detectors['DetectorIds'][0]
print(f"使用现有Detector: {detector_id}")
return detector_id
# 启用GuardDuty
detector_id = enable_guardduty()
3.2 配置数据源
def configure_data_sources(detector_id):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
# 配置数据源
response = client.update_detector(
DetectorId=detector_id,
Enable=True,
FindingPublishingFrequency='SIX_HOURS',
DataSources={
'S3Logs': {
'Enable': True
},
'Kubernetes': {
'AuditLogs': {
'Enable': True
}
},
'MalwareProtection': {
'ScanEc2InstanceWithFindings': {
'EbsVolumes': True
}
}
}
)
print("数据源配置完成")
configure_data_sources(detector_id)
3.3 设置S3保护
def enable_s3_protection(detector_id):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
response = client.update_detector(
DetectorId=detector_id,
DataSources={
'S3Logs': {
'Enable': True
}
}
)
print("S3保护已启用")
enable_s3_protection(detector_id)
4. 管理调查结果
4.1 获取调查结果
def list_findings(detector_id, severity_threshold=4):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
# 构建筛选条件
finding_criteria = {
'Criterion': {
'severity': {
'Gte': severity_threshold # 只获取高严重性发现
}
}
}
response = client.list_findings(
DetectorId=detector_id,
FindingCriteria=finding_criteria,
MaxResults=50
)
findings = client.get_findings(
DetectorId=detector_id,
FindingIds=response['FindingIds']
)
return findings['Findings']
# 获取高严重性发现
high_severity_findings = list_findings(detector_id, severity_threshold=7)
for finding in high_severity_findings:
print(f"发现ID: {finding['Id']}")
print(f"类型: {finding['Type']}")
print(f"严重性: {finding['Severity']}")
print(f"标题: {finding['Title']}")
print("---")
4.2 更新发现状态
def update_finding_status(detector_id, finding_ids, status, comments=""):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
response = client.update_findings_feedback(
DetectorId=detector_id,
FindingIds=finding_ids,
Feedback=status, # 'USEFUL', 'NOT_USEFUL', 'VALID', 'FALSE_POSITIVE'
Comments=comments
)
print(f"已更新 {len(finding_ids)} 个发现的状态为: {status}")
# 示例:将发现标记为误报
# update_finding_status(detector_id, ['finding-id-1'], 'FALSE_POSITIVE', '这是正常的业务操作')
5. 自动化响应机制
5.1 创建CloudWatch Events规则
def create_guardduty_event_rule():
client = boto3.client('events')
rule_response = client.put_rule(
Name='guardduty-high-severity-findings',
EventPattern='''{
"source": ["aws.guardduty"],
"detail": {
"severity": [{"numeric": [">=", 7]}]
}
}''',
State='ENABLED',
Description='高严重性GuardDuty发现的事件规则'
)
print(f"事件规则已创建: {rule_response['RuleArn']}")
return rule_response['RuleArn']
rule_arn = create_guardduty_event_rule()
5.2 配置自动响应
def setup_automated_response(rule_arn):
client = boto3.client('events')
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
# 创建Lambda函数(这里需要提前创建好响应函数)
# 假设我们有一个名为guardduty-response-function的Lambda函数
response = client.put_targets(
Rule='guardduty-high-severity-findings',
Targets=[
{
'Id': 'guardduty-lambda-target',
'Arn': 'arn:aws:lambda:region:account-id:function:guardduty-response-function',
'InputTransformer': {
'InputPathsMap': {
'detail-type': '$.detail-type',
'severity': '$.detail.severity',
'finding_id': '$.detail.id',
'resource_type': '$.detail.resource.resourceType'
},
'InputTemplate': '''{
"finding_details": {
"severity": <severity>,
"finding_id": <finding_id>,
"resource_type": <resource_type>,
"event_type": <detail-type>
}
}'''
}
}
]
)
print("自动响应配置完成")
setup_automated_response(rule_arn)
5.3 示例响应Lambda函数
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
"""
处理GuardDuty高严重性发现的Lambda函数
"""
print(f"收到事件: {json.dumps(event)}")
finding_details = event.get('finding_details', {})
severity = finding_details.get('severity', 0)
finding_id = finding_details.get('finding_id')
resource_type = finding_details.get('resource_type')
# 根据发现类型执行不同的响应动作
if severity >= 8:
# 严重威胁,立即隔离资源
if resource_type == 'Instance':
isolate_ec2_instance(finding_details)
elif resource_type == 'AccessKey':
disable_iam_access_key(finding_details)
elif severity >= 7:
# 高严重性威胁,发送详细告警
send_high_severity_alert(finding_details)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('GuardDuty响应处理完成')
}
def isolate_ec2_instance(finding_details):
"""隔离EC2实例"""
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
# 从发现中提取实例ID
instance_id = extract_instance_id(finding_details)
if instance_id:
# 修改安全组,隔离实例
try:
response = ec2.modify_instance_attribute(
InstanceId=instance_id,
Groups=['sg-isolation'] # 隔离安全组,只允许管理访问
)
print(f"已隔离实例: {instance_id}")
# 可选:停止实例
# ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=[instance_id])
except Exception as e:
print(f"隔离实例失败: {str(e)}")
def send_high_severity_alert(finding_details):
"""发送高严重性告警"""
sns = boto3.client('sns')
message = f"""
检测到高严重性安全威胁!
