整体思路
- 启动Socket服务,循环的接收浏览器请求
- 接收到请求之后,将流中的数据取出
- 判断目标资源是否存在,若不存在,返回404
- 若存在,将目标资源通过输出流响应给客户端
实现这个服务器应有的类及其功能
- Server:用于开启Socket服务
- Request:用于封装请求,处理请求相关的业务
- Response:封装响应,处理响应相关业务
- Test:测试类
具体代码实现
Server类
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyHttpServer {
//端口
private int port=8080;
//ip为服务器的ip
//接收请求的方法
public void receiving(){
try {
//创建Socket服务
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(port);
//循环接收请求
while (true){
//循环接收请求,获取 Socket 对象,获取到了连接对象
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
//获取连接对象的输入流
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
//创建Request对象
MyHttpRequest request=new MyHttpRequest(inputStream);
//解析请求
request.parse();
//开始响应,创建Response
//获取连接对象的输出流
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
MyHttpResponse response=new MyHttpResponse(outputStream);
//根据获取的uri进行响应
response.sendRedirect(request.getUri());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Request类
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyHttpRequest {
//接收连接对象的输入流并解析
private InputStream inputStream;
//目标资源的路径
private String uri;
public MyHttpRequest(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
//解析输入流
public void parse(){
try {
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
//把输入流中的东西读到数组中
inputStream.read(bytes);
//封装成字符串
/*
GET /a.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Connection: keep-alive
sec-ch-ua: "Chromium";v="106", "Microsoft Edge";v="106", "Not;A=Brand";v="99"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/106.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/106.0.1370.47
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*`............
*/
String request=new String(bytes);
//获取请求的目标资源路径,如http://localhost:8080/a.html中的a.html
parseUri(request);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void parseUri(String request){
int index1,index2;
index1=request.indexOf(' ');
index2=request.indexOf(' ',index1+1);
this.uri=request.substring(index1+1,index2);
System.out.println(uri);
}
//返回uri
public String getUri(){
return this.uri;
}
}
Response类
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//根据解析得到的uri判断请求的资源是否存在,存在做出相应,不存在404
public class MyHttpResponse {
private OutputStream outputStream;
public MyHttpResponse(OutputStream outputStream) {
this.outputStream = outputStream;
}
public void sendRedirect(String uri){
//判断uri是否存在,是否再目标工程中
//不存在返回404
//存在,直接返回目标资源
//得到请求资源的整体路径
String path=System.getProperty("user.dir")+"/WebContent"+ uri;
//根据路径创建一个file对象
File file=new File(path);
//判断文件是否存在
if(file.exists()){
try {
//存在返回目标资源数据,根据目标资源路径,获取资源
FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes=new byte[(int)file.length()];
fileInputStream.read(bytes);
//得到资源内容
String result =new String(bytes);
//返回浏览器能显示的格式
String response=getResponseMessage("200",result);
this.outputStream.write(response.getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
try {
//不存在返回404,getResponseMessage返回浏览器能显示的格式
String error=getResponseMessage("404","404 File Not Found!");
this.outputStream.write(error.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//返回浏览器能显示的格式
public String getResponseMessage(String code,String message){
return "HTTP/1.1"+code+"\r\n"
+"Content-type:text/html\r\n"
+"Content-Length:"+message.length()
+"\r\n"
+"\r\n"
+message;
}
}
测试
建立一个WebContent文件夹,用于存放请求的html资源
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Server startup successfully");
MyHttpServer server=new MyHttpServer();
server.receiving();
}
}
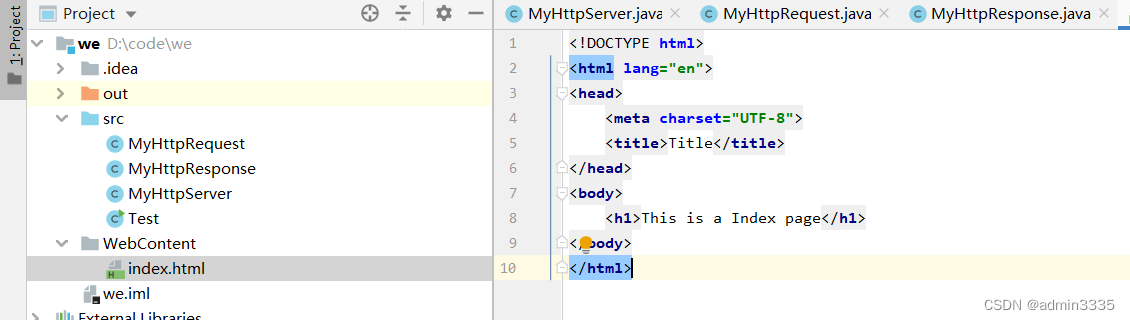
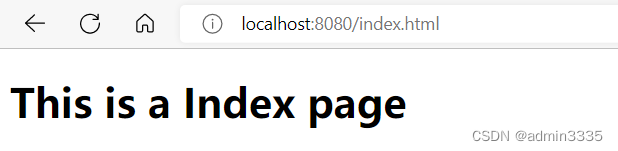
请求存在的资源时,端口号为8080
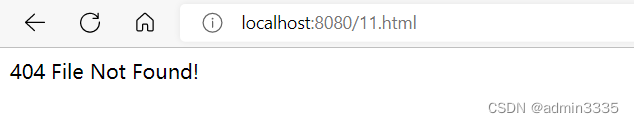
请求不存在的资源时




 本文介绍了如何手动实现一个简单的Web服务器。首先,通过启动Socket服务并循环接收浏览器请求。然后,解析请求,检查资源是否存在。如果资源存在,服务器将响应发送回客户端;如果不存在,则返回404错误。文章详细讲解了Server、Request和Response类的设计与实现,并提供了测试步骤,包括创建WebContent文件夹来存储HTML资源。
本文介绍了如何手动实现一个简单的Web服务器。首先,通过启动Socket服务并循环接收浏览器请求。然后,解析请求,检查资源是否存在。如果资源存在,服务器将响应发送回客户端;如果不存在,则返回404错误。文章详细讲解了Server、Request和Response类的设计与实现,并提供了测试步骤,包括创建WebContent文件夹来存储HTML资源。
















 1026
1026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








