java面试题—交换两个变量
下面程序的运行结果
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int a=10;
int b=100;
swap(a,b);
System.out.println(a+" "+b);
}
public static void swap(int a,int b){
int temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
结果: 10 100
解释:
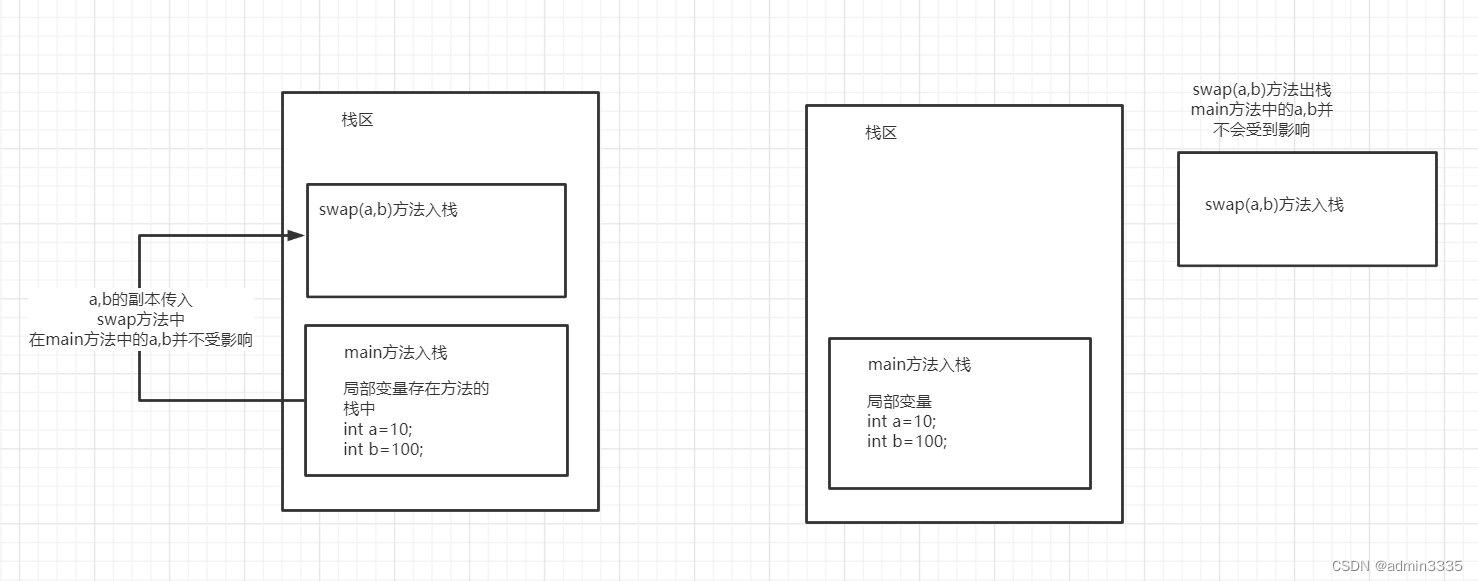
下面的程序运行结果
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Integer a=10;
Integer b=100;
swap(a,b);
System.out.println(a+" "+b);
}
public static void swap(Integer a,Integer b){
int temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
结果: 10 100
解释:
