条件变量
应用场景:生产者消费者问题,是线程同步的一种手段。
必要性:为了实现等待某个资源,让线程休眠。提高运行效率
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
使用步骤:
初始化:
静态初始化
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; //初始化条件变量
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //初始化互斥量
或使用动态初始化
pthread_cond_init(&cond);
生产资源线程:
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
开始产生资源
pthread_cond_sigal(&cond); //通知一个消费线程
或者
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond); //广播通知多个消费线程
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
消费者线程:
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (如果没有资源){ //防止惊群效应
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
有资源了,消费资源
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
注意:
1 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex),在没有资源等待是是先unlock 休眠,等资源到了,再lock
所以pthread_cond_wait 和 pthread_mutex_lock 必须配对使用。

2 如果pthread_cond_signal或者pthread_cond_broadcast 早于 pthread_cond_wait ,则有可能会丢失信号。
3 pthead_cond_broadcast 信号会被多个线程收到,这叫线程的惊群效应。所以需要加上判断条件while循环。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
pthread_cond_t hasTaxi=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
struct taxi{
struct taxi *next;
int num;
};
struct taxi *Head=NULL;
void *taxiarv(void *arg){
printf("taxi arrived thread\n");
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
struct taxi *tx;
int i=1;
while(1){
tx = malloc(sizeof(struct taxi));
tx->num = i++;
printf("taxi %d comming\n",tx->num);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
tx->next = Head;
Head = tx;
pthread_cond_signal(&hasTaxi);
//pthread_cond_broadcast(&hasTaxi);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(0);
}
void *takeTaxi(void *arg){
printf("take taxi thread\n");
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
struct taxi *tx;
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
while(Head==NULL)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&hasTaxi,&lock);
}
tx = Head;
Head=tx->next;
printf("%d,Take taxi %d\n",(int)arg,tx->num);
free(tx);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
pthread_exit(0);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,taxiarv,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,takeTaxi,(void*)1);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,takeTaxi,(void*)2);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,takeTaxi,(void*)3);
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
}
}
线程池概念和使用
概念:
通俗的讲就是一个线程的池子,可以循环的完成任务的一组线程集合
必要性:
我们平时创建一个线程,完成某一个任务,等待线程的退出。但当需要创建大量的线程时,假设T1为创建线程时间,T2为在线程任务执行时间,T3为线程销毁时间,当 T1+T3 > T2,这时候就不划算了,使用线程池可以降低频繁创建和销毁线程所带来的开销,任务处理时间比较短的时候这个好处非常显著。
线程池的基本结构:
1 任务队列,存储需要处理的任务,由工作线程来处理这些任务
2 线程池工作线程,它是任务队列任务的消费者,等待新任务的信号
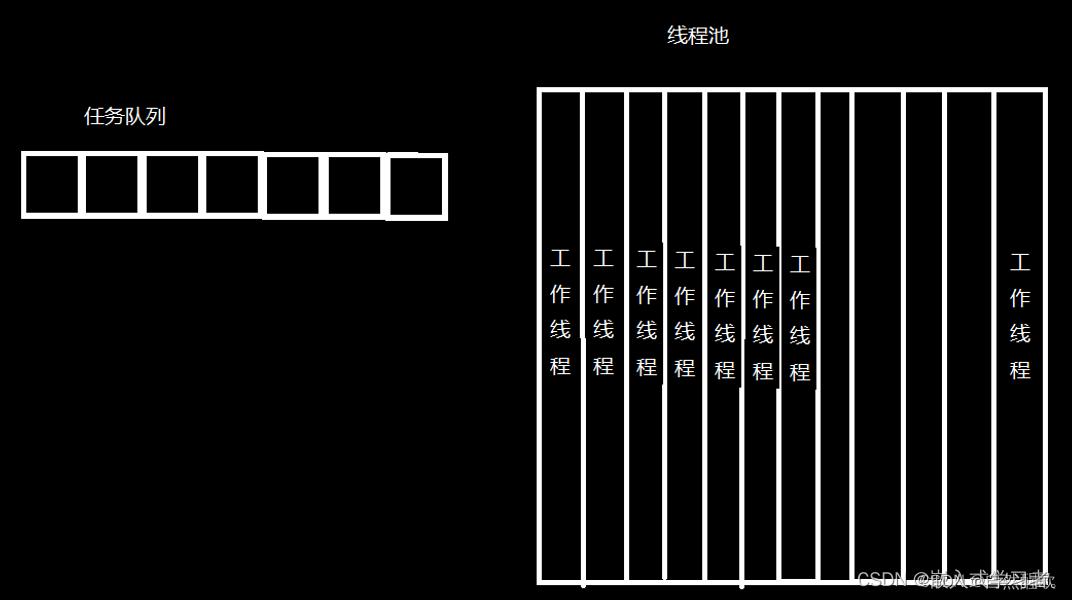
线程池的实现:
1创建线程池的基本结构:
任务队列链表
typedef struct Task;
线程池结构体
typedef struct ThreadPool;
2.线程池的初始化:
pool_init()
{
创建一个线程池结构
实现任务队列互斥锁和条件变量的初始化
创建n个工作线程
}
3.线程池添加任务
pool_add_task
{
判断是否有空闲的工作线程
给任务队列添加一个节点
给工作线程发送信号newtask
}
4.实现工作线程
workThread
{
while(1){
等待newtask任务信号
从任务队列中删除节点
执行任务
}
}
5.线程池的销毁
pool_destory
{
