结构型模式:③组合模式(Bridge Pattern)
核心思想
将 “单个对象(叶子节点)” 和 “对象组合(容器节点)” 统一视为 “组件”,通过抽象组件定义统一接口,使客户端无需区分叶子和容器,能以一致的方式处理 “部分” 和 “整体” 的层次结构(如文件系统、部门架构、树形菜单)。
核心本质
抽象统一接口 + 递归组合结构,容器节点可嵌套包含叶子节点或其他容器节点,形成任意深度的层次结构,客户端通过抽象接口透明操作整个结构。
C语言编写
关键要点
1.抽象接口统一:用 FileComponent 结构体定义 display/add/remove 统一接口,叶子和容器都实现该接口(叶子的 add/remove 做空实现或错误提示),确保客户端操作一致。
2.递归结构核心:容器节点(Folder)通过数组存储子组件,display 方法递归遍历所有子组件,实现 “整体操作”(如遍历整个文件系统)。
3.模拟继承:叶子(File)和容器(Folder)都包含 FileComponent 结构体作为 “基类”,通过强制类型转换实现接口调用,模拟面向对象的继承关系。
4.内存安全:容器节点的 destroy 方法需递归销毁所有子组件,避免仅销毁容器导致的子组件内存泄漏。
5.客户端透明性:客户端仅依赖 FileComponent 抽象接口,无需判断操作的是文件还是文件夹,实现对 “部分” 和 “整体” 的统一处理。
6.层次扩展:新增组件类型(如 “视频文件”“压缩文件夹”)时,只需实现 FileComponent 接口,无需修改客户端和现有组件,符合开闭原则。
场景示例
文件系统:
抽象组件(FileComponent):定义文件 / 文件夹的统一接口(显示、添加、移除);
叶子节点(File):单个文件,无法添加子组件;
容器节点(Folder):文件夹,可添加文件或子文件夹,支持递归遍历。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_CHILDREN 10 // 容器节点最大子组件数量(简化示例,实际可动态扩容)
// -------------------------- 1. 抽象组件(Component):统一接口 --------------------------
typedef struct FileComponent {
char name[32]; // 组件名称(文件名/文件夹名)
// 统一接口:客户端仅通过这些方法操作组件
void (*display)(struct FileComponent* self, int depth); // 显示组件(depth:层级深度)
int (*add)(struct FileComponent* self, struct FileComponent* child); // 添加子组件(叶子返回失败)
int (*remove)(struct FileComponent* self, const char* child_name); // 移除子组件(叶子返回失败)
void (*destroy)(struct FileComponent* self); // 销毁组件(容器需递归销毁子组件)
} FileComponent;
// -------------------------- 2. 叶子节点(Leaf):单个文件 --------------------------
// 叶子节点结构体:仅包含抽象组件(无额外子组件)
typedef struct File {
FileComponent base; // 模拟继承:包含抽象组件接口
} File;
// 叶子节点:显示文件(depth表示层级,用空格缩进)
void file_display(FileComponent* self, int depth) {
// 打印层级缩进
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) printf(" ");
printf("- 文件:%s\n", self->name);
}
// 叶子节点:无法添加子组件(返回-1表示失败)
int file_add(FileComponent* self, FileComponent* child) {
printf("错误:文件[%s]不能添加子组件!\n", self->name);
return -1;
}
// 叶子节点:无法移除子组件(返回-1表示失败)
int file_remove(FileComponent* self, const char* child_name) {
printf("错误:文件[%s]没有子组件可移除!\n", self->name);
return -1;
}
// 叶子节点:销毁(仅释放自身)
void file_destroy(FileComponent* self) {
if (self != NULL) {
free(self);
}
}
// 创建文件(叶子节点)
FileComponent* create_file(const char* name) {
File* file = (File*)malloc(sizeof(File));
strncpy(file->base.name, name, sizeof(file->base.name));
// 绑定抽象接口(叶子节点的add/remove为空实现)
file->base.display = file_display;
file->base.add = file_add;
file->base.remove = file_remove;
file->base.destroy = file_destroy;
return (FileComponent*)file;
}
// -------------------------- 3. 容器节点(Composite):文件夹 --------------------------
// 容器节点结构体:包含抽象组件 + 子组件集合
typedef struct Folder {
FileComponent base; // 模拟继承:包含抽象组件接口