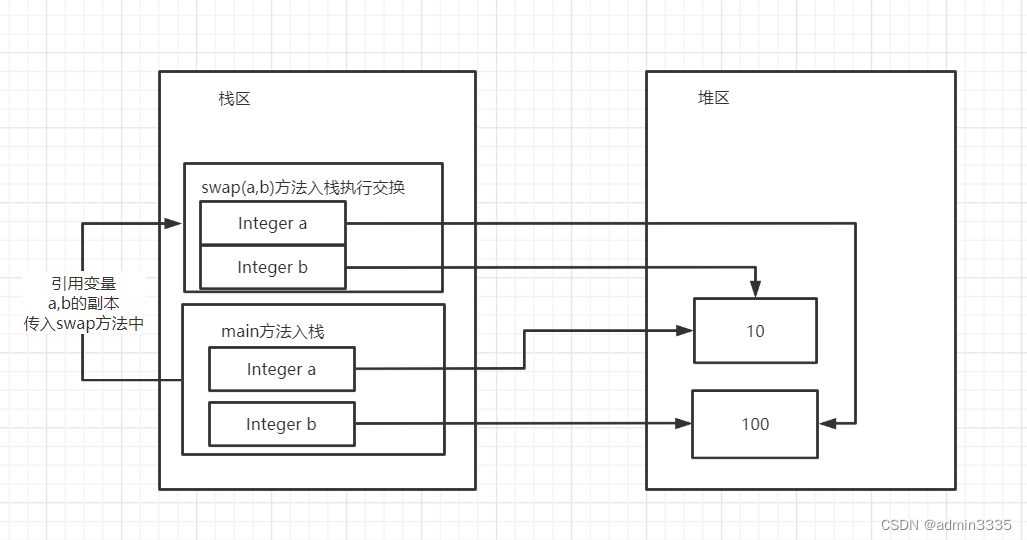
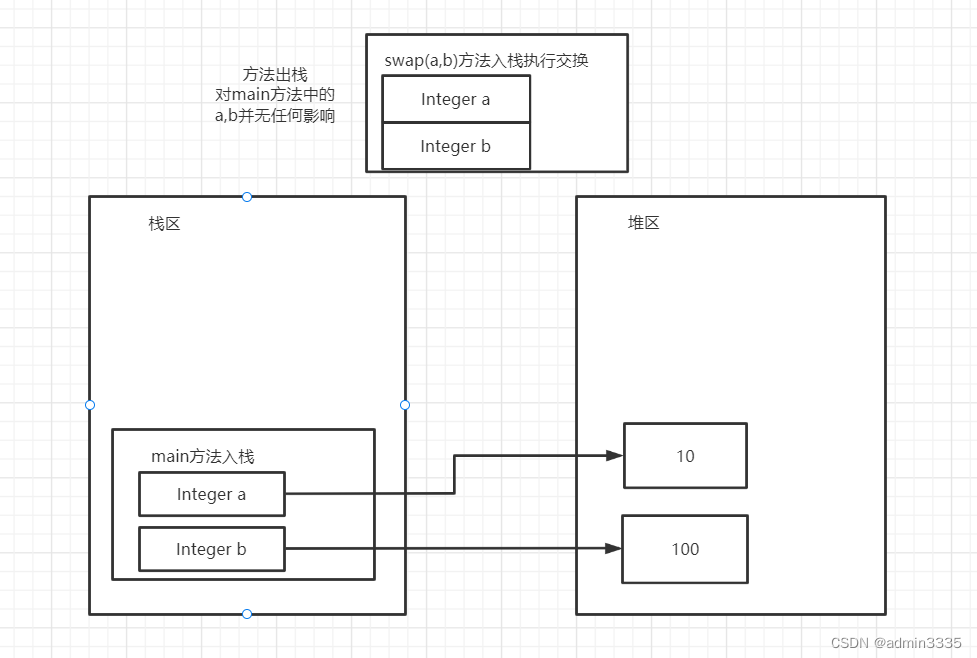




 这篇博客探讨了在Java中交换两个变量值时可能出现的意外情况。通过两个示例程序展示了当使用基本类型`int`和对象类型`Integer`进行交换时的不同结果。在第一个例子中,由于基本类型的值直接在栈上交换,导致交换成功。而在第二个例子中,由于`Integer`是对象,交换过程中涉及到引用的改变而非实际值的交换,因此交换并未生效。这提醒我们在编程时需要注意基本类型和引用类型的区别。
这篇博客探讨了在Java中交换两个变量值时可能出现的意外情况。通过两个示例程序展示了当使用基本类型`int`和对象类型`Integer`进行交换时的不同结果。在第一个例子中,由于基本类型的值直接在栈上交换,导致交换成功。而在第二个例子中,由于`Integer`是对象,交换过程中涉及到引用的改变而非实际值的交换,因此交换并未生效。这提醒我们在编程时需要注意基本类型和引用类型的区别。
















 367
367

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