删除任务队列链表所有节点,释放空间
删除所有的互斥锁条件变量
删除线程池,释放空间
}
编译错误:
error: ‘ThreadPool {aka struct ThreadPool}’ has no member named ‘head’
意义:ThreadPool 结构体没有head这个成员。
解决:检查是否拼写错误。
error: too few arguments to function ‘pthread_mutex_init’
意思:pthread_mutex_init这个函数参数少了
解决:检查函数的参数,添加对应的参数
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define POOL_NUM 10
typedef struct Task
{
void *(*func)(void *arg);
void *arg;
struct Task *next;
}Task;
typedef struct ThreadPool
{
pthread_mutex_t taskLock;
pthread_cond_t newTask;
pthread_t tid[POOL_NUM];
Task *queue_head;
int busywork;
}ThreadPool;
ThreadPool *pool;
void *workThread(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->taskLock);
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->newTask,&pool->taskLock);
Task *ptask = pool->queue_head;
pool->queue_head = pool->queue_head->next;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->taskLock);
ptask->func(ptask->arg);
pool->busywork--;
}
}
void *realwork(void *arg)
{
printf("Finish work %d\n",(int)arg);
}
void pool_add_task(int arg)
{
Task *newTask;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->taskLock);
while(pool->busywork>=POOL_NUM)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->taskLock);
usleep(10000);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->taskLock);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->taskLock);
newTask = malloc(sizeof(Task));
newTask->func = realwork;
newTask->arg = arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->taskLock);
Task *member = pool->queue_head;
if(member==NULL)
{
pool->queue_head = newTask;
}
else
{
while(member->next!=NULL)
{
member=member->next;
}
member->next = newTask;
}
pool->busywork++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->newTask);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->taskLock);
}
void pool_init()
{
pool = malloc(sizeof(ThreadPool));
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->taskLock,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&pool->newTask,NULL);
pool->queue_head = NULL;
pool->busywork=0;
for(int i=0;i<POOL_NUM;i++)
{
pthread_create(&pool->tid[i],NULL,workThread,NULL);
}
}
void pool_destory(){
Task *head;
while(pool->queue_head!=NULL)
{
head = pool->queue_head;
pool->queue_head = pool->queue_head->next;
free(head);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->taskLock);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->newTask);
free(pool);
}
int main(){
pool_init();
sleep(20);
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
pool_add_task(i);
}
sleep(5);
pool_destory();
}
线程的GDB调试:
设置断点
b 行号
运行
run
显示线程
info thread
切换线程
thread id
GDB为特定线程设置断点
break location thread id
GDB设置线程锁,
set scheduler-locking on/off
on:其他线程会暂停。可以单独调试一个线程
b 6 thread 3 第三个线程第六行设断点。





 本文介绍了条件变量在生产者消费者问题中的应用及其必要性,并通过示例代码展示了如何使用条件变量实现线程间的同步。此外,还探讨了线程池的概念、必要性和基本结构,提供了线程池实现的具体步骤。
本文介绍了条件变量在生产者消费者问题中的应用及其必要性,并通过示例代码展示了如何使用条件变量实现线程间的同步。此外,还探讨了线程池的概念、必要性和基本结构,提供了线程池实现的具体步骤。

















 612
612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