FileComponent* children[MAX_CHILDREN]; // 子组件集合(文件/子文件夹)
int child_count; // 当前子组件数量
} Folder;
// 容器节点:显示文件夹(递归显示所有子组件)
void folder_display(FileComponent* self, int depth) {
// 转换为容器节点指针,访问子组件
Folder* folder = (Folder*)self;
// 打印当前文件夹(层级缩进)
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) printf(" ");
printf("+ 文件夹:%s(包含%d个子组件)\n", self->name, folder->child_count);
// 递归显示所有子组件(深度+1)
for (int i = 0; i < folder->child_count; i++) {
folder->children[i]->display(folder->children[i], depth + 1);
}
}
// 容器节点:添加子组件(文件/子文件夹)
int folder_add(FileComponent* self, FileComponent* child) {
Folder* folder = (Folder*)self;
if (folder->child_count >= MAX_CHILDREN) {
printf("警告:文件夹[%s]已达最大容量,无法添加更多子组件!\n", self->name);
return -1;
}
// 添加子组件到集合
folder->children[folder->child_count++] = child;
printf("成功:向文件夹[%s]添加%s[%s]\n", self->name,
(child->add == file_add) ? "文件" : "文件夹", child->name);
return 0;
}
// 容器节点:移除子组件(按名称查找)
int folder_remove(FileComponent* self, const char* child_name) {
Folder* folder = (Folder*)self;
for (int i = 0; i < folder->child_count; i++) {
if (strcmp(folder->children[i]->name, child_name) == 0) {
// 找到子组件,销毁并移位
folder->children[i]->destroy(folder->children[i]);
for (int j = i; j < folder->child_count - 1; j++) {
folder->children[j] = folder->children[j + 1];
}
folder->child_count--;
printf("成功:从文件夹[%s]移除%s[%s]\n", self->name,
(folder->children[i]->add == file_add) ? "文件" : "文件夹", child_name);
return 0;
}
}
printf("错误:文件夹[%s]中未找到子组件[%s]!\n", self->name, child_name);
return -1;
}
// 容器节点:销毁(递归销毁所有子组件)
void folder_destroy(FileComponent* self) {
if (self != NULL) {
Folder* folder = (Folder*)self;
// 递归销毁子组件
for (int i = 0; i < folder->child_count; i++) {
folder->children[i]->destroy(folder->children[i]);
}
free(folder);
}
}
// 创建文件夹(容器节点)
FileComponent* create_folder(const char* name) {
Folder* folder = (Folder*)malloc(sizeof(Folder));
strncpy(folder->base.name, name, sizeof(folder->base.name));
folder->child_count = 0; // 初始子组件数量为0
// 绑定抽象接口(容器节点实现add/remove/display)
folder->base.display = folder_display;
folder->base.add = folder_add;
folder->base.remove = folder_remove;
folder->base.destroy = folder_destroy;
return (FileComponent*)folder;
}
// -------------------------- 测试代码(客户端) --------------------------
// 客户端:统一操作抽象组件,无需区分文件和文件夹
void client_traverse(FileComponent* root) {
printf("=== 遍历文件系统 ===\n");
root->display(root, 0); // 从根节点开始递归遍历(深度0)
}
int main() {
// 1. 创建根文件夹(容器节点)
FileComponent* root = create_folder("我的电脑");
// 2. 创建子文件夹和文件(组合层次结构)
FileComponent* doc_folder = create_folder("文档");
FileComponent* pic_folder = create_folder("图片");
FileComponent* work_file = create_file("工作笔记.txt");
FileComponent* photo_file = create_file("旅行.jpg");