发现ID: {finding_details.get('finding_id')}
严重性: {finding_details.get('severity')}
资源类型: {finding_details.get('resource_type')}
请立即检查AWS控制台中的GuardDuty发现。
"""
sns.publish(
TopicArn='arn:aws:sns:region:account-id:security-alerts',
Message=message,
Subject='[紧急] GuardDuty高严重性安全发现'
)
6. 多账户架构配置
6.1 设置管理员账户
def enable_organization_admin(admin_detector_id):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
# 启用多账户管理
response = client.update_organization_configuration(
DetectorId=admin_detector_id,
AutoEnable=True,
DataSources={
'S3Logs': {
'AutoEnable': True
},
'Kubernetes': {
'AuditLogs': {
'AutoEnable': True
}
}
}
)
print("组织级配置已更新")
# 在管理账户中执行
enable_organization_admin(detector_id)
6.2 添加成员账户
def add_member_accounts(admin_detector_id, account_ids):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
for account_id in account_ids:
try:
# 创建成员账户
response = client.create_members(
DetectorId=admin_detector_id,
AccountDetails=[
{
'AccountId': account_id,
'Email': f'security+{account_id}@company.com'
}
]
)
print(f"已添加成员账户: {account_id}")
# 邀请成员账户
invite_response = client.invite_members(
DetectorId=admin_detector_id,
AccountIds=[account_id],
Message='请加入GuardDuty多账户威胁检测'
)
print(f"已发送邀请给账户: {account_id}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理账户 {account_id} 时出错: {str(e)}")
# 添加成员账户
member_accounts = ['123456789012', '234567890123']
add_member_accounts(detector_id, member_accounts)
7. 安全态势评估与报告
7.1 生成安全报告
def generate_security_report(detector_id, days=30):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
# 获取发现统计
end_time = datetime.utcnow()
start_time = end_time - timedelta(days=days)
findings = list_findings(detector_id, severity_threshold=1)
# 按类型分类发现
finding_types = {}
severity_counts = {1: 0, 2: 0, 3: 0, 4: 0, 5: 0, 6: 0, 7: 0, 8: 0}
for finding in findings:
finding_type = finding['Type']
severity = finding['Severity']
if finding_type not in finding_types:
finding_types[finding_type] = 0
finding_types[finding_type] += 1
# 统计严重性分布
severity_level = min(8, max(1, int(severity)))
severity_counts[severity_level] += 1
# 生成报告
report = {
'report_period': {
'start': start_time.isoformat(),
'end': end_time.isoformat()
},
'total_findings': len(findings),
'finding_types': finding_types,
'severity_distribution': severity_counts,
'high_severity_count': sum(severity_counts[i] for i in range(7, 9))
}
return report
# 生成月度报告
monthly_report = generate_security_report(detector_id, 30)
print("安全报告:", json.dumps(monthly_report, indent=2))
8. 最佳实践和优化建议
8.1 成本优化策略
-
调整发现发布频率:
-
生产环境:ONE_HOUR
-
开发/测试环境:SIX_HOURS
-
-
使用发现筛选器:
def create_finding_filter(detector_id, filter_name, criteria):
client = boto3.client('guardduty')
response = client.create_filter(
DetectorId=detector_id,
Name=filter_name,
Action='ARCHIVE', # 或 NOOP
Description='过滤已知的误报',
FindingCriteria=criteria,
Rank=1
)
print(f"筛选器 {filter_name} 已创建")
# 示例:过滤特定IP范围的发现
ip_criteria = {
'Criterion': {
'service.action.networkConnectionAction.remoteIpDetails.ipAddressV4': {
'NotEquals': ['10.0.0.0/8', '192.168.0.0/16']
}
}
}
create_finding_filter(detector_id, 'internal-ip-filter', ip_criteria)
8.2 安全加固建议
-
启用所有数据源:
-
CloudTrail 日志
-
VPC 流日志
-
DNS 查询日志
-
S3 数据事件
-
EKS 审计日志
-
-
集成安全中心:
-
将GuardDuty与Security Hub集成
-
使用AWS Config进行合规性检查
-
通过Lambda实现自动化修复
-
9. 总结
Amazon GuardDuty提供了强大的云环境威胁检测能力,通过本文介绍的配置方法和最佳实践,您可以:
-
快速部署 GuardDuty监控体系
-
自动化响应 安全事件
-
管理多账户 安全态势
-
生成可视化 安全报告
-
优化成本 同时保持安全可见性
建议定期审查GuardDuty发现,优化检测规则,并与您现有的安全运维流程集成,构建全方位的云安全防护体系。




















 272
272

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