FileComponent* sub_folder = create_folder("重要文档");
FileComponent* report_file = create_file("项目报告.pdf");
// 3. 组合结构:根文件夹 → 文档/图片文件夹;文档 → 工作笔记+重要文档;重要文档 → 项目报告
root->add(root, doc_folder);
root->add(root, pic_folder);
doc_folder->add(doc_folder, work_file);
doc_folder->add(doc_folder, sub_folder);
sub_folder->add(sub_folder, report_file);
pic_folder->add(pic_folder, photo_file);
// 4. 客户端统一遍历整个文件系统(无需区分文件和文件夹)
client_traverse(root);
// 5. 测试移除子组件
printf("\n=== 测试移除组件 ===\n");
doc_folder->remove(doc_folder, "工作笔记.txt"); // 移除文件
root->remove(root, "图片"); // 移除文件夹(含子文件)
// 6. 再次遍历验证
client_traverse(root);
// 7. 销毁整个结构(递归销毁,避免内存泄漏)
root->destroy(root);
return 0;
}
C++ 实现(类 + 继承 + 多态 + 递归)
文件系统(抽象组件 FileComponent、叶子 File、容器 Folder),客户端统一遍历和操作。
通过 “抽象基类 + 纯虚函数” 定义统一接口,容器节点用 std::vector 存储子组件智能指针,递归遍历更简洁、类型更安全。
关键要点
1.抽象基类统一接口:FileComponent 定义纯虚函数 Display/Add/Remove,强制叶子(File)和容器(Folder)实现统一接口,确保客户端操作一致性。
2.多态核心:客户端通过 FileComponent 智能指针调用方法,实际执行子类(File/Folder)的实现,无需区分组件类型。
3.递归遍历:容器节点 Folder 的 Display 方法通过 for 循环遍历 children_ 集合,递归调用子组件的 Display,自然实现 “整体操作”。
4.内存安全:使用 std::shared_ptr 管理子组件内存,容器销毁时自动递归销毁所有子组件,避免内存泄漏;虚析构函数确保子类析构被正确调用。
5.类型判断:通过 dynamic_cast 判断子组件是文件还是文件夹(仅用于日志输出,客户端无需关心),C++ 类型转换更安全。
6.灵活扩展:新增组件类型(如 VideoFile 视频文件、ZipFolder 压缩文件夹)时,只需继承 FileComponent 并实现纯虚函数,无需修改客户端和现有组件,完全符合开闭原则。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory> // 智能指针(自动管理内存)
// -------------------------- 1. 抽象组件(Component):统一接口 --------------------------
class FileComponent {
public:
explicit FileComponent(std::string name) : name_(std::move(name)) {}
virtual ~FileComponent() = default; // 虚析构:确保子类析构被调用
// 纯虚函数:统一接口(强制子类实现)
virtual void Display(int depth) const = 0; // 显示组件(depth:层级深度)
virtual bool Add(std::shared_ptr<FileComponent> child) = 0; // 添加子组件(叶子返回false)
virtual bool Remove(const std::string& child_name) = 0; // 移除子组件(叶子返回false)
protected:
std::string name_; // 组件名称
};
// -------------------------- 2. 叶子节点(Leaf):单个文件 --------------------------
class File : public FileComponent {
public:
explicit File(std::string name) : FileComponent(std::move(name)) {}
// 实现显示接口:打印文件信息(层级缩进)
void Display(int depth) const override {
std::string indent(depth, ' ');
std::cout << indent << "- 文件:" << name_ << std::endl;
}
// 叶子节点:无法添加子组件(返回false)
bool Add(std::shared_ptr<FileComponent> child) override {
std::cout << "错误:文件[" << name_ << "]不能添加子组件!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 叶子节点:无法移除子组件(返回false)
bool Remove(const std::string& child_name) override {
std::cout << "错误:文件[" << name_ << "]没有子组件可移除!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
};
// -------------------------- 3. 容器节点(Composite):文件夹 --------------------------
class Folder : public FileComponent {
public:
explicit Folder(std::string name) : FileComponent(std::move(name)) {}
// 实现显示接口:递归显示所有子组件
void Display(int depth) const override {
std::string indent(depth, ' ');
// 打印当前文件夹
std::cout << indent << "+ 文件夹:" << name_ << "(包含" << children_.size() << "个子组件)" << std::endl;
// 递归显示子组件(深度+1)
for (const auto& child : children_) {
child->Display(depth + 1);
}
}
// 实现添加接口:添加子组件(文件/子文件夹)
bool Add(std::shared_ptr<FileComponent> child) override {
children_.push_back(child);
std::cout << "成功:向文件夹[" << name_ << "]添加"
<< (dynamic_cast<File*>(child.get()) ? "文件" : "文件夹")
<< "[" << child->name_ << "]" << std::endl;
return true;
}
// 实现移除接口:按名称查找并移除子组件
bool Remove(const std::string& child_name) override {
for (auto it = children_.begin(); it != children_.end(); ++it) {
if ((*it)->name_ == child_name) {
// 智能指针自动销毁子组件,无需手动delete
children_.erase(it);
std::cout << "成功:从文件夹[" << name_ << "]移除"
<< (dynamic_cast<File*>((*it).get()) ? "文件" : "文件夹")
<< "[" << child_name << "]" << std::endl;
return true;
}
}
std::cout << "错误:文件夹[" << name_ << "]中未找到子组件[" << child_name << "]!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
private:
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<FileComponent>> children_; // 子组件集合(智能指针自动管理内存)
};
// -------------------------- 测试代码(客户端) --------------------------
// 客户端:统一操作抽象组件,无需区分叶子和容器
void ClientTraverse(const std::shared_ptr<FileComponent>& root) {
std::cout << "\n=== 遍历文件系统 ===" << std::endl;
root->Display(0); // 从根节点递归遍历(深度0)
}
int main() {
// 1. 创建组件(智能指针自动管理内存)
auto root = std::make_shared<Folder>("我的电脑");
auto docFolder = std::make_shared<Folder>("文档");
auto picFolder = std::make_shared<Folder>("图片");
auto workFile = std::make_shared<File>("工作笔记.txt");
auto photoFile = std::make_shared<File>("旅行.jpg");
auto subFolder = std::make_shared<Folder>("重要文档");
auto reportFile = std::make_shared<File>("项目报告.pdf");
// 2. 组合层次结构:根 → 文档/图片;文档 → 工作笔记+重要文档;重要文档 → 项目报告
root->Add(docFolder);
root->Add(picFolder);
docFolder->Add(workFile);
docFolder->Add(subFolder);
subFolder->Add(reportFile);
picFolder->Add(photoFile);
// 3. 客户端统一遍历
ClientTraverse(root);
// 4. 测试移除组件
std::cout << "\n=== 测试移除组件 ===" << std::endl;
docFolder->Remove("工作笔记.txt"); // 移除文件
root->Remove("图片"); // 移除文件夹(含子文件)
// 5. 再次遍历验证
ClientTraverse(root);
return 0; // 智能指针自动销毁所有组件,无需手动释放
}
组合模式核心总结(C vs C++)
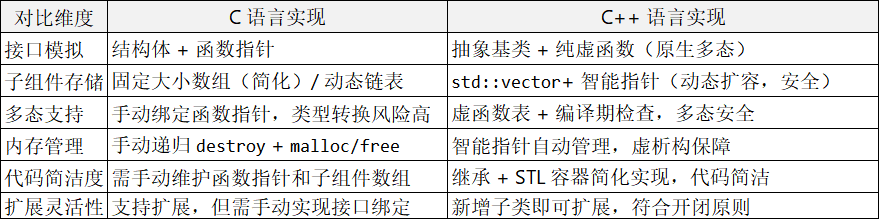
设计原则
1.开闭原则:新增组件类型(叶子 / 容器)无需修改现有代码,仅需实现抽象接口;
2.单一职责:叶子专注于自身业务(如文件的显示),容器专注于子组件管理(添加 / 移除 / 遍历);
3.依赖倒置:客户端依赖抽象组件(Component),不依赖具体实现(File/Folder)。





















 809
809

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








